116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
给定一个完美二叉树,其所有叶子节点都在同一层,每个父节点都有两个子节点。二叉树定义如下:
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
示例:
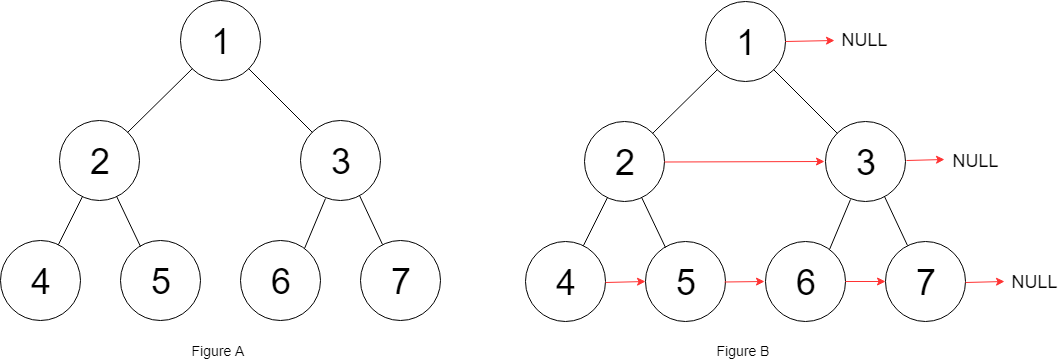
分析:
next指针的作用实际上是将二叉树的每一层连了起来。由二叉树的层次遍历可以联想到BFS。
同时可以看出,每个结点的next,可以由它的父结点给出。
代码(C++):
#include <queue>
class Solution {
public:
// 利用next
Node* connect1(Node* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return root;
// 取每一层最左侧结点
Node* leftmost = root;
// 当还有下一层
while (leftmost->left != nullptr) {
Node* head = leftmost;
while (head != nullptr) {
// CONNECTION 1:当前结点左子结点的next指向右子结点
if (head->left != nullptr) head->left->next = head->right;
// CONNECTION 2:当前结点右子结点next指向当前结点next结点的左子结点
if (head->next != nullptr) head->right->next = head->next->left;
// 遍历该层所有结点
head = head->next;
}
// 遍历所有层
leftmost = leftmost->left;
}
return root;
}
// bfs
Node* connect2(Node* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return root;
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
int size = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node* node = q.front(), q.pop();
if (i < size - 1) node->next = q.front();
if (node->left != nullptr) q.push(node->left);
if (node->right != nullptr) q.push(node->right);
}
}
return root;
}
};