hive是基于Hadoop的一个数据仓库工具,用来进行数据提取、转化、加载,这是一种可以存储、查询和分析存储在Hadoop中的大规模数据的机制。hive数据仓库工具能将结构化的数据文件映射为一张数据库表,并提供SQL查询功能,能将SQL语句转变成MapReduce任务来执行。Hive的优点是学习成本低,可以通过类似SQL语句实现快速MapReduce统计,使MapReduce变得更加简单,而不必开发专门的MapReduce应用程序。hive是十分适合数据仓库的统计分析和Windows注册表文件。
drop、delete与truncate的区别
三者都表示删除,但是三者有一些差别:
|
Delete |
Truncate |
Drop |
|
| 类型 | 属于DML | 属于DDL | 属于DDL |
| 回滚 | 可回滚 | 不可回滚 | 不可回滚 |
| 删除内容 | 表结构还在,删除表的全部或者一部分数据行 | 表结构还在,删除表中的所有数据 | 从数据库中删除表,所有的数据行,索引和权限也会被删除 |
| 删除速度 | 删除速度慢,需要逐行删除 | 删除速度快 | 删除速度最快 |
因此,在不再需要一张表的时候,用drop;在想删除部分数据行时候,用delete;在保留表而删除所有数据的时候用truncate。
15. UNION与UNION ALL的区别?
-
如果使用UNION ALL,不会合并重复的记录行
-
效率 UNION 高于 UNION ALL
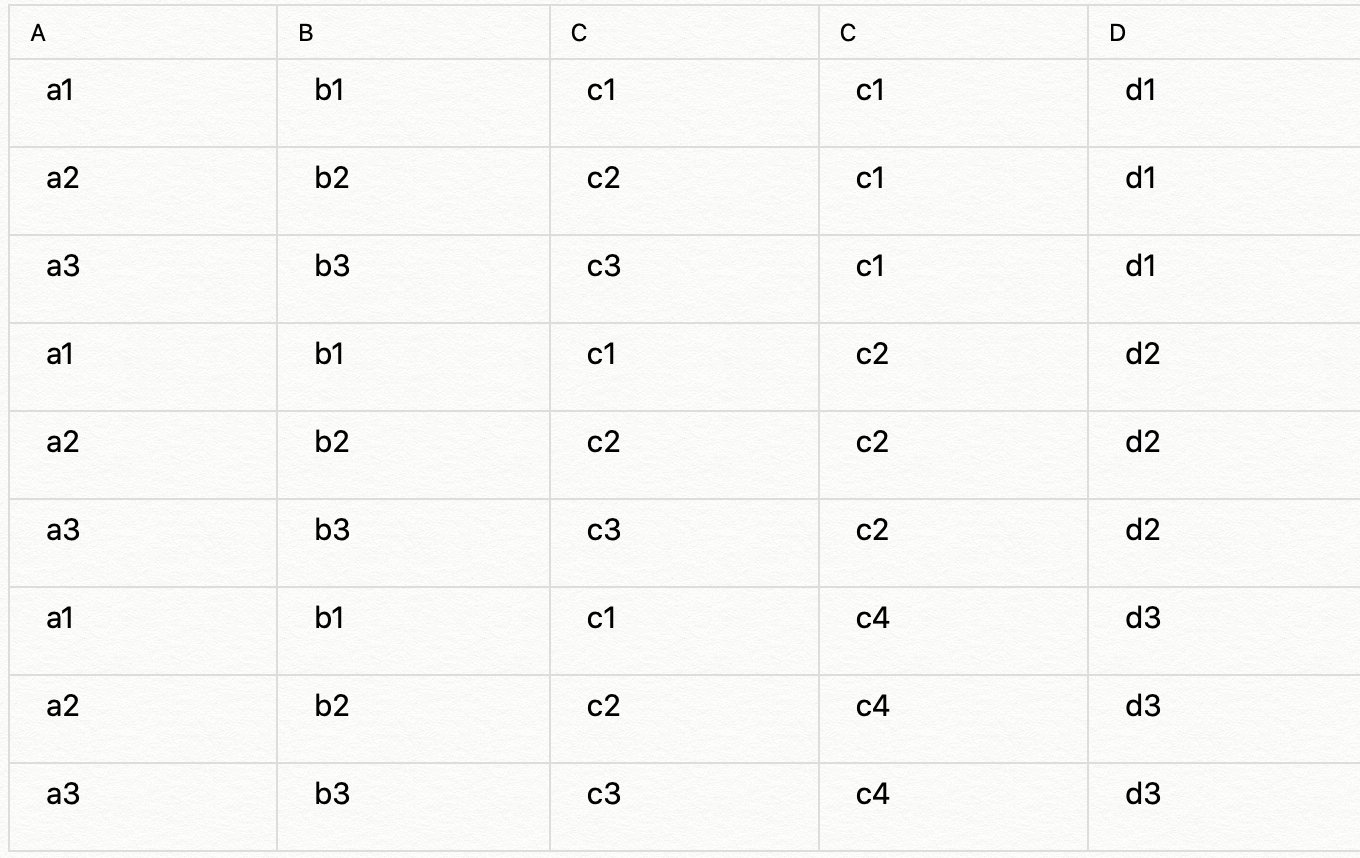
有2张表,1张R、1张S,R表有ABC三列,S表有CD两列,表中各有三条记录。
R表
|
A |
B |
C |
| a1 | b1 | c1 |
| a2 | b2 | c2 |
| a3 | b3 | c3 |
S表
|
C |
D |
| c1 | d1 |
| c2 | d2 |
| c4 | d3 |
-
交叉连接(笛卡尔积):
select r.*,s.* from r,s
数据倾斜也是常见的业务逻辑问题,假设在数据量非常大时,在某个节点需要通过区分key值来做不同的运算,便非常容易遇到数据倾斜的问题。解决实时处理中的数据倾斜问题通常有两种方式:
-
去重指标分桶:通过对去重值进行分桶哈希,相同的值一定会落到同一个桶中,最后把每个桶的值进行加总,便得到了最终结果,该方式主要利用分散的内存资源;
-
非去重指标分桶:数据随机分发到每个桶中,最后把每个桶的值进行加总,并得到了最终结果,该方式主要利用分散的CPU计算能力。
hive使用concat_ws()函数进行列转行
# 借用concat_ws()和collect_set()函数进行相同列的重复数据转换
# collect_set()函数可以将相关列合并成array<>类型;concat_ws()函数会将array<>类型根据指定的分隔符进行合并
## 示例数据
hive> select * from tmp_jiangzl_test;
tmp_jiangzl_test.col1 tmp_jiangzl_test.col2 tmp_jiangzl_test.col3
a b 1
a b 2
a b 3
c d 4
c d 5
c d 6
## 对于以上数据,我们可以将col3列根据列col1和col2进行合并
hive> select col1,col2,concat_ws(',',collect_set(col3)) from tmp_jiangzl_test group by col1,col2;
col1 col2 _c2
a b 1,2,3
c d 4,5,6
# case多条件判断
hive (ods)> select name,salary,
> case when salary < 800 then 'low'
> when salary >= 800 and salary <=5000 then 'middle'
> when salary >5000 and salary <10000 then 'high'
> else 'very high'
> end as bracket
> from emp1;
针对相同的表进行的连接被称为“自连接”(self join),这个技巧常常被人们忽视,其实是有挺多妙用的
1、删除重复行
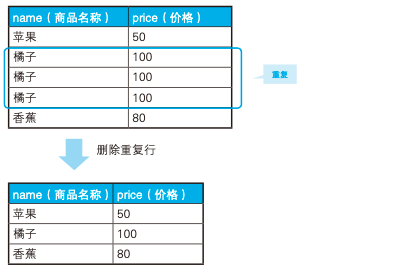
上图中有三个橘子,需要把这些重复的行给删掉,用如下自连接可以解决:
DELETE FROM Products P1
WHERE id < ( SELECT MAX(P2.id)
FROM Products P2
WHERE P1.name = P2.name
AND P1.price = P2.price ); 2、排序
在 db 中,我们经常需要按分数,人数,销售额等进行排名,有 Oracle, DB2 中可以使用 RANK 函数进行排名,不过在 MySQL 中 RANK 函数未实现,这种情况我们可以使用自连接来实现,如对以下 Products 表按价格高低进行排名
使用自连接可以这么写:
-- 排序从 1 开始。如果已出现相同位次,则跳过之后的位次
SELECT P1.name,
P1.price,
(SELECT COUNT(P2.price)
FROM Products P2
WHERE P2.price > P1.price) + 1 AS rank_1
FROM Products P1
ORDER BY rank_1;
结果如下:
name price rank
----- ------ ------
橘子 100 1
西瓜 80 2
苹果 50 3
葡萄 50 3
香蕉 50 3
柠檬 30 6
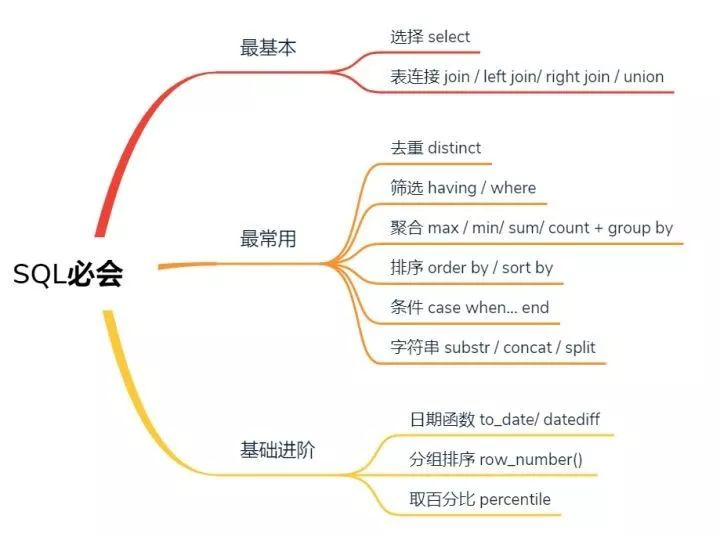
SQL 性能优化技巧
一、参数是子查询时,使用 EXISTS 代替 IN
二、 尽量避免使用否定形式:用大于或者小于来代替
- <>
- !=
- NOT IN
-
想要的数据在多张表里,想取多个字段,该怎么办?—— 表连接
-- table_1中有id,age; table_2中有id,sex。想取出id,age,sex 三列信息-- 将table_1,table_2 根据主键id连接起来select a.id,a.age,b.sex from(select id,age from table_1) a--将select之后的内容存为临时表ajoin(select id, sex from table_2) b--将select之后的内容存为临时表bon a.id =b.id
在这里先介绍一下几种join: (敲重点,很容易问的哦)
join : hive的join默认是inner join,找出左右都可匹配的记录;
left join: 左连接,以左表为准,逐条去右表找可匹配字段,如果有多条会逐次列出,如果没有找到则是NULL;
right join:右连接,以右表为准,逐条去左表找可匹配字段,如果有多条会逐次列出,如果没有找到则是NULL;
full outer join: 全连接,包含两个表的连接结果,如果左表缺失或者右表缺失的数据会填充NULL。
每种join 都有on ,>join 之前要确保关联键是否去重,是不是刻意保留非去重结果。
-
两张表数据的字段一样,想合并起来,怎么办?
-- 不去重,合并两张表的数据select * from(select id from table_1UNION ALLselect id from table_2)t;
union和union all 均基于列合并多张表的数据,所合并的列格式必须完全一致。union的过程中会去重并降低效率,union all 直接追加数据。union 前后是两段select 语句而非结果集。
-
如果有千万用户数据,想知道有多少去重的用户数?—— 去重 distinct
-- 优化版本的count distinctselect count(*) from(select distinct id from table_1) tb
-
想分性别进行统计,看看男女各多少?—— 聚合函数和group by
-- 统计不同性别(F、M)中,不同的id个数select count(distinct id) from table_1group by sex-- 其它的聚合函数例如:max/min/avg/sum-- 统计最大/最小/平均年龄select max(age), min(age),avg(age) fromtable_1group by id
-
只想查看A公司的男女人数数据?—— 筛选 where/having
-- 统计A公司的男女人数select count(distinct id) from table_1where company = 'A'group by sex-- 统计各公司的男性平均年龄,并且仅保留平均年龄30岁以上的公司select company, avg(age) from table_1where sex = 'M'group by companyhaving avg(age)>30;-- 按年龄全局倒序排序取最年迈的10个人select id,age from table_1 order by age DESClimit 10
-
将数值型的变量转化为分类型的变量?—— case when 条件函数
-- 收入区间分组select id,(case when CAST(salary as float)<50000 Then '0-5万'when CAST(salary as float)>=50000 and CAST(salary as float)<100000 then '5-10万'when CAST(salary as float) >=100000 and CAST(salary as float)<200000 then '10-20万'when CAST(salary as float)>200000 then '20万以上'else NULL endfrom table_1;
-
case 函数的格式为(case when 条件1 then value1 else null end), 其中else 可以省,但是end不可以省。
- 在这个例子里也穿插了一个CAST的用法,它常用于string/int/double型的转换。
-
字符串
1. concat( A, B...)返回将A和B按顺序连接在一起的字符串,如:concat('foo', 'bar') 返回'foobar'
select concat('www','.iteblog','.com') fromiteblog;--得到 www.iteblog.com
2. split(str, regex)用于将string类型数据按regex提取,分隔后转换为array。
-- 以","为分隔符分割字符串,并转化为arraySelect split("1,2,3",",")as value_array from table_1;-- 结合array index,将原始字符串分割为3列select value_array[0],value_array[1],value_array[2] from(select split("1,2,3",",")as value_array from table_1 )t
3. substr(str,0,len) 截取字符串从0位开始的长度为len个字符。
select substr('abcde',3,2) fromiteblog;-- 得到cd
-
不想全局排序,需要分组排序?—— row_number()
-- 按照字段salary倒序编号select *, row_number() over (order by salary desc) as row_num from table_1;-- 按照字段deptid分组后再按照salary倒序编号select *, row_number() over (partition by deptid order by salary desc) as rank from table_1;
-- 获取income字段的top10%的阈值select percentile(CAST (salary AS int),0.9)) as income_top10p_threshold from table_1;-- 获取income字段的10个百分位点select percentile(CAST (salary AS int),array(0.0,0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5,0.6,0.7,0.8,0.9,1.0)) as income_percentilesfrom table_1;
-
想要对时间字段进行操作?—— 时间函数
-- 转换为时间数据的格式select to_date("1970-01-01 00:00:00") as start_time from table_1;-- 计算数据到当前时间的天数差select datediff('2016-12-30','2016-12-29');-- 得到 "1"
to_date函数可以把时间的字符串形式转化为时间类型,再进行后续的计算;
-
常用的日期提取函数包括 year()/month()/day()/hour()/minute()/second()
-
日期运算函数包括datediff(enddate,stratdate) 计算两个时间的时间差(day);
-
date_sub(stratdate,days) 返回开始日期startdate减少days天后的日期。
-
date_add(startdate,days) 返回开始日期startdate增加days天后的日期。
4. 常见笔试/面试题
例:有3个表S,C,SC:S(SNO,SNAME)代表(学号,姓名)C(CNO,CNAME,CTEACHER)代表(课号,课名,教师)SC(SNO,CNO,SCGRADE)代表(学号,课号,成绩)
问题:1. 找出没选过“黎明”老师的所有学生姓名。2. 列出2门以上(含2门)不及格学生姓名及平均成绩。3. 既学过1号课程又学过2号课所有学生的姓名。
1. -- 考察条件筛选select sname from s where sno not in( select sno from sc where cno in(select distinct cno from c where cteacher='黎明'));2. -- 考察聚合函数,条件筛选select s.sname, avg_grade from sjoin(select sno from sc where scgrade < 60 group by sno having count(*) >= 2) t1on s.sno = t1.snojoin(select sno, avg(scgrade) as avg_grade from sc group by sno ) t2on s.sno = t2.sno;3. -- 考察筛选、连接select sname from( select sno from sc where cno = 1) ajoin(select sno from sc where cno = 2) bon a.sno = b.sn
参考资料:
1、https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/muqi-4xQ4sGeuHaW5dDEHQ
2、https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/qdWUVDfu1j3v_JFI_ANEMw
3、https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/8UZAaDyB38gsZANPLxNKgg
4、https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/xdS0SbatZ1X794SXBF8CgQ
5、https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Q5aFn9T5LNDj2y0LrcLjgw
6、https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/LGfE29ch1xsHb2bNhdVPCQ
7、https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Q5aFn9T5LNDj2y0LrcLjgw
8、https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/HOftenkXawBMF0cJg_yS_w
9、https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QxPK-KOlihqhI_PpQGsiTQ
10、https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/qZZEb6-nSKJ3tWv98drSOQ