多态
设计角度讲:
定义:父类的同一种动作或者行为,在不同的子类上有不同的实现。
作用:1.在继承的基础上,体现类型的个性化。
2.增强程序扩展性,体现开闭原则。
重写:
子类实现了父类中相同的方法(方法名、参数)。
在调用该方法时,实际执行的是子类的方法。
快捷键(ctrl + O)
内置可重写函数:
python中,以双下划线开头、双下划线结尾的是系统定义的成员。我们可以在自定义类中进行重写,从而改变其行为。
转换字符串
__str__函数:将对象转换为字符串
运算符重载
定义:让自定义的类生成的对象(实例)能够使用运算符进行操作。
算术运算符
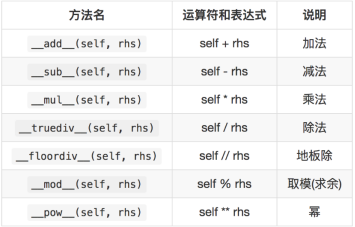
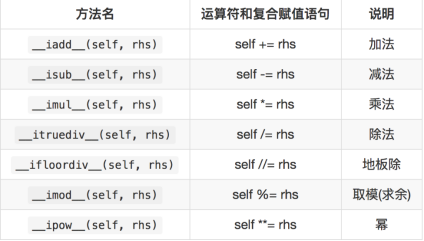
复合运算符重载
比较运算符重载

__str__

class Person(object): def __init__(self, name="", age=0, sex=""): self.name = name self.age = age self.sex = sex def __str__(self): return f"我叫{self.name},今年{self.age}岁,性别{self.sex}." ak = Person("安康", 26, "男") # <__main__.Person object at 0x7f5ea31cde10> print(ak) # 直接打印自定义对象 # 本质: # 1. 调用自定义对象的__str__ content = ak.__str__() # 2. 显示返回的字符串 print(content)
__add__
class Vector2: """ 二维向量 """ def __init__(self, x, y): self.x = x self.y = y def __str__(self): return "x分量:%d,y分量%d" % (self.x, self.y) def __add__(self, other): x = self.x + other.x y = self.y + other.y return Vector2(x, y) pos01 = Vector2(1, 2) pos02 = Vector2(3, 4) print(pos01 + pos02) # pos01.__add__(pos02)
运算符重载
+=
对于可变对象,+=应该在原对象基础上改变
对于不可变对象,+=应该创建新对象
class Vector2: def __init__(self, x, y): self.x = x self.y = y def __str__(self): return "x分量:%d,y分量%d" % (self.x, self.y) # + # def __add__(self, other): # x = self.x + other.x # y = self.y + other.y # return Vector2(x, y) # += def __iadd__(self, other): self.x += other.x self.y += other.y return self # 返回原有数据 pos01 = Vector2(1, 2) pos02 = Vector2(3, 4) print(id(pos01)) pos01 += pos02 print(id(pos01)) print(pos01) list01 = [1] # print(id(list01)) list01 += [2] # print(id(list01)) print(list01) # [1,2] 在原有列表基础上添加 tuple01 = (1,) tuple01 += (2,) print(tuple01) # (1,2) 产生新容器
__eq__ 和 __lt__
class Commodity: def __init__(self, cid=0, name="", price=0): self.cid = cid self.name = name self.price = price # 比较是否相同的判断标准: def __eq__(self, other): return self.cid == other.cid # 比较是否大小的判断标准: def __lt__(self, other): return self.price < other.price list_commodity_infos = [ Commodity(1001, "屠龙刀", 10000), Commodity(1002, "倚天剑", 10000), Commodity(1003, "金箍棒", 52100), Commodity(1004, "口罩", 20), Commodity(1005, "酒精", 30), ] c01 = Commodity(1001, "屠龙刀", 10000) c02 = Commodity(1001, "屠龙刀", 20000) # 以下内置函数,需要自定义类重写__eq__ print(c01 == c02) # true # count 判断列表中存储在元素数量 print(list_commodity_infos.count(c01)) # print(list_commodity_infos.remove(c01)) print(c01 in list_commodity_infos) # 以下内置函数,需要自定义类重写__lt__ # list_commodity_infos.sort() # print(list_commodity_infos) min_commodity = min(list_commodity_infos) print(min_commodity.__dict__)
"""
老张开车去东北
需求变化:飞机、船、小黄车...
封装:分
人 车
继承:隔
多态
缺点:违反面向对象设计原则 - 开闭
允许增加新功能,不允许修改客户端代码
"""
class Person: def __init__(self, name=""): self.name = name def go_to(self, vehicle): print("去...") # 如果是汽车 if type(vehicle) == Car: vehicle.run() # 否则如果是飞机 elif type(vehicle) == Airplane: vehicle.fly() class Car: def run(self): print("汽车行驶") class Airplane: def fly(self): print("嗖嗖嗖") zl = Person("老张") bm = Car() fj = Airplane() zl.go_to(bm)
"""
老张开车去东北
需求变化:飞机、船、小黄车...
封装:分
人 车
继承:隔
交通工具
多态:做
完成汽车、飞机等具体交通工具的逻辑实现
"""
class Person: def __init__(self, name=""): self.name = name def go_to(self, vehicle): print("去...") # 如果传入的是交通工具 if isinstance(vehicle, Vehicle): # 先确定调用方法 # 编码时调用的父类 # 运行时执行的子类 vehicle.transport() class Vehicle: def transport(self): pass class Car(Vehicle): def transport(self): print("滴滴滴") class Airplane(Vehicle): def transport(self): print("嗖嗖嗖") zl = Person("老张") bm = Car() fj = Airplane() zl.go_to(bm)
