先看一张图, 从这张图里, 能看到请求是如何从CLR进入HttpRuntime的.
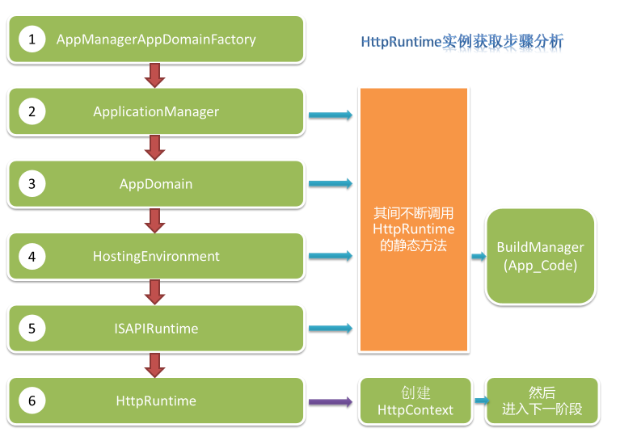
一、AppManagerAppDomainFactory
看到这张图是从 AppManagerAppDomainFactory 开始的, 按照汤姆大叔博文中所说, 是在CLR初始化加载的时候, 来加载这个类的. 那么来看一下这个类吧.
使用Reflector反编译搜索AppManagerAppDomainFactory 类, 可以看到(由于这个类并不多, 那么我先贴一个完整的出来吧):
[SecurityPermission(SecurityAction.LinkDemand, Unrestricted=true)] public sealed class AppManagerAppDomainFactory : IAppManagerAppDomainFactory { // Fields private ApplicationManager _appManager = ApplicationManager.GetApplicationManager(); // Methods public AppManagerAppDomainFactory() { this._appManager.Open(); } internal static string ConstructSimpleAppName(string virtPath) { if (virtPath.Length > 1) { return virtPath.Substring(1).ToLower(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture).Replace('/', '_'); } if (!BuildManagerHost.InClientBuildManager && HostingEnvironment.IsDevelopmentEnvironment) { return "vs"; } return "root"; } [return: MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.Interface)] public object Create(string appId, string appPath) { object obj2; try { if (appPath[0] == '.') { FileInfo info = new FileInfo(appPath); appPath = info.FullName; } if (!StringUtil.StringEndsWith(appPath, '\')) { appPath = appPath + @""; } ISAPIApplicationHost appHost = new ISAPIApplicationHost(appId, appPath, false); ISAPIRuntime o = (ISAPIRuntime) this._appManager.CreateObjectInternal(appId, typeof(ISAPIRuntime), appHost, false, null); o.StartProcessing(); obj2 = new ObjectHandle(o); } catch (Exception) { throw; } return obj2; } public void Stop() { this._appManager.Close(); } }
至于这里详细的解说, 推荐去 MVC之前的那些事儿 去瞧瞧, 这里并不是我想表述的重点, 就不介绍了.
只要知道, 按照大叔的说法, 这里, 在CreateObjectInternal方法中, 创建了AppDomain, 创建了HostingEnvironment等一些列操作.
后续所有的比如HttpRuntime, HttpContext等, 都是依托于这个AppDomain.
二、主题
经过各种我不知道的内部处理, 非托管代码开始正式调用 ISAPIRuntime 的 ProcessRequest(后面简称为PR方法)了.
(ISPAIRuntime继承了IISPAIRuntime接口,该接口可以和COM进行交互,并且暴露了ProcessRequest接口方法)
不要问我为什么会调用PR方法, 因为我也不知道, 但是真的是这个方法.
public sealed class ISAPIRuntime : MarshalByRefObject, IISAPIRuntime, IISAPIRuntime2, IRegisteredObject { // Fields private static int _isThisAppDomainRemovedFromUnmanagedTable; private const int WORKER_REQUEST_TYPE_IN_PROC = 0; private const int WORKER_REQUEST_TYPE_IN_PROC_VERSION_2 = 2; private const int WORKER_REQUEST_TYPE_OOP = 1; // Methods [SecurityPermission(SecurityAction.Demand, Unrestricted=true)] public ISAPIRuntime(); [SecurityPermission(SecurityAction.LinkDemand, Unrestricted=true)] public void DoGCCollect(); public override object InitializeLifetimeService(); [SecurityPermission(SecurityAction.LinkDemand, Unrestricted=true)] public int ProcessRequest(IntPtr ecb, int iWRType); internal static void RemoveThisAppDomainFromUnmanagedTable(); [SecurityPermission(SecurityAction.LinkDemand, Unrestricted=true)] public void StartProcessing(); [SecurityPermission(SecurityAction.LinkDemand, Unrestricted=true)] public void StopProcessing(); [TargetedPatchingOptOut("Performance critical to inline this type of method across NGen image boundaries")] void IISAPIRuntime2.DoGCCollect(); [TargetedPatchingOptOut("Performance critical to inline this type of method across NGen image boundaries")] int IISAPIRuntime2.ProcessRequest(IntPtr ecb, int iWRType); [TargetedPatchingOptOut("Performance critical to inline this type of method across NGen image boundaries")] void IISAPIRuntime2.StartProcessing(); [TargetedPatchingOptOut("Performance critical to inline this type of method across NGen image boundaries")] void IISAPIRuntime2.StopProcessing(); void IRegisteredObject.Stop(bool immediate); }
这里有个方法, 看名字就觉得好熟悉, 好吧, 点进去看一下:

GC 一个叫垃圾回收的东东, 好熟悉的名字. OK, 这不是重点, 接下来继续.
[SecurityPermission(SecurityAction.LinkDemand, Unrestricted=true)] public int ProcessRequest(IntPtr ecb, int iWRType) { IntPtr zero = IntPtr.Zero; if (iWRType == 2) { zero = ecb; ecb = UnsafeNativeMethods.GetEcb(zero); } ISAPIWorkerRequest wr = null; try { bool useOOP = iWRType == 1; wr = ISAPIWorkerRequest.CreateWorkerRequest(ecb, useOOP); wr.Initialize(); string appPathTranslated = wr.GetAppPathTranslated(); string appDomainAppPathInternal = HttpRuntime.AppDomainAppPathInternal; if ((appDomainAppPathInternal == null) || StringUtil.EqualsIgnoreCase(appPathTranslated, appDomainAppPathInternal)) { HttpRuntime.ProcessRequestNoDemand(wr); return 0; } HttpRuntime.ShutdownAppDomain(ApplicationShutdownReason.PhysicalApplicationPathChanged,
SR.GetString("Hosting_Phys_Path_Changed",
new object[] { appDomainAppPathInternal, appPathTranslated })); return 1; } catch (Exception exception) { try { WebBaseEvent.RaiseRuntimeError(exception, this); } catch { } if ((wr == null) || !(wr.Ecb == IntPtr.Zero)) { throw; } if (zero != IntPtr.Zero) { UnsafeNativeMethods.SetDoneWithSessionCalled(zero); } if (exception is ThreadAbortException) { Thread.ResetAbort(); } return 0; } }
第一个注意到的就是该方法的IntPtr类型的参数ecb,ecb是啥?ecb是一个非托管的指针,全称是Execution Control Block,在整个Http Request Processing过程中起着非常重要的作用,我们现在来简单介绍一个ECB。
非托管环境ISAPI对ISAPIRuntime的调用,需要传递一些必须的数据,比如ISAPIRuntime要获取Server Variable的数据,获取通过Post Mehod传回Server的数据;以及最终将Response的内容返回给非托管环境ISAPI,然后呈现给Client用户。一般地ISAPIRuntime不能直接调用ISAPI,所以这里就通过一个对象指针实现对其的调用,这个对象就是ECB,ECB实现了对非托管环境ISAPI的访问。
还有一点特别需要强调的是,ISAPI对ISAPIRutime的调用是异步的,也就是说ISAPI调用ISAPIRutime之后立即返回。这主要是出于Performance和Responsibility考虑的,因为ASP.NET Application天生就是一个多线程的应用,为了具有更好的响应能力,异步操作是最有效的解决方式。但是这里就会有一个问题,我们知道我们对ASP.NET 资源的调用本质上是一个Request/Response的Message Exchange Pattern,异步调用往往意味着ISAPI将Request传递给ISAPIRuntime,将不能得到ISAPIRuntime最终生成的Response,这显然是不能接受的。而ECB解决了这个问题,ISAPI在调用ISAPIRutime的ProcessRequest方法时会将自己对应的ECB的指针传给它,ISAPIRutime不但可以将最终生成的Response返回给ISAPI,还能通过ECB调用ISAPI获得一些所需的数据。
1. CreateWorkerRequest
这个方法还是要看一下的, 有收获哦.
internal static ISAPIWorkerRequest CreateWorkerRequest(IntPtr ecb, bool useOOP) { if (useOOP) { EtwTrace.TraceEnableCheck(EtwTraceConfigType.DOWNLEVEL, IntPtr.Zero); if (EtwTrace.IsTraceEnabled(5, 1)) { EtwTrace.Trace(EtwTraceType.ETW_TYPE_APPDOMAIN_ENTER, ecb, Thread.GetDomain().FriendlyName, null, false); } return new ISAPIWorkerRequestOutOfProc(ecb); } int num = UnsafeNativeMethods.EcbGetVersion(ecb) >> 0x10; if (num >= 7) { EtwTrace.TraceEnableCheck(EtwTraceConfigType.IIS7_ISAPI, ecb); } else { EtwTrace.TraceEnableCheck(EtwTraceConfigType.DOWNLEVEL, IntPtr.Zero); } if (EtwTrace.IsTraceEnabled(5, 1)) { EtwTrace.Trace(EtwTraceType.ETW_TYPE_APPDOMAIN_ENTER, ecb, Thread.GetDomain().FriendlyName, null, true); } if (num >= 7) { return new ISAPIWorkerRequestInProcForIIS7(ecb); } if (num == 6) { return new ISAPIWorkerRequestInProcForIIS6(ecb); } return new ISAPIWorkerRequestInProc(ecb); }
通过判断ecb和type类型的具体内容,来决定创建什么类型的WorkerRequest(上述类型的ISPAIWorkerRequest都继承于HttpWorkerRequest),上面的代码可以看出对不同版本的IIS进行了不同的包装,通过其Initialize方法来初始化一些基本的信息(比如:contentType, querystring的长度,filepath等相关信息)。
2. ProcessRequestNoDemand
这个方法, 是真正进入ASP.NET Runtime Pipeline的唯一入口, 传递的参数是上面屏蔽了差异化以后的WorkerRequest对象实例.来看一下这个方法
internal static void ProcessRequestNoDemand(HttpWorkerRequest wr) { RequestQueue queue = _theRuntime._requestQueue; wr.UpdateInitialCounters(); if (queue != null) { wr = queue.GetRequestToExecute(wr); } if (wr != null) { CalculateWaitTimeAndUpdatePerfCounter(wr); wr.ResetStartTime(); ProcessRequestNow(wr); } }
Ok, 接下来, 继续看, PRNow方法, 其实内部调用的是 HttpRuntime的 ProcessRequestInternal 方法.
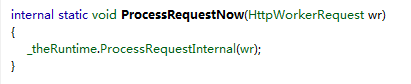
private void ProcessRequestInternal(HttpWorkerRequest wr) { Interlocked.Increment(ref this._activeRequestCount); if (this._disposingHttpRuntime) { try { wr.SendStatus(0x1f7, "Server Too Busy"); wr.SendKnownResponseHeader(12, "text/html; charset=utf-8"); byte[] bytes = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("<html><body>Server Too Busy</body></html>"); wr.SendResponseFromMemory(bytes, bytes.Length); wr.FlushResponse(true); wr.EndOfRequest(); } finally { Interlocked.Decrement(ref this._activeRequestCount); } } else { HttpContext context; try { context = new HttpContext(wr, false); } catch { try { wr.SendStatus(400, "Bad Request"); wr.SendKnownResponseHeader(12, "text/html; charset=utf-8"); byte[] data = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("<html><body>Bad Request</body></html>"); wr.SendResponseFromMemory(data, data.Length); wr.FlushResponse(true); wr.EndOfRequest(); return; } finally { Interlocked.Decrement(ref this._activeRequestCount); } } wr.SetEndOfSendNotification(this._asyncEndOfSendCallback, context); HostingEnvironment.IncrementBusyCount(); try { try { this.EnsureFirstRequestInit(context); } catch { if (!context.Request.IsDebuggingRequest) { throw; } } context.Response.InitResponseWriter(); IHttpHandler applicationInstance = HttpApplicationFactory.GetApplicationInstance(context); if (applicationInstance == null) { throw new HttpException(SR.GetString("Unable_create_app_object")); } if (EtwTrace.IsTraceEnabled(5, 1)) { EtwTrace.Trace(EtwTraceType.ETW_TYPE_START_HANDLER, context.WorkerRequest,
applicationInstance.GetType().FullName, "Start"); } if (applicationInstance is IHttpAsyncHandler) //异步处理 { IHttpAsyncHandler handler2 = (IHttpAsyncHandler) applicationInstance; context.AsyncAppHandler = handler2; handler2.BeginProcessRequest(context, this._handlerCompletionCallback, context); } else //同步处理 { applicationInstance.ProcessRequest(context); this.FinishRequest(context.WorkerRequest, context, null); } } catch (Exception exception) { context.Response.InitResponseWriter(); this.FinishRequest(wr, context, exception); } } }
最让人开心的, 可能就是看到, 在这个方法中创建了 HttpContext 对象和 HttpApplication 对象.
接下来, 分别看一下这两个对象的创建.
1). HttpContext
internal HttpContext(HttpWorkerRequest wr, bool initResponseWriter) { this._timeoutStartTimeUtcTicks = -1L; this._timeoutTicks = -1L; this._threadAbortOnTimeout = true; this.ThreadContextId = new object(); this._wr = wr; this.Init(new HttpRequest(wr, this), new HttpResponse(wr, this)); if (initResponseWriter) { this._response.InitResponseWriter(); } PerfCounters.IncrementCounter(AppPerfCounter.REQUESTS_EXECUTING); }
我们又看到了2个惊喜的代码,HttpRequest和HttpResponse的实例化,通过对WorkerRequest和对HttpContext对象this参数的传递,将获取各自需要的信息
2). HttpApplication
这个对象的创建, 是后面那句标红的部分.
IHttpHandler applicationInstance = HttpApplicationFactory.GetApplicationInstance(context);
通过HttpApplicationFactory的GetApplicationInstance静态方法,获取我们熟悉的HttpApplication对象实例,由于HttpApplication对象是继承IHttpAsyncHandler,而IHttpAsyncHandler又继承于IHttpHandler,所以上面app的类型是IHttpHandler是没有错的。继续看后面的if (app is IHttpAsyncHandler)代码,就知道了app肯定走这里的分支,然后执行调用asyncHandler.BeginProcessRequest方法了。
至此,HttpRuntime已经正式发挥其无可替代的作用了,也正式通过此对象正式进入了HttpApplication对象的创建以及大家熟知的HttpApplication以后的生命周期了。
转载参考: