前言:作为安全人员,代理大家用的都很多,那什么是java中的动态代理呢?事实上,java中的“动态”也就意味着使用了反射,因此动态代理是基于反射机制的一种代理模式。
简介:
代理是一种常用的设计模式,其目的就是为其他对象提供一个代理以控制对某个对象的访问。代理类负责为委托类预处理消息,过滤消息并转发消息,以及进行消息被委托类执行后的后续处理。为了保持行为的一致性,代理类和委托类通常会实现相同的接口,所以在访问者看来两者没有丝毫的区别。通过代理类这中间一层,能有效控制对委托类对象的直接访问,也可以很好地隐藏和保护委托类对象,同时也为实施不同控制策略预留了空间,从而在设计上获得了更大的灵活性。Java 动态代理机制以巧妙的方式近乎完美地实践了代理模式的设计理念。
public interface subject { void simpleSubject(); }
realSubject实现类
public class realSubject implements subject{ public void simpleSubject(){ System.out.println("this is simpleSubject"); } }
每一个realSubject对象都拥有这个simpleSubject接口,但如果某个对象希望在运行的时候动态的附加一些hardSubject功能,应该怎么做呢?我们通过实现一个代理对象并在代理对象上附加hardSubject功能(或者附加一些信息)来实现。实现方式是通过Proxy.newProxyInstance生成一个代理对象,在生成代理对象的同时给这个代理对象绑定一个Handler,该handler即调用处理器(InvocationHandler)对象。
首先实现一个proxyHandler在原来的接口方法的前或后面来添加hardSubject功能(这里说功能或许不太准确)
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class proxyHandler implements InvocationHandler { private realSubject subject; public proxyHandler(realSubject subject){ this.subject = subject; } public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("I'am the added hardSubject1"); method.invoke(subject); System.out.println("I'am the added hardSubject2"); return null; } }
查看InvocationHandler接口的源码注解可以知道,它实现的功能是:在代理对象原本的接口方法被调用时,会绑定执行InvocationHandler中定义的方法。

接着我们编写一个测试类来实例一个代理对象
proxyTest 测试类
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; public class proxyTest { public static void main(String[] args){ realSubject rs = new realSubject(); InvocationHandler h = new proxyHandler(rs); Class clazz = rs.getClass(); subject s = (subject)Proxy.newProxyInstance(clazz.getClassLoader(),clazz.getInterfaces(),h); s.simpleSubject(); System.out.println(s.getClass()); } }
Proxy的newProxyInstance方法的三个参数,分别是realSubject的类装载器,接口和我们定义的proxyHandler实例对象
看一下源码:
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces, InvocationHandler h) throws IllegalArgumentException { Objects.requireNonNull(h); final Class<?>[] intfs = interfaces.clone(); final SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager(); if (sm != null) { checkProxyAccess(Reflection.getCallerClass(), loader, intfs); } /* * Look up or generate the designated proxy class. */ Class<?> cl = getProxyClass0(loader, intfs); /* * Invoke its constructor with the designated invocation handler. */ try { if (sm != null) { checkNewProxyPermission(Reflection.getCallerClass(), cl); } final Constructor<?> cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams); final InvocationHandler ih = h; if (!Modifier.isPublic(cl.getModifiers())) { AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() { public Void run() { cons.setAccessible(true); return null; } }); } return cons.newInstance(new Object[]{h}); } catch (IllegalAccessException|InstantiationException e) { throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { Throwable t = e.getCause(); if (t instanceof RuntimeException) { throw (RuntimeException) t; } else { throw new InternalError(t.toString(), t); } } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e); } }
代码中我加粗的部分即是关键部分,第一步利用反射获取到代理类的Class对象cl(这个代理类是如何生成的我们暂且不论,只需要知道用到了被代理类的类加载器,实现的接口以及反射。深入需要再往下跟代码跟到ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass来生成代理类,这里就只分析这段代码) 再通过代理类的Class对象cl使用getConstructor获取构造方法,最后通过构造方法反射获得一个代理类对象,可以看到在用newInstance生成代理类对象的时候我们传入了proxyHandler对象h
值得一提的是这个代理对象给的引用是subject接口类,这个对象其实是不属于realSubject和proxyHandler的,但因为它实现了subject接口,所以可以给它一个安全的类型转换到subject引用。但事实上我们运行这段代码,s.getClass()的输出是
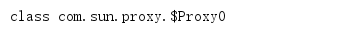
也就是说它不属于任何我们看到的类,但它所属的类的父类是proxy类,这个代理对象属于$Proxy0类,这个代理类是放在内存中的,当有多个代理对象时,0会依次递增
最后我们来总结一下动态代理实现的步骤:
1.通过实现 InvocationHandler 接口创建自己的调用处理器;
2.通过为 Proxy 类指定 ClassLoader 和一组 interface 来创建动态代理类;
3.通过反射机制获得动态代理类的构造函数,其唯一参数类型是调用处理器接口类型;
4.通过构造函数创建动态代理类实例,构造时调用处理器对象作为参数被传入。
2020.4.1更新:
拿到$Proxy0类的class文件用jd-gui打开看一下生成的$Proxy0类的代码,看看到底是怎么做到当调用实现类的接口函数时,绑定执行了h中的invoke方法的
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.lang.reflect.UndeclaredThrowableException; public final class $Proxy0 extends Proxy implements subject { private static Method m1; private static Method m3; private static Method m2; private static Method m0; public $Proxy0(InvocationHandler paramInvocationHandler) { super(paramInvocationHandler); } public final boolean equals(Object paramObject) { try { return ((Boolean)this.h.invoke(this, m1, new Object[] { paramObject })).booleanValue(); } catch (Error|RuntimeException error) { throw null; } catch (Throwable throwable) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(throwable); } } public final void simpleSubject() { try { this.h.invoke(this, m3, null); return; } catch (Error|RuntimeException error) { throw null; } catch (Throwable throwable) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(throwable); } } public final String toString() { try { return (String)this.h.invoke(this, m2, null); } catch (Error|RuntimeException error) { throw null; } catch (Throwable throwable) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(throwable); } } public final int hashCode() { try { return ((Integer)this.h.invoke(this, m0, null)).intValue(); } catch (Error|RuntimeException error) { throw null; } catch (Throwable throwable) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(throwable); } } static { try { m1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("equals", new Class[] { Class.forName("java.lang.Object") }); m3 = Class.forName("subject").getMethod("simpleSubject", new Class[0]); m2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("toString", new Class[0]); m0 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("hashCode", new Class[0]); return; } catch (NoSuchMethodException noSuchMethodException) { throw new NoSuchMethodError(noSuchMethodException.getMessage()); } catch (ClassNotFoundException classNotFoundException) { throw new NoClassDefFoundError(classNotFoundException.getMessage()); } } }
从生成的代理类字节码反编译的结果中可以看出,当调用s.simpleSubject(),执行了h.invoke方法
(前面已经说过该代理类的生成是通过ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass直接创建类的字节码再加载到jvm中,这也解释了为什么叫动态代理)
一个问题:
Class<?> cl = getProxyClass0(loader, intfs) 这行代码就已经拿到了生成代理类的Class对象,为什么不直接使用Class的newInstance方法创建对象?
答: 因为在前面反射的文章里就说过Class对象的newInstance方法只能调用该类的的无参构造函数,而这里可以看到该类的构造函数是有参构造函数,参数就是h