环境和测试代码
vue 2.6.11, vuex 3.1.3
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>vue test</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<button @click="doAdd">do add 2</button>
{{vCount}}
<button-counter></button-counter>
</div>
<!-- Vue.js v2.6.11 -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vuex/3.1.3/vuex.js"></script>
<script>
Vue.component('button-counter', {
data: function () {
return {}
},
mounted() {
console.log('child ', this.$store);
},
template: '<button v-on:click="doChildAdd">do add 5</button>',
methods: {
doChildAdd() {
store.commit('increment', 5)
}
}
});
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 1
},
mutations: {
increment (state, n = 1) {
state.count += n;
}
}
})
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
store,
computed: {
vCount () {
return this.$store.state.count
},
},
mounted() {
console.log('parent ', this.$store);
},
methods: {
doAdd() {
store.commit('increment', 2)
}
}
})
console.log(app);
// var event = new CustomEvent('test', { 'detail': 5 }); window.dispatchEvent(event);
</script>
</body>
</html>
总结
侵入每个 vue 组件注册了 $store 属性,而所有 $store 属性都指向一个 store 实例,这样就能做到所有 vue 组件访问的都是同一份全局变量。
vue 组件里用户定义取 store 上的变量用于渲染或者其他逻辑,而后改动 this.store.xxx 时,vue 本身核心依赖收集能知道要更新哪些视图,就完成了。
分析
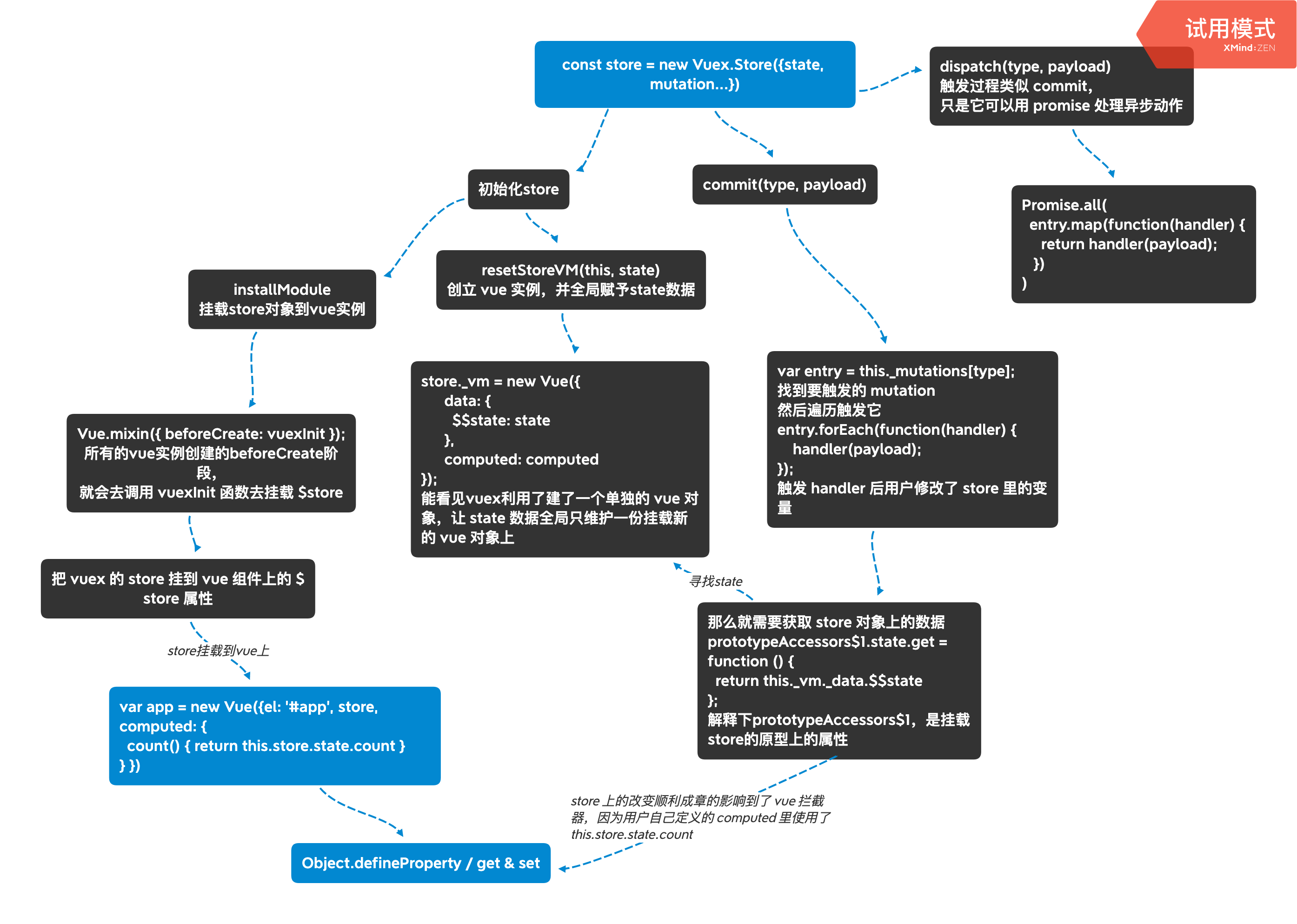
首先给出 store 的定义代码,注意下文的 installModule 和 resetStoreVM,这是两个关键的步骤
var Store = function Store (options) {
// ...
this._actions = Object.create(null);
this._actionSubscribers = [];
this._mutations = Object.create(null);
this._wrappedGetters = Object.create(null);
this._modules = new ModuleCollection(options);
this._modulesNamespaceMap = Object.create(null);
this._subscribers = [];
// bind commit and dispatch to self
var store = this;
var ref = this;
var dispatch = ref.dispatch;
var commit = ref.commit;
this.dispatch = function boundDispatch (type, payload) {
return dispatch.call(store, type, payload)
};
this.commit = function boundCommit (type, payload, options) {
return commit.call(store, type, payload, options)
};
var state = this._modules.root.state;
// init root module.
// this also recursively registers all sub-modules
// and collects all module getters inside this._wrappedGetters
installModule(this, state, [], this._modules.root);
// initialize the store vm, which is responsible for the reactivity
// (also registers _wrappedGetters as computed properties)
resetStoreVM(this, state);
// ...
};
resetStoreVM(this, state) 方法
store._vm = new Vue({
data: {
$$state: state
},
computed: computed
});
而 install(window.Vue); 方法是用来挂载 store 对象到 vue 实例的,里面做了件事 Vue.mixin({ beforeCreate: vuexInit });
vuexInit 函数里就做了把 store 复制给 vue 组件的 this.$store 属性.
function vuexInit () {
var options = this.$options;
// store injection
if (options.store) {
this.$store = typeof options.store === 'function'
? options.store()
: options.store;
} else if (options.parent && options.parent.$store) {
this.$store = options.parent.$store;
}
}
commit
下文关键部分是 this._withCommit 里的匿名函数,它遍历 entry,执行用户自定义的 handler 处理函数,
就上文的测试代码来说,这个 handler 就是 commit 里的函数 increment (state, n = 1) { state.count += n; }
接着 handler 里要读取 state.count,就会去获取 state,return this._vm._data.$$state
Store.prototype.commit = function commit(_type, _payload, _options) {
var this$1 = this;
// check object-style commit
var ref = unifyObjectStyle(_type, _payload, _options);
var type = ref.type;
var payload = ref.payload;
var options = ref.options;
var mutation = { type: type, payload: payload };
var entry = this._mutations[type];
this._withCommit(function() {
entry.forEach(function commitIterator(handler) {
handler(payload);
});
});
// ...
};
// _withCommit 执行它所传入的 fn,它遍历 entry,执行用户自定义的 handler 处理函数,
// 这个 handler 就是我们定义的 commit 里的函数 increment (state, n = 1) { state.count += n; },总之要变动 state.count,就会进入 state 的拦截器,
prototypeAccessors$1.state.get = function () {
return this._vm._data.$$state
};
// 一旦触发去 vue 的 _data 上有 vue 自己的拦截器 get,而动作做 state.count += n 后,就触发了 vue 自己拦截器里的 set。最后这样就开始vue自身的渲染逻辑。
最后修改了 state.count 后,等于说用户也变动了在 vue 组件里那个 computed,自然而然的进入 vue 组件自身的 get/set 以及渲染逻辑。
computed: {
vCount () {
return this.$store.state.count
},
},
dispatch
dispatch 与 commit 的流程大体相同,不同点是他会使用 Promise.all 来保证 handler 函数的异步触发,并且最后也会 return 一个 promise 对象出去而已。
Store.prototype.dispatch = function dispatch(_type, _payload) {
var this$1 = this;
// check object-style dispatch
var ref = unifyObjectStyle(_type, _payload);
var type = ref.type;
var payload = ref.payload;
var action = { type: type, payload: payload };
var entry = this._actions[type];
entry.length > 1
? Promise.all(
entry.map(function(handler) {
return handler(payload);
})
)
: entry[0](payload);
return result.then(function(res) {
return res;
});
};