这篇文章主要记录下Android的常用控件以及使用的方法,Android 给我们提供了大量的UI控件,合理地使用这些控件就可以非常轻松地编写出相当不错的界面,这些是Android学习的基础,没有什么业务逻辑,比较好入手。
这里主要涉及到的控件包括:
文本类控件
TextView 负责展示文本,非编辑
EditText 可编辑文本控件
按钮类控件
Button 按钮
ImageButton 图片按钮
RadioButton与RadioGroup 单选按钮
CheckBox 复选按钮
图片控件
ImageView 负责显示图片
进度条控件
ProgressBar 进度条
设置控件的属性有两种方法,一种是在布局文件中设置参数,另一种是在代码中调用对应方法实现,以下描述的都只是在布局文件中设置参数的方法。
介绍这些控件之前先介绍下所有控件都有的4个属性id、layout_width以及layout_height,以及android:visibility。
android:id = "@+id/xxx" @+id/xxx表示新增控件命名为xxx
android:layout_width = "xxx"
android:layout_height = "xxx"
//下面这个属性默认可以省略
android:visibility = "visible"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
其中layout_width以及layout_height属性可选值有两种 match_parent和wrap_content(其实从Android 2.2开始fill_parent改名为match_parent ,从API Level为8开始我们可以直接用match_parent来代替fill_parent):
match_parent表示让当前控件的大小和父布局的大小一样,也就是由父布局来决定当前控件的大小;
wrap_content表示让当前控件的大小能够刚好包含住里面的内容,也就是由控件内容决定当前控件的大小。
android:visibility表示控件的可见属性,所有的Android控件都具有这个属性,可以通过 android:visibility 进行指定,可选值有三种,visible、invisible 和 gone。visible 表示控件是可见的,这个值是 默认值,不指定 android:visibility 时,控件都是可见的。invisible 表示控件不可见,但是它仍 然占据着原来的位置和大小,可以理解成控件变成透明状态了。gone 则表示控件不仅不可见, 而且不再占用任何屏幕空间。一般用在Activity中通过setVisibility方法来指定呈现与否。
1. 文本类控件TextView
TextView是 Android 程序开发中最常用的控件之一,主要功能是向用户展示文本的内容,它是不可编辑的 ,只能通过初始化设置或在程序中修改。
以下介绍一些常见的属性,更多属性可以参考TextView属性大全
<TextView
//控件id
android:id = "@+id/xxx" @+id/xxx表示新增控件命名为xxx
//宽度与高度
android:layout_width="wrap_content" //wrap_content或者match_parent
android:layout_height="wrap_content" //wrap_content或者match_parent
//文本文字
android:text="@string/hello_world" //两种方式,直接具体文本或者引用values下面的string.xml里面的元素
//字体大小
android:textSize="24sp" //以sp为单位
//字体颜色
android:textColor="#0000FF" //RGB颜色
//字体格式
android:textStyle="normal" //normal,bold,italic分别为正常,加粗以及斜体,默认为normal
//文本显示位置
android:gravity="center" //来指定文字的对齐方式,可选值有 top、bottom、left、right、center 等
//是否只在一行内显示全部内容
android:singleLine="true" //true或者false,默认为false- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
一般不对TextView文本进行修改,所以在Activity中的使用此处略。
2. 文本类控件EditText
相比TextView, EditText是可以编辑的,可以用来与用户进行交互,其用法和TextView也是类似的,同样,下面介绍一些常见的参数,更多参数可以参考EditText属性大全
//控件id
android:id = "@+id/xxx" @+id/xxx表示新增控件命名为xxx
//宽度与高度
android:layout_width="wrap_content" //wrap_content或者match_parent
android:layout_height="wrap_content" //wrap_content或者match_parent
//文本文字
android:text="@string/hello_world" //两种方式,直接具体文本或者引用values下面的string.xml里面的元素
//文本提示内容
android:hint="hello_world" //android:text和android:hint区别是后者只是提示作用,真正需要输入的时候提示的内容会消失
//字体大小
android:textSize="24sp" //以sp为单位
//字体颜色
android:textColor="#0000FF" //RGB颜色
//字体格式
android:textStyle="normal" //normal,bold,italic分别为正常,加粗以及斜体,默认为normal
//文本显示位置
android:gravity="center" //来指定文字的对齐方式,可选值有 top、bottom、left、right、center 等
//是否只在一行内显示全部内容
android:singleLine="true" //true或者false,默认为false
//输入内容设置为password类型
android:password="true" //输入的内容会变成······
//输入内容设置为phoneNumber类型
android:phoneNumber="true" //只能输入数字
//设定光标为显示/隐藏
android:cursorVisible = "false" //true或者false,默认为true显示- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
在Activity中简单用法:
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
//声明一个EditText
private EditText edittext;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
//给当前的活动加载一个布局
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//初始化edittext
edittext=(EditText) findViewById(R.id.edit_text);
}
...
...
//在方法中调用给edittext赋值
edittext.setText("success");
...
...
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
3.按钮类控件Button
Button控件也是使用过程中用的最多的控件之一,所以需要好好掌握。用户可以通过单击 Button 来触发一系列事件,然后为 Button 注册监听器,来实现 Button 的监听事件。
首先来看下Button的配置属性,其实和TextView差不多设置更简单点,主要是显示到Button上面的文字提示:
<Button
//控件id
android:id = "@+id/xxx" @+id/xxx表示新增控件命名为xxx
//宽度与高度
android:layout_width="wrap_content" //wrap_content或者match_parent
android:layout_height="wrap_content" //wrap_content或者match_parent
//按钮上显示的文字
android:text="theButton" //两种方式,直接具体文本或者引用values下面的string.xml里面的元素@string/button
//按钮字体大小
android:textSize="24sp" //以sp为单位
//字体颜色
android:textColor="#0000FF" //RGB颜色
//字体格式
android:textStyle="normal" //normal,bold,italic分别为正常,加粗以及斜体,默认为normal
//是否只在一行内显示全部内容
android:singleLine="true" //true或者false,默认为false- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
然后我们需要在Activity中为Button的点击事件注册一个监听器,以下介绍两种方式来实现按钮监听事件,更多方法可以参考下Android的按钮单击事件及监听器的实现方式
1.通过匿名内部类作为事件监听器类,这种方法适用于事件监听器只是临时使用一次,因为大部分时候,事件处理器都没有什么利用价值(可利用代码通常都被抽象成了业务逻辑方法),这是一种使用最广泛的方法:
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private EditText edittext;
private Button button;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
edittext=(EditText) findViewById(R.id.edit_text);
button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button);
//为button按钮注册监听器,并通过匿名内部类实现
button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//点击Button会改变edittext的文字为"点击了Button"
edittext.setText("点击了Button");
}
});
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
2.使用实现接口的方式来进行注册,让Activity类实现了OnClickListener事件监听接口,从而可以在该Activity类中直接定义事件处理器方法:onClick(view v),当为某个组件添加该事件监听器对象时,直接使用this作为事件监听器对象即可:
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
private EditText edittext;
private Button button;
private Button button2;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
edittext=(EditText) findViewById(R.id.edit_text);
button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button);
button2 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button2);
button.setOnClickListener(this);
button2.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
//用switch区分是哪个id
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()){
case R.id.button:
edittext.setText("点击了Button");
break;
case R.id.button2:
edittext.setText("点击了Button2");
break;
}
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
4.按钮类控件ImageButton
ImageButton和Button类似,是一个按钮,ImageButton可以实现我们任何想要的图片按钮的效果,比如我们租一个下载的按钮等等。它要比button实现的要好看,并且体验要好很多, 不过它是以图片作为背景,没有文字。利用属性android:src="图片位置"来设置图片背景。
下面还是先给出一些常见的属性:
<ImageButton
//控件id
android:id = "@+id/xxx" @+id/xxx表示新增控件命名为xxx
//宽度与高度
android:layout_width="wrap_content" //wrap_content或者match_parent
android:layout_height="wrap_content" //wrap_content或者match_parent
//此外,可以具体设置高度和宽度显示的像素,不过这样设置如果图片尺寸大于设置的显示的尺寸,则图片是显示不全的,这是可以配合android:scaleType属性。
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
//把原图按照指定的大小在View中显示,拉伸显示图片,不保持原比例,填满ImageButton.
android:scaleType="fitXY"
//其他的关于android:scaleType的参数解释,也可以参考下面的直观图
//android:scaleType="center" 在视图中心显示图片,并且不缩放图片
//android:scaleType="centercrop" 按比例缩放图片,使得图片长 (宽)的大于等于视图的相应维度
//android:scaleType="centerinside" 按比例缩放图片,使得图片长 (宽)的小于等于视图的相应维度
//android:scaleType="fitcenter" 按比例缩放图片到视图的最小边,居中显示
//android:scaleType="fitend" 按比例缩放图片到视图的最小边,显示在视图的下部分位置
//android:scaleType="fitstart" 把图片按比例扩大/缩小到视图的最小边,显示在视图的上部分位置
//android:scaleType="matrix" 用矩阵来绘制
//图片来源,需要将图片复制放到res/drawable文件夹里面,引用的时候不需要写图片的后缀
android:src ="@drawable/beautiful"> - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
附上android:scaleType不同参数对应效果图: 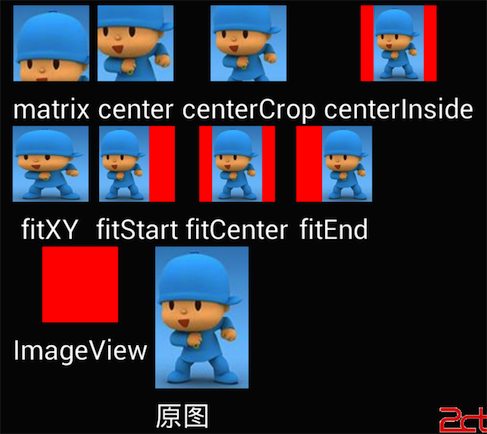
ImageButton的用法在Button在Activity中的用法基本一致,可以参考上面关于Button的用法,此处略。
5.按钮类控件RadioButton与RadioGroup
RadioButton(单选按钮)在 Android 平台上也比较常用,比如一些选择项会用到单选按钮。它是一种单个圆形单选框双状态的按钮,可以选择或不选择。在 RadioButton 没有 被选中时,用户通过单击来选中它。但是,在选中后,无法通过单击取消选中。
RadioGroup 是单选组合框,用于 将 RadioButton 框起来。在多个 RadioButton被 RadioGroup 包含的情况下,同一时刻只可以选择一个 RadioButton,并用 setOnCheckedChangeListener 来对 RadioGroup 进行监听。
下面介绍RadioGroup的常用的属性,因为其中包含有RadioButton:
<RadioGroup
android:id="@+id/radio_group"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
//设置RadioButton的排列方式,分为水平排列horizontal与垂直排列vertical
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/rd1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
//设置单选后紧跟的文本提示文字
android:text="北京"
//设置文字的大小
android:textSize="30sp"
//设置文字的颜色
android:textColor="#0000FF"
//字体格式
android:textStyle="normal" //normal,bold,italic分别为正常,加粗以及斜体,默认为normal
/>
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/rd2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="30sp"
android:text="上海" />
</RadioGroup>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
下面给出在Activity中用 setOnCheckedChangeListener 来对 RadioGroup 进行监听的代码, 注意RadioGroup中的RadioButton也都是需要声明和通过控件的id来得到代表控件的对象。
public class MainActivity extends Activity{
////对控件对象进行声明
private TextView textView;
private RadioGroup radiogroup;
private RadioButton radiobutton1;
private RadioButton radiobutton2;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//通过控件的ID来得到代表控件的对象
textView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text_view);
radiogroup = (RadioGroup) findViewById(R.id.radio_group);
radiobutton1 = (RadioButton) findViewById(R.id.rd1);
radiobutton2 = (RadioButton) findViewById(R.id.rd2);
//调用setOnCheckedChangeListener来对RadioGroup进行监听的代码
radiogroup.setOnCheckedChangeListener(new RadioGroup.OnCheckedChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(RadioGroup group, int checkedId) {
if(checkedId == radiobutton1.getId()){
textView.setText("北京");
}else if(checkedId == radiobutton2.getId()){
textView.setText("上海");
}
}
});
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
6.按钮类控件CheckBox
CheckBox(复选按钮),顾名思义是一种可以进行多选的按钮,默认以矩形表示。与 RadioButton 相同,它也有选中或者不选中双状态。我们可以先在布局文件中定义多选按钮, 然后对每一个多选按钮进行事件监听 setOnCheckedChangeListener,通过 isChecked 来判断 选项是否被选中,做出相应的事件响应。
下面给出CheckBox在布局文件中的常用的属性以及用法:
<CheckBox
android:id="@+id/cb1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
//设置复选按钮后紧跟的文本提示文字
android:text="北京"
//设置文字的大小
android:textSize="30sp"
//设置文字的颜色
android:textColor="#0000FF"
//字体格式
android:textStyle="normal" //normal,bold,italic分别为正常,加粗以及斜体,默认为normal/>
<CheckBox
android:id="@+id/cb2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="上海"
android:textSize="30sp"
android:textColor="#0000FF"/>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
在Activity中调用的代码如下:
public class MainActivity extends Activity{
////对控件对象进行声明
private TextView textView;
private CheckBox checkbox1;
private CheckBox checkbox2;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//通过控件的ID来得到代表控件的对象
textView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text_view);
checkbox1 = (CheckBox) findViewById(R.id.cb1);
checkbox2 = (CheckBox) findViewById(R.id.cb2);
//为第一个 CheckBox 注册监听
checkbox1.setOnCheckedChangeListener(new OnCheckedChangeListener(){
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(CompoundButton buttonView, boolean isChecked) {
//如果第一个 CheckBox 被选中
if(isChecked == true){
textView.setText("CheckBox选中北京");
}
}
});
//为第二个 CheckBox 注册监听
checkbox2.setOnCheckedChangeListener(new OnCheckedChangeListener(){
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(CompoundButton buttonView, boolean isChecked) {
//如果第二个 CheckBox 被选中
if(isChecked == true){
textView.setText("CheckBox选中上海");
}
}
});
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
7.图片控件ImageView
ImageView 是一个图片控件,负责显示图片,图片的来源可以是系统提供的资源文件,也可以是 Drawable 对象,相对来说,图片空间还是比较好掌握的,因为前面有讲过ImageButton, 很多属性都是相同的。
下面直接给出在布局中的属性:
<ImageView
//控件id
android:id = "@+id/xxx" @+id/xxx表示新增控件命名为xxx
//宽度与高度
android:layout_width="wrap_content" //wrap_content或者match_parent
android:layout_height="wrap_content" //wrap_content或者match_parent
//此外,可以具体设置高度和宽度显示的像素,不过这样设置如果图片尺寸大于设置的显示的尺寸,则图片是显示不全的,这是可以配合android:scaleType属性。
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
//把原图按照指定的大小在View中显示,拉伸显示图片,不保持原比例,填满ImageButton.
android:scaleType="fitXY"
//其他的关于android:scaleType的参数解释,也可以参考下面的直观图
//android:scaleType="center" 在视图中心显示图片,并且不缩放图片
//android:scaleType="centercrop" 按比例缩放图片,使得图片长 (宽)的大于等于视图的相应维度
//android:scaleType="centerinside" 按比例缩放图片,使得图片长 (宽)的小于等于视图的相应维度
//android:scaleType="fitcenter" 按比例缩放图片到视图的最小边,居中显示
//android:scaleType="fitend" 按比例缩放图片到视图的最小边,显示在视图的下部分位置
//android:scaleType="fitstart" 把图片按比例扩大/缩小到视图的最小边,显示在视图的上部分位置
//android:scaleType="matrix" 用矩阵来绘制
//图片来源,需要将图片复制放到res/drawable文件夹里面,引用的时候不需要写图片的后缀
android:src ="@drawable/beautiful"> - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
在Activity中因为不需要设置监听,较简单,用法略。
8.进度条控件ProgressBar
ProgressBar 用于在界面上显示一个进度条,表示我们的程序正在加载一些数据,运行程序,会看到屏幕中有一个圆形进度条正在旋转。
在布局xml文件中的用法非常简单:
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/pb"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
//默认是圆形进度条,可以知道样式设置为水平进度条
style="?android:attr/progressBarStyleHorizontal"/>
//指定成水平进度条后,我们还可以通过 android:max属性给进度条设置一个最大值,然后在代码中动态地更改进度条的进度
android:max="100"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
那么如何才能让进度条在数据加载完成时消失呢,这里我们就需要用一开始所讲的Android 控件的可见属性。
可以通过代码来设置控件的可见性,使用的是 setVisibility()方法,可以传入 View.VISIBLE、View.INVISIBLE 和 View.GONE 三种值。
下面实现点击一下按钮让进度条消失,再点击一下按钮让进度条出现的这种效果,这里只给出按钮监听的代码:
button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//通过 getVisibility()方法来判断 ProgressBar 是否可见
if (progressBar.getVisibility() == View.GONE) {
progressBar.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
} else {
progressBar.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
}
});- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
至此,关于Android的常用控件都已经讲了一遍,此处再对将关于TextView中文字单独在一行显示的时候实现跑马灯的方法补充下,这里直接给出代码,也可以参考下这篇blog下android:ellipsize实现跑马灯效果总结
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="TextViewTextViewTextViewTextViewTextViewTextViewTextViewTextView"
//主要是以下5个
android:ellipsize="marquee"
android:marqueeRepeatLimit="marquee_forever"
android:focusable="true"
android:focusableInTouchMode ="true"
android:singleLine="true" />