The algorithm behind TCP must deal with more than merely moving lots of bytes from application to application. It must also ensure that it acts in a manner that will not overwhelm the routers in between. This lecture will discuss those aspects of TCP where it tries to be a good neighbor. We will discuss the basic congestion control schemes, including slow-start, additive-increase multiplicative-decrease and fast-retransmission.

AIMD: Probing for additional bandwidth
Lesson Objectives
By the end of this lesson, the student will be able to:
- describe the mission, operation and mechanisms for flow control in TCP.
- list causes, costs and consequences of network congestion.
- describe the operations of, as well as advantages and disadvantages of, different feedback mechanisms.
- describe the overall congestion control mechanisms used in TCP, including the congwin variable, self-clocking nature, and interaction of various phases.
- describe the slow start component of TCP congestion control; including starting conditions, reactions to ACKs and ending conditions.
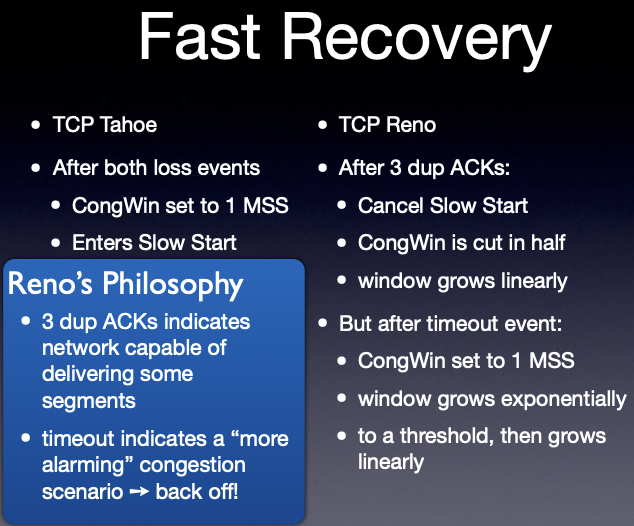
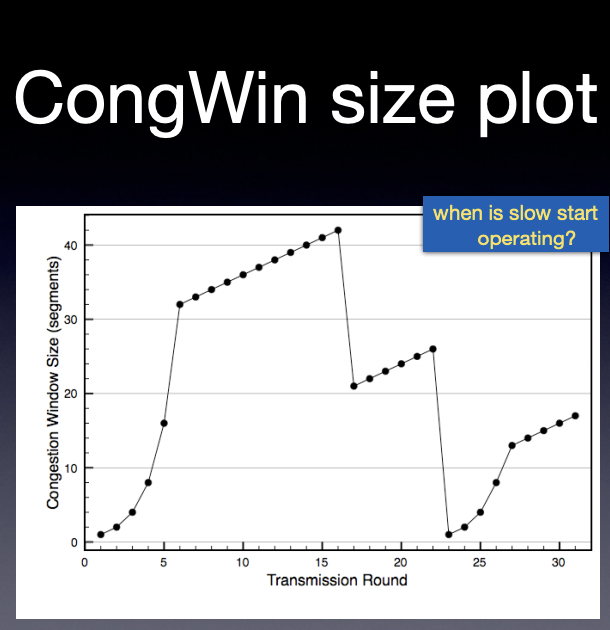
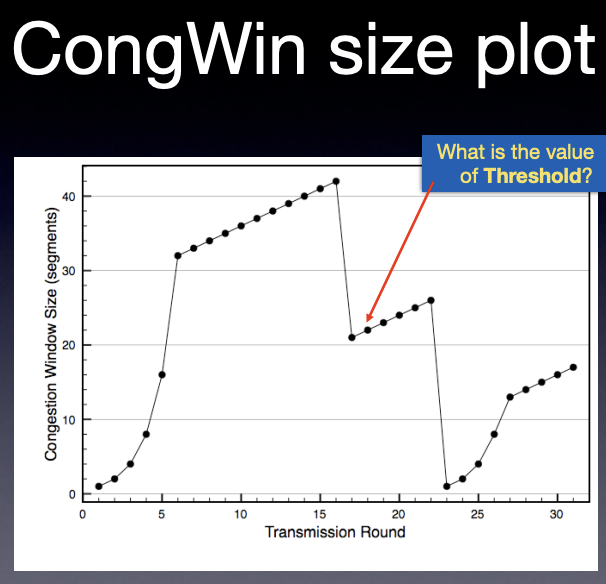
- describe the congestion avoidance component of TCP congestion control; including starting conditions, ending conditions, reactions to loss, reactions to ACKs and differences between Reno and Tahoe versions.
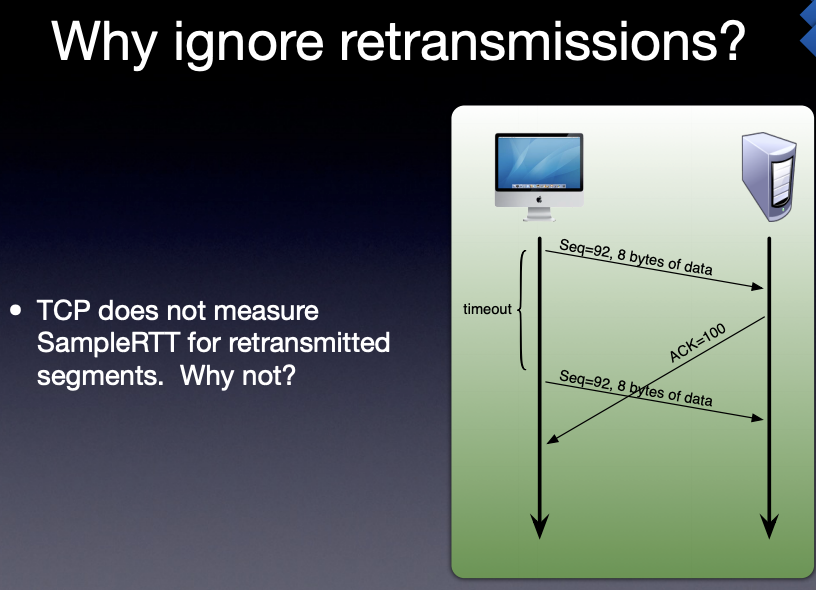
- describe how TCP sets timeout values.
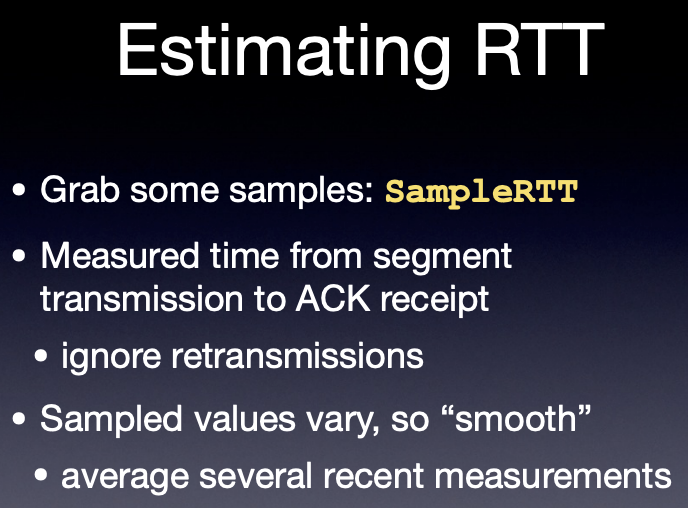
- calculate EstimatedRTT, DevRTT and TimeoutInterval.
Reading
- KR Ch 3.6 - 3.7
- Congestion avoidance / control [Jacobson88]
Slides
Due
- Paper Review: Jacobson88
Video








2 fast coming data flows and 1 slow exiting data flow




find a way to stay in the "knee"


Net assisted CC => bad idea, more packets need to be sent from the router
End-end CC => self-aware
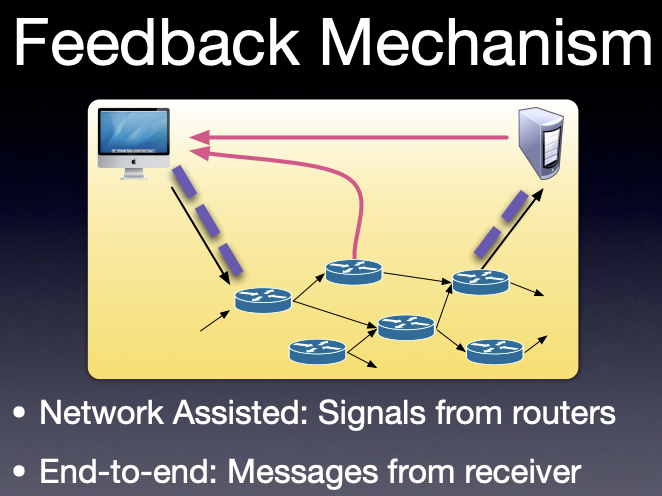

TCP uses End2end congestion control, whereas UDP doesnt have CC.


believe every packet lost is due to congestion



sending too many data at one time
move backwards means timeout and resending message


increasing exponentially and then converge to a steady speed
double the packet number => exponentially increasing

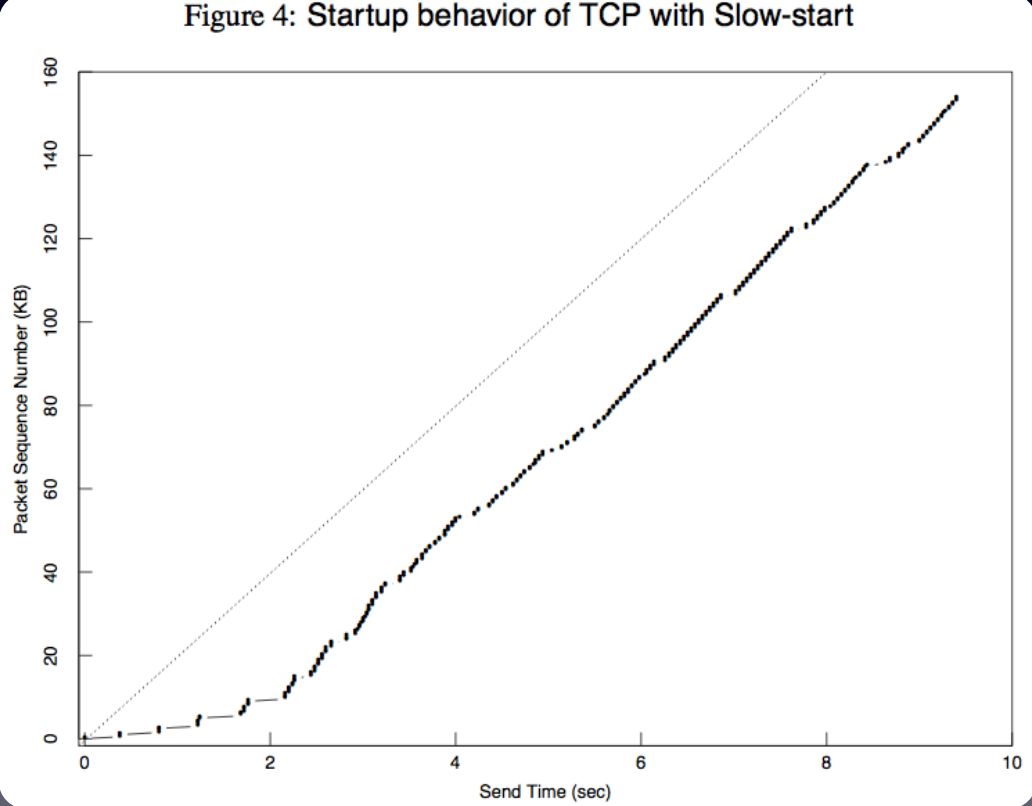
no much resend => a good manner
ANY COUNTERPART IN STOCHASTIC OPTIMIZATION?
https://sgugger.github.io/sgd-variants.html





next class: