Raspberry Pi Linux LESSON 16: Search Inside Files with Grep
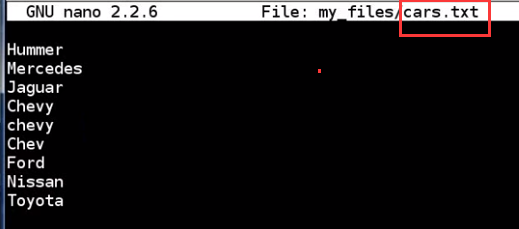
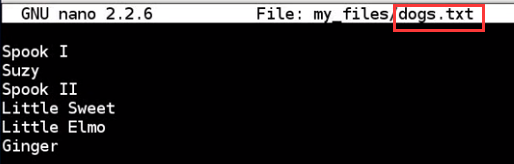
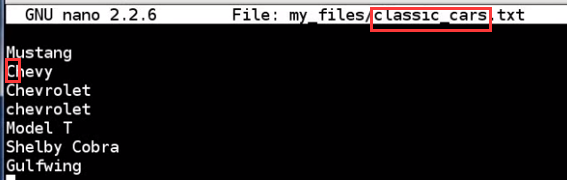
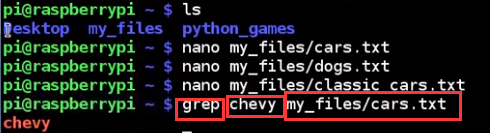
no mazda

-r
means recursively
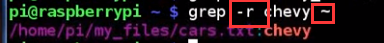

all three command dont get "Chevy", because grep is case sensitive
what if we want case insensitive search?
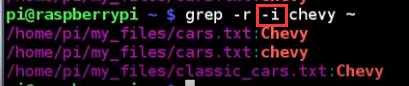
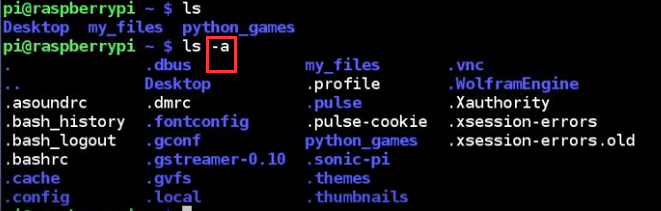
find all "Ch" in every file under home folder, but get to many files. What happened?
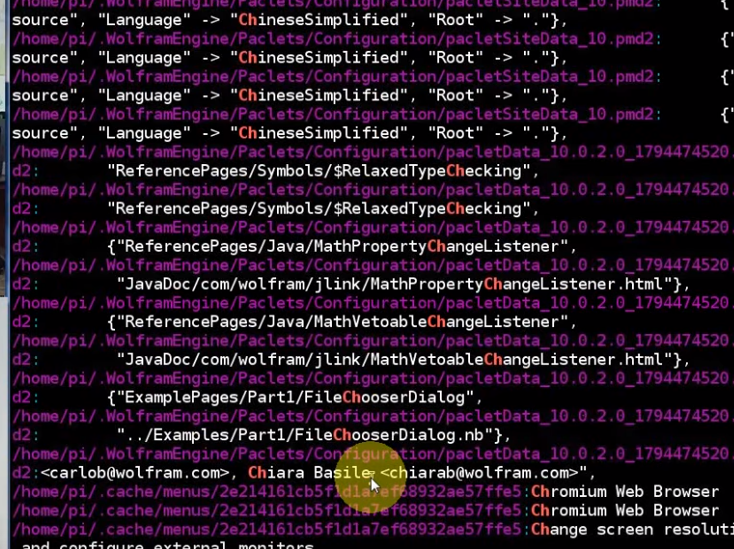
because we have a lot of invisible folders and files
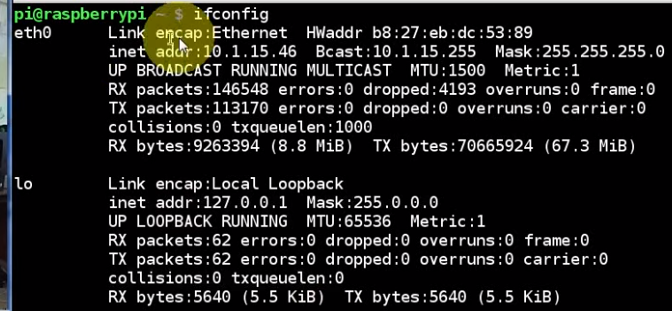
Raspberry PI Linux LESSON 17: Finding the Raspberry Pi IP Address
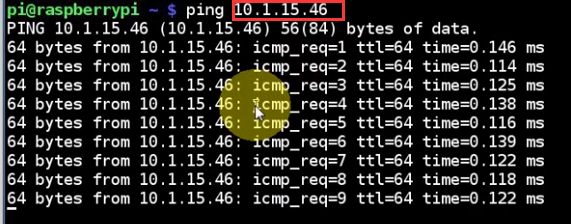
ping yourself
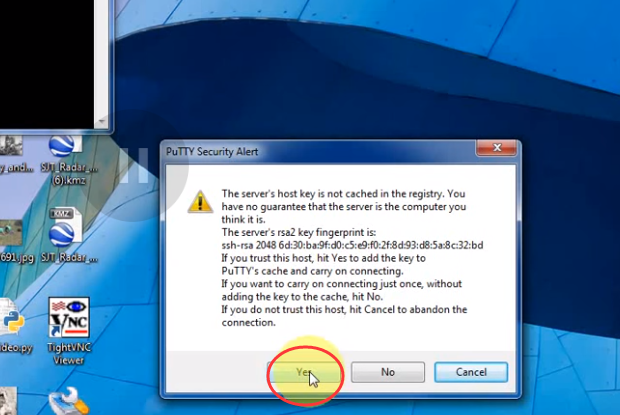
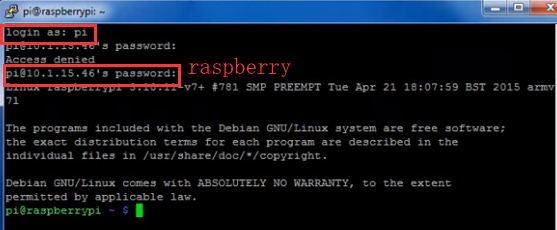
LESSON 18: Remotely Connect from Windows with Putty SSH Telnet Client


LESSON 19: Adding New Users
first see how many users we have?
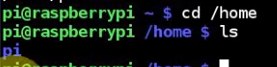
only one user "pi"
-m : make directory for him
-s: he's going to use bin

becomes austin now, and see some welcome words here
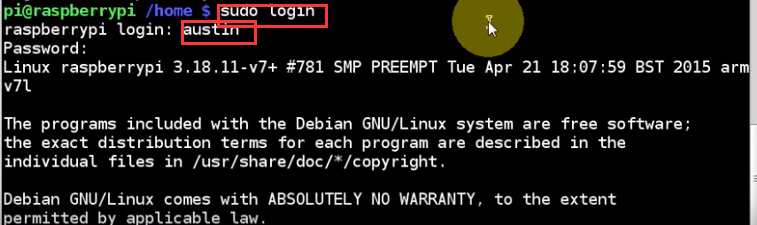
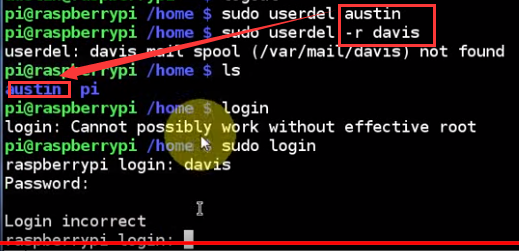
what if austin wants to use davis' folder?
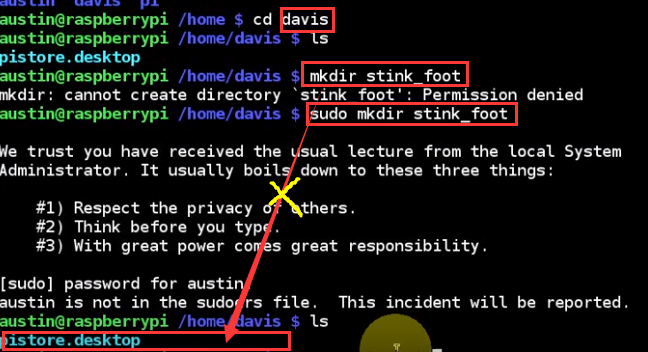
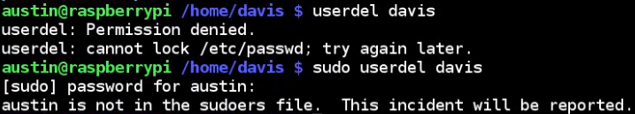
also, austin can't delete davis as an account
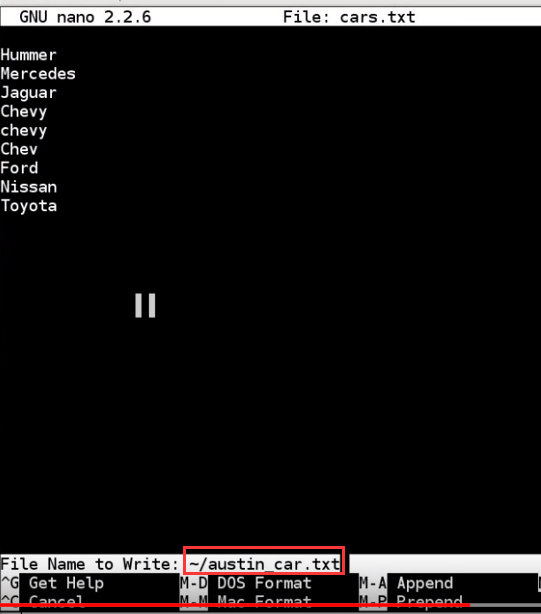
succeed copy files from other users

return to "pi"
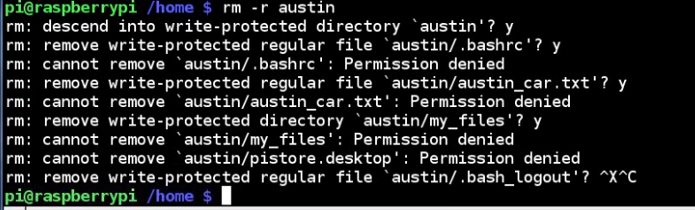
delete austin and davis, but with a "-r", the user's folder will also be deleted
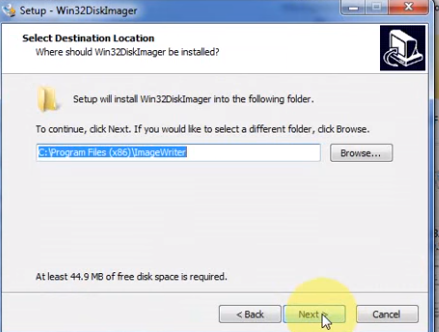
LESSON 20: Backing Up your SD Card and Operating System
remove the SD card

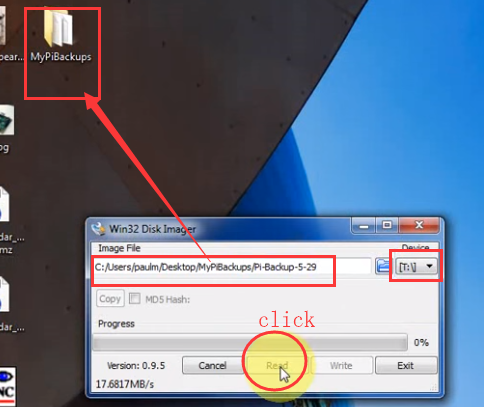
backup
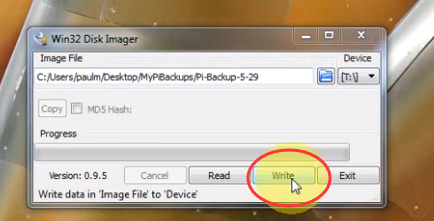
load system from backup
LESSON 21: Create a New admin User Like Pi
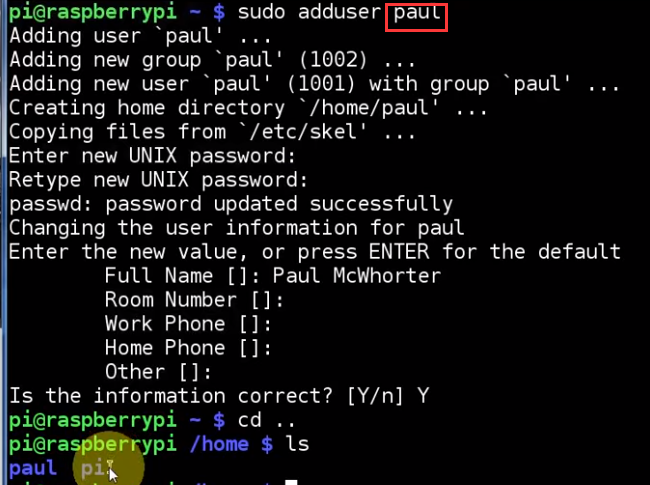
how to make paul like "pi"?
now paul has the privilege


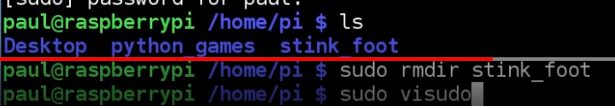

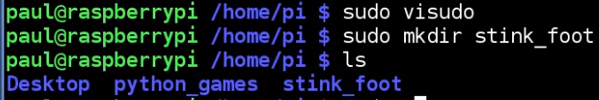
now paul is exactly like "pi"
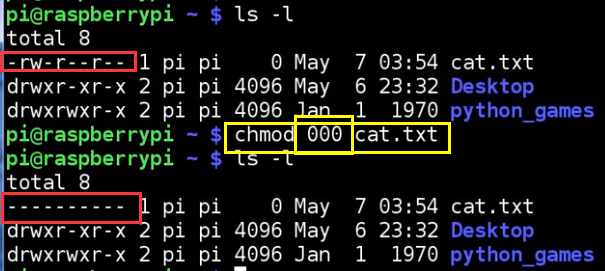
LESSON 22: Understanding Linux File and Folder Permissions
start with "-" -> files
with "d" -> folder
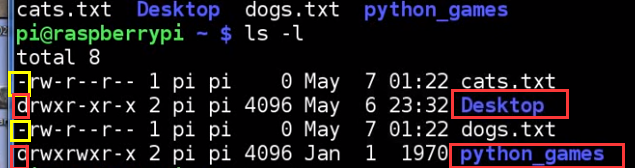
r -> read
w -> write
x -> excute
here, txt files are not excutable
xxx,yyy,zzz
x: owner
y: part of group that owns it
z: anyone else
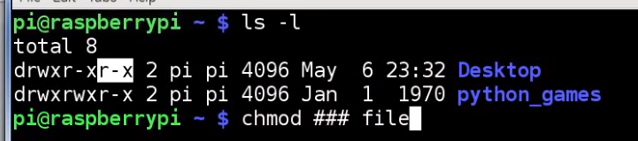
LESSON 23: How to Change File Permissions



LESSON 24: Running Python on the Raspberry Pi



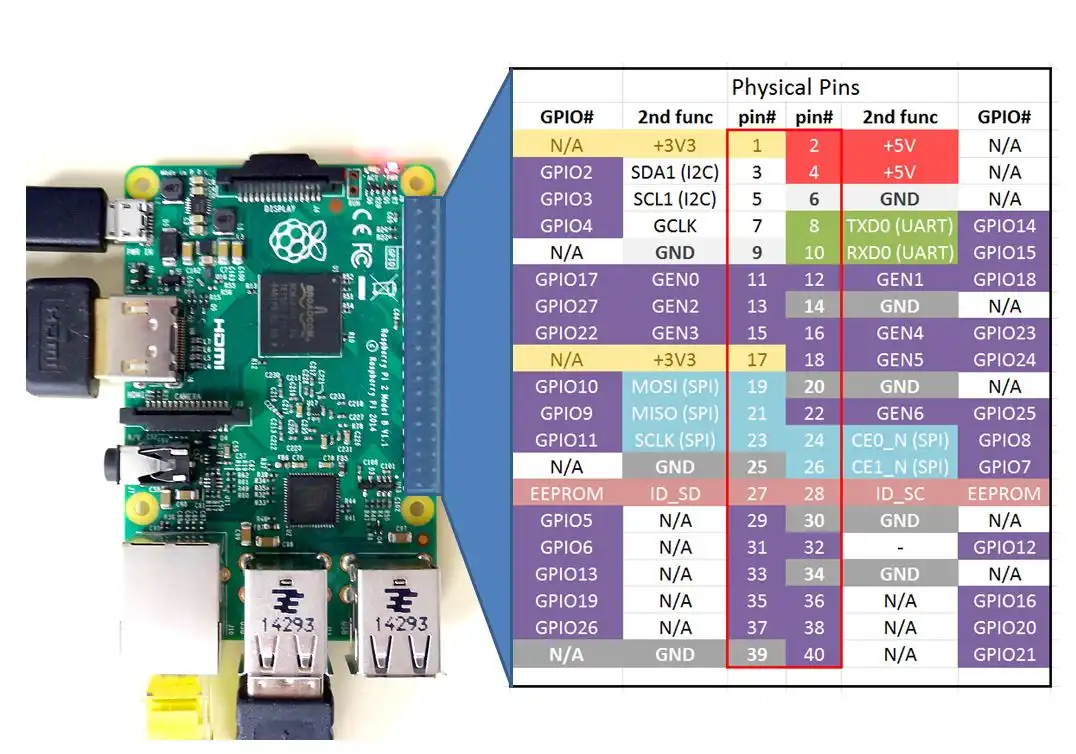
LESSON 25: GPIO Pinout for the Raspberry Pi 2
left and right most are BCM number scheme
Two central columns are BOARD number scheme
LESSON 26: Controlling the Raspberry Pi GPIO pins from Python

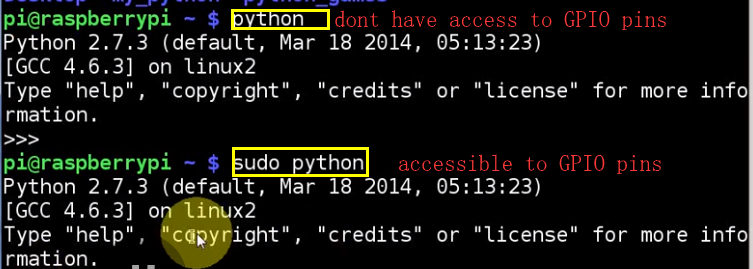

if you dont have the library, exit and:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
GPIO.BOARD is the normal scheme of pin number
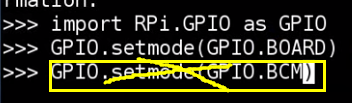
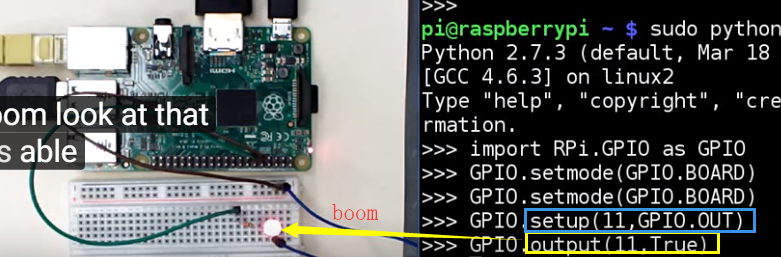
True = 1
False = 0

clean all the pin setting. A good epilogue


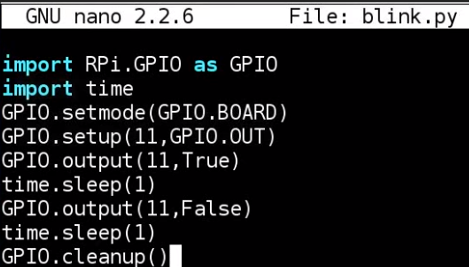

light: ON-OFF-ON-OFF
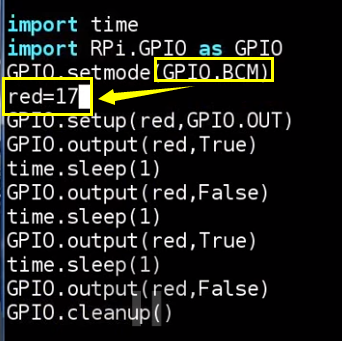
Use BCM number scheme to control pin 11
LESSON 27: PWM Output on GPIO Pins from Python


voltage line drops down on oscilloscope screen
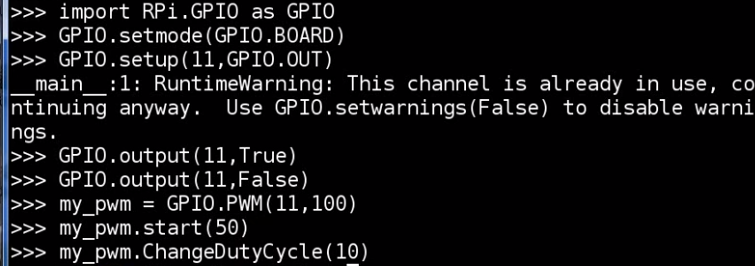
set PWM(11,100)
100 means the cycle is 10 ms
start(50) means half the cycle has high voltage

ChangeDutyCycle(??) :
change the started propotion of high voltage to 10% and 90%



change frequency set on the first step






import RPi.GPIO as g g.setmode(g.BOARD) red = 11 g.setup(red,g.OUTPUT) my_pwm = g.PWM(red,100) my_pwm.start(0) while(1): bright = input("How bright do you want?") #0-100 my_pwm.ChangeDutyCycle(bright) my_pwm.stop() g.cleanup()
LESSON 28. Controlling a Servo with Raspberry Pi and Python
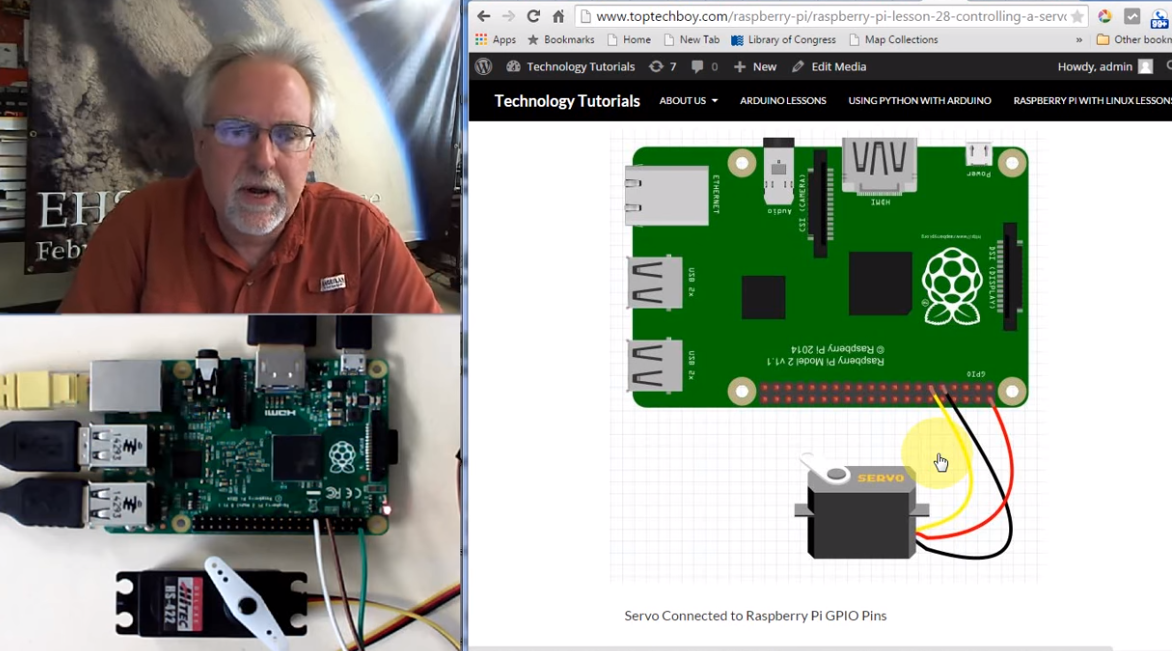
raspberry pi can only put out so much current.
if you hook a big old servo to your rasp that wants more current than what your rasp can produce, you can actually damage your rasp.
if you are not sure, connect your input wires to an external 5v rasp output pin.


here, black is ground, yellow is control, red is power
in arduino, it's super easy to control servo, with writeAngle(...)
but in rasp, you have to know more:


ok, let's do some experiments!
import RPi.GPIO as g g.setmode(g.BOARD) g.setup(11,g.OUT) pwm = g.OWM(11,50) pwm.start(5) pwm.ChangeDutyCycle(2) pwm.ChargeDutyCycle(12)
pwm.stop()
g.cleanup()



import RPi.GPIO as g g.setmode(g.BOARD) g.setup(11,OUTPUT) pwm = g.PWM(11,50) pwm.start(7) for i in range(20): desiredPosition = input("Where do you wan the servo to be 0-180?") DC = desiredPosition/18 + 2 pwm.ChangeDutyCycle(DC) pwm.stop() g.cleanup()
recurrently rotate from 0-180° and 180-0°
import RPi.GPIO as g import time g.setmode(g.BOARD) g.setup(11,OUTPUT) pwm = g.PWM(11,50) pwm.start(7) while(1): for i in range(180): DC = i/18 + 2 pwm.ChangeDutyCycle(DC) time.sleep(0.02) # use 0.05 makes servo slower for i in range(180,0,-1): DC = i/18 + 2 pwm.ChangeDutyCycle(DC) time.sleep(0.02) pwm.stop() g.cleanup()