yarn
初始化
yarn init yes
添加依赖
yarn add [package]
升级依赖
yarn upgrade [package]
移出依赖
yarn remove [package]
npm
npm i
npm init --yes
npm i gulp-pug gulp-debug gulp-sass
//生产依赖
npm i gulp -P
//开发依赖
npm i gulp -D
//不添加到package.json
npm i gulp --no-save
指定下载版本
npm i vue@2.5.15
卸载package包
npm uninstall vue //可以使用rm un r
全局安装
-g
强制清除缓存
npm cache clean --fore
bower
它是从github下载的
初始化
bower init yes
更新
bower update 包名
卸载
bower uninstall 包名
删除缓存
bower cache clean
添加依赖
bower install 包名
webpack
初始化
npm init -y
全局安装
npm install webpack -g //不推荐
本地安装
npm install webpack webpack-cli -D //-D 开发依赖
执行webpack
npx webpack //打包
npm install lodash -D
npm install webpack-dev-server -D
npm install html-webpack-plugin -D
//css
npm install style-loader css-loader -D
webpack.config.js
module: { // 所有 非.js 结尾的第三方文件类型,都可以在 module 节点中进行配置
rules: [ // rules 是匹配规则,如果 webpack 在打包项目的时候,发现,某些 文件的后缀名是 非 .js 结尾的
// webpack 默认处理不了,此时,webpack 查找 配置文件中的 module -> rules 规则数组;
{ test: /.css$/, use: ['style-loader', 'css-loader'] }
]
}
//less
npm install less-loader less -D
{ test: /.less$/, use: ['style-loader', 'css-loader', 'less-loader'] }
//sass
npm install sass-loader node-sass -D
{ test: /.scss$/, use: ['style-loader', 'css-loader', 'sass-loader'] }
//加载图片
npm install url-loader file-loader -D
{ test: /.jpg|png|gif|bmp$/, use: 'url-loader' }
vue指令
npm install webpack webpack-cli -g
npm install -g vue-cli
vue init webpack vue_demo
cd vue_demo
npm install
npm run dev
vue
beforeCreate created 初始化后
beforeMounted mounted 挂载后
ref 获取dom节点
<p ref="myp">{{msg}}</p>
this.$refs.myp获取这个div
由于dom的渲染是异步的 $nextTick 如果数据变化后想获取真实dom中内容,需要等待页面刷新后在去获取
所有的dom操作最后用$nextTick中
全局组件
Vue.component('my-handsom',{
template:'<div>{{msg}}</div>',
data(){
return {msg:'我很英剧'}
},
});
局部组件
components
三步取: 创建 注册 使用
let handsome={template:'<div>{{msg}}</div>',data(){
return {msg:'张三'}
}};
components:{
handsome,
methods:{
}
}
在页面上使用这个标签
子传父
let vm=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
money:400,
},
methods:{
things(val){
this.money=val;
}
},
components:{
child:{
props:['m'],
template:'<div>儿子{{m}} <button @click="getMoney">多要钱</button></div>',
methods:{
getMoney(){
this.$emit('child-msg', 800);//触发自己的自定义事件,让父亲方法执行
}
}
}
}
})
//儿子的自定义方法方法执行父亲的方法,
<div id="app">
父亲:{{money}}
<child :m="money" @child-msg="things"></child>
</div>
简单的理解子组件传递参数给父组件
子组件
<button @click.self="$emit('patch')">加一块钱</button>
$emit()里面的第一个参数是传递给父组件的自定义方法,第二个参数是一个对象,可以是需要传递给父组件的对象
父组件
<User @patch="ttt"/>
//methods 执行这个方法
ttt() {
this.money++
}
slot
<div id="app">
<modal>
<a href='http://www.baidu.com'>去百度</a>
<p slot="content">是否删除</p>
<h1 slot="title" @click="fn">是否删除??</h1>
</modal>
</div>
<!--slot作用 定制模板-->
<!--模板中只能有一个根元素,可以通过元素属性定制模板-->
<!--slot 中可以放置一些默认的内容,如果传递了内容则替换掉-->
<!--如果没有名字的标签默认会放置到default-->
<template id="modal">
<!-- 这里放的内容属于父级当前模板的,只有属性名是属于组件的-->
<div>
<slot name="title">默认标题</slot>
<slot name="content">这是一个默认标签</slot>
<slot name="default">这是一个默认标签</slot>
</div>
</template>
let vm=new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
},
components:{
modal
},
methods:{
fn(){
alert(1)
}
}
})
操作挂载后组件的dom
<loading ref="load"></loading>
mounted(){//ref 如果放在组件上,获取的是组建的实例,并不是组件的DOM元素
// this.$refs.load.hide(); 想操作dom 就加一个$nextTick
this.$refs.load.$el.style.backgroundColor = 'red';
},
----------------
<div id="app">
<input type="radio" v-model="radio" value="home">home
<input type="radio" v-model="radio" value="list">list
<!--一般用作缓存:为的是后面路由做准备-->
<keep-alive>
<component :is="radio"></component>
</keep-alive>
</div>
/* 子组件和父组件同时拥有mounted方法,会先走谁*/
/*需要等待子组件挂载完成后在触发父组件的挂载*/
let home = {template:"<div>home</div>"};
let list = {template:"<div>list</div>"};
let vm=new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
radio:'home'
},
components:{
home,list
}
------------
向子组件传送数据是通过props实现的
<foo-component :foo-message="fooMessage"></foo-component>
fooMessage 是父组件的变量
/*type 能够指定的类型
String Number Boolean Function Object Array Symbol
required 声明这个参数是否必须传入
default 选项来指定当父组件未传入参数是props变量的默认值
当type的类型为Array或者Object的时候default必须是一个函数
自定义函数校对
* */
props:{
fooMessage: {type:[Number,String],required:true}
},
template:'<div>{{fooMessage}}</div>'
//props总结
props: {
// fooA只接受数值类型的参数
fooA: Number,
// fooB可以接受字符串和数值类型的参数
fooB: [String, Number],
// fooC可以接受字符串类型的参数,并且这个参数必须传入
fooC: {
type: String,
required: true
},
// fooD接受数值类型的参数,如果不传入的话默认就是100
fooD: {
type: Number,
default: 100
},
// fooE接受对象类型的参数
fooE: {
type: Object,
// 当为对象类型设置默认值时必须使用函数返回
default: function(){
return { message: 'Hello, world' }
}
},
// fooF使用一个自定义的验证器
fooF: {
validator: function(value){
return value>=0 && value<=100;
}
}
}
slot 绑定数据
父组件
因为组件中只能包一个div,所以可以用template包起来
slot-scope是让slot具有私有性
<div slot="wang" slot-scope="item">
<div v-for="sex in item.data">
{{sex}}
</div>
</div>
子组件
<slot name="wang" :data="sexArr"></slot>
data(){return { sexArr:['男','女']
}
}
父组件与子组件的数据通信
父组件
<TodoFooter :class1="class1"/>
data(){
return{
class1:'zhangsan'
}
}
子组件
props: ['class1']
子组件与父组件
$emit
父组件
<button-counter v-on:increment="incrementTotal"></button-counter>
methods: {
incrementTotal () {
this.total++
}
}
子组件
metheds: {
incrementCounter () {
this.$emit('increment')
this.counter++
}
}
--------
父组件
<custom @childByValue="childByValue"/>
childByValue(childValue){
console.log(childValue);
}
子组件
<button @click.self="childClick">点我触发</button>
childClick(){
this.$emit('childByValue',this.childValue)
//第一个参数是 @父组件的方法,第二个参数是本组件的数据
}
//非组件的传值
注册一个空vue
对象.$emit()
mounted(){
对象.$on('方法',function(传的参数))
}
不建议,太复杂的建议用vuex
vue 消息订阅与发布
缓存路由
<keep-alive>
<router-view></router-view>
</keep-alive>
向路由组件传递数据
$route.params.id
注意是route不是router不要写错了
编程式路由导航
this.$router.push(path) :想当于点击路由链接(可以返回到当前路由界面)
this.$router.replace(path):用新路由替换当前路由(不可以返回到当前路由界面)
this.$router.back() 请求(返回)上一个记录路由
this.$router.go(-1) 请求返回上一个记录路由
动态组件
vue 中 <component> 用 :is 来挂载不同的组件
<component :is="currentView"></component>
<button @click="handleChangeView('A')">A</button>
<button @click="handleChangeView('B')">B</button>
<button @click="handleChangeView('C')">C</button>
components:{
comA:{
template:`
<div>组件A</div>
`
},
comB:{
template:`
<div>组件B</div>
`
},
comC:{
template:`
<div>组件C</div>
`
}
},
data:{
currentView:'comA'
},
methods:{
handleChangeView:function(component){
this.currentView='com'+component;
}
}
向路由组件传递数据和编程式路由导航
父组件
<template>
<div>
<!--<p>{{// $router.params.id}}</p>-->
<ul>
<li v-for="(message,index) in messages" :key="message.id">
<router-link :to="`/home/message/detail/${message.id}`">{{message.title}}</router-link>
<button @click="pushShow(message.id)">push查看</button>
<button @click="reqplaceShow(message.id)">replace查看</button>
</li>
</ul>
<button @click="$router.back()">回退</button>
<hr>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Message",
data(){
return{
messages:[],
}
},
methods:{
pushShow(id){
this.$router.push(`/home/message/detail/${id}`)
},
reqplaceShow(id){
this.$router.replace(`/home/message/detail/${id}`)
},
},
mounted(){
//模拟ajax请求从后台获取数据
setTimeout(()=>{
const messgesd=[
{
id:1,
title:'message001',
content:'message001 content...'
},
{
id:2,
title:'message002',
content:'message002 content...'
},
{
id:4,
title:'message004',
content:'message004 content...'
}
];
this.messages=messgesd;
})
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
子组件
<template>
<div>
<p>{{$route.params.id}}</p>
<ul>
<li>id:{{messageDetail.id}}</li>
<li>title:{{messageDetail.title}}</li>
<li>content:{{messageDetail.content}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "MessageDetail",
data(){
return{
messageDetail:{
}
}
},
mounted(){
setTimeout(()=>{
const allMessageDetails=[
{
id:1,
title:'message001',
content:'message001 content...'
},
{
id:2,
title:'message002',
content:'message002 content...'
},
{
id:4,
title:'message004',
content:'message004 content...'
}
];
this.allMessageDetails=allMessageDetails;
const id=this.$route.params.id*1;
this.messageDetail=allMessageDetails.find(detail=>detail.id===id)
},1000)
},
watch:{
$route:function (value) {
const ids=value.params.id*1;
this.messageDetail=this.allMessageDetails.find(detail=>detail.id===ids)
}
}
}
vuex
npm install vuex -D
style中的scoped是限定样式的作用范围
JavaScript 风格指南
代码整洁的 JavaScript
JavaScript 代码简洁之道
vue-cli@3
yarn global add @vue/cli
vue create 项目名
cd 项目名
yarn serve
为什么data是一个函数:每一个实例的data属性都是独立的,不会相互影响的
.self修饰符
self是只执行子级本身的函数
.stop和.self的区别,前者是防止事件冒泡,后者则是忽略了事件冒泡和事件捕获的影响。只有直接作用在 该元素上的事件才会被调用
<div class="mid" @click.self="getTarget($event)">
去掉webstrom的单词波浪线
光标选中该单词,alt+enter,关闭相应选项即可。
vue编译报错
注意别再routes/index里面写内联组件const={template:'
这种会报错的'}在目录下新建一个
vue-config.jsmodule.exports={ runtimeCompiler: true };
vuex的流程
//store.js
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
Vue.use(Vuex);
const state={
count:1
};
const mutations={
increment(state) {
state.count++
},
decrement(state) {
state.count--
}
};
const actions={
increment:({commit})=>{
commit('increment');
},
decrement:({commit})=>{
commit('decrement');
}
};
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
mutations,
actions,
})
//在mian.js导入
在实例上挂载
<h1>vuex {{$store.state.count}}</h1>
<button @click.self="increment">增加</button>
<button @click.self="decrement">删减</button>
import {mapActions} from 'vuex'
export default {
methods:mapActions([
'increment',
'decrement'
])
}
====
state
在方法中通过 this.$store.state 获取
在计算属性中通过 this.$store.commit("方法函数")获取
辅助函数 mapState
import {mapState} from 'vuex';
computed:mapState({
count:'count',//第一种写法
sex:(state)=>state.sex,//第二种写法
from: function (state) { // 用普通函数this指向vue实例,要注意,取得事data的属性或者computed里面的属性,因为箭头函数没有this
return this.ddd + ':' + state.from
},
//简化
from(state) { // 用普通函数this指向vue实例,要注意
return this.ddd + ':' + state.from
},
}),
computed: {
localComputed () { /* ... */ },
// 使用对象展开运算符将此对象混入到外部对象中
...mapState({
// ...
})
}
// 在 store 中定义“getter”(可以认为是 store 的计算属性)。就像计算属性一样
//自带的第一个参数是store,第二个参数是getters(是自己,可以访问自己的属性)
//mapGetters辅助函数
computed: {
// 使用对象展开运算符将 getter 混入 computed 对象中
...mapGetters({
coneCount:'doneTodoss',
doneTodo:'doneTodoCounts',
// ...
})
}
可以用数组和对象的形式
...mapGetters([
'doneTodosCount',
'anotherGetter',
// ...
])
======
更改Vuex的store中的状态唯一方法是提交mutation
Action
* Action提交的是mutation,而不是直接变更状态
* Action 可以包含任意异步操作
Action 是通过 store.dispatch('里面放着方法',{传入的对象})方法触发的

methods: {
...mapActions([
'increment',
'decrement'
])
},
computed: {
doneTodosCount() {
return this.$store.state.arr.filter(todo => todo > 2);
},
...mapGetters({
coneCount: 'doneTodoss',
doneTodo: 'doneTodoCounts',
})
}
}
====
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
Vue.use(Vuex);
const state = {
count: 1,
name: 'dkr',
sex: '男',
from: 'china',
arr: [2, 3, 5, 6, 7],
todos: [
{id: 1, text: '...', done: true},
{id: 2, text: '...', done: false}
]
};
const mutations = {
//大多说第二个参数载荷是一个对象,也可以是一个数字
increment(state, n) {
console.log(state.count);
state.count += n
},
decrement(state,payload) {
state.count-=payload.amount
}
};
const actions = {
increment: ({commit}) => {
commit('increment', 10);
},
decrement: ({commit}) => {
// commit('decrement',{amount:10}); 也可以写成一个包含type属性的对象
commit({type:'decrement', amount: 10});
}
};
//getters getters.js
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
getters: {
doneTodoss: state => {
return state.todos.filter(todo => todo.done);
},
doneTodoCounts(state, getters) {
return getters.doneTodoss.length
}
},
mutations,
actions,
})
vuex中的modules
目录结构
─ store
├── index.js # 我们组装模块并导出 store 的地方
├── actions.js # 根级别的 action
├── mutations.js # 根级别的 mutation
└── modules
├── cart.js # 购物车模块
└── products.js # 产品模块
store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
import login from './modules/login'
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules:{
login
}
})
=====
store/modules/login.js
const state = {
useName: "sam"
};
const mutations = {
};
const actions = {
};
const getters = {
};
// 不要忘记把state, mutations等暴露出去。
export default {
namespaced: true, //单词别写错了,记得一定要设置呀
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters
}
使用
...mapState('login',{
useName:state=>state.useName
})
...mapGetters("login", ["localJobTitle"])
...mapState({
useName:state=>state.login.useName
})
...mapActions('login', ['alertName'])
...mapGetters({useName:'login/useName'})// 避免重名可以这样写
this.$store.dispatch("login/alertName")
客户端的路由实现方式两种:基于hash和HTML5 history api
vue-router其本质就是:建立并管理url和对应组件之间的映射关系
配置路由 yarn add vue-router 新建router/index.js ---- import Vue from 'vue' import VueRouter from 'vue-router' //导入自己的路由模块 import xxx from '../templates/xxx.vue' Vue.use(VueRouter) export default new VueRouter({ routes:[ {path:'/xxx',component:xxx, children:[{ //在子路由中父路由要有 path:'/子路由', component:xxx, redirect:'/重定向' ]} ] }) ---- 在main.js 导入 import router from './router' new Vue({ router }) 页面实现(html模板中) <router-link to=""></router-link> <router-view></router-view> //动态路径参数 以冒号开头,也就是只有传入动态参数才能进入子页面 {path:'/user/:id',component:xxx} 对应的值都会设置 $route.params={username:'event'} 或者 $route.params={id:1} 命名路由,可以给router-link 的to 属性传递一个对象 <router-link :to="{ name: 'user', params: { userId: 123 }}">User</router-link> router.push({name:'user',params:{userID:123}}) 两种方法都会把路由导航到 /user/123 路径 命名视图 有 sidebar (侧导航) 和 main (主内容) 两个视图 <router-view class="view one"></router-view> <router-view class="view two" name="a"></router-view> <router-view class="view three" name="b"></router-view> 对于同个路由,多个视图就需要多个组件,确保components配置记得加(s) const router = new VueRouter({ routes: [ { path: '/', components: { default: Foo, a: Bar, b: Baz } } ] }) 简写 <div> <h1>User Settings</h1> <NavBar/> <router-view/> <router-view name="helper"/> </div> 重定向 { path: '/a', redirect: '/b' } //命名路由 { path: '/a', redirect: { name: 'foo' }} //动态返回重定向目标的方法 { path: '/dynamic-redirect/:id?', redirect: to => { const { hash, params, query } = to if (query.to === 'foo') { return { path: '/foo', query: null } } if (hash === '#baz') { return { name: 'baz', hash: '' } } if (params.id) { return '/with-params/:id' } else { return '/bar' } } } 这里return的值是path值,必须是一个已经存在的path才能进行路由重定向。而且这个path不能使自身,如果是自身就变成的死循环了 <!-- 带查询参数,下面的结果为 /register?plan=private --> <router-link :to="{ path: 'register', query: { plan: 'private' }}">Register</router-link>
比较好的vue-router的文档
import User from '@/components/User' //这里可以省略.vue
// 给路由命令,设置的name要唯一
{path:'/user',name:'user',component:User}
//路由懒加载:单页面应用,首页时,加载内容时间过长.运用懒加载对页面组件进行划分,减少首页加载时间
{
path:'/Page',
name:'Page',
component:resolve => require(['@/components/Page'],resolve)
//此时component则不需要在第一步import}
// 把组件按组分块
component:() => import(/* webpackChunkName: "group-foo" */ './Foo.vue')
如果打包报错,就把
router,routes,route分不清楚
$router : 路由实例
routes : 指router路由实例的routes API,用来配置多个routes路由对象
$route : 当前路由对象
vue-router默认使用hash模式,使用url的hash来模拟一个完整的url
路由对象属性介绍this.$route 注意不是$router
$route.path: 类型string, 对应当前路由的路径,总是解析绝对路径,'/foo/bar'
$route.params: 类型Object ,一个key/value对象,包含动态片段和全匹配片段,如果没有路由,就是一个空对象
$route.query: 类型Object,一个key/value,表示url查询参数,对于路径
/foo?user=1则有$route.query.user==1,如果没有查询参数,则是个空对象$route.name 当前路由的名称,如果有,最好给每个路由对象命名,方便以后编程式导航,不过记住name必须唯一
$route.hash 类型:
string当前路由的 hash 值 (带#) ,如果没有 hash 值,则为空字符串。$route.fullPath 类型:
string完成解析后的 URL,包含查询参数和 hash 的完整路径。$route.matched 类型:
Array<RouteRecord>一个数组,包含当前路由的所有嵌套路径片段的路由记录 。路由记录就是routes配置数组中的对象副本 (还有在children数组)。$route.redirectedFrom 如果存在重定向,即为重定向来源的路由的名字。
别名
//这时,路径'/fxxksky'和'/two-dogs' 都会跳转到A
routes: [
{ path: '/fxxksky', component: A, alias: '/two-dogs' }
//当有多个别名时,alias也可以写成数组形式. alias: ['/two-dogs', 'three-dogs','four-dogs','five-dogs']
]
params进行配置
- 一个路径参数使用':'冒号进行标记.
- 当匹配到一个路由时,参数就会被设置到
this.$route.params,可以在每个组件内使用.例如/user/foo在this.$route.params.id就为foo
| 模式 | 匹配路径 | $route.params |
|---|---|---|
| /user/:username | /user/evan | { username: 'evan' } |
| /user/:username/post/:post_id | /user/evan/post/123 | { username: 'evan', post_id: 123 } |
routes:[
{path:'/user/:shot/foo/:id', component:shotCat}
]
<p>
<router-link to="/user/shot/foo">/user/shot/foo</router-link>
<!--无法匹配到对应路由-->
<router-link to="/user/shot/cat/foo">/user/shot/cat/foo</router-link>
<!--无法匹配到对应路由-->
<router-link to="/user/foo/foo/foo">/user/foo/foo/foo</router-link>
<!--成功匹配,$route.params.shot为foo;$route.params.cat为foo;-->
<router-link to="/user/shot/foo/cat">/user/shot/foo/cat</router-link>
<!--成功匹配,$route.params.shot为shot;$route.params.cat为cat;-->
</p>
<router-view></router-view>
vue路由导航
导航守卫主要用来通过跳转或取消的方式守卫导航
导航守卫分为: 全局的,单个路由独享的,组件内的三种
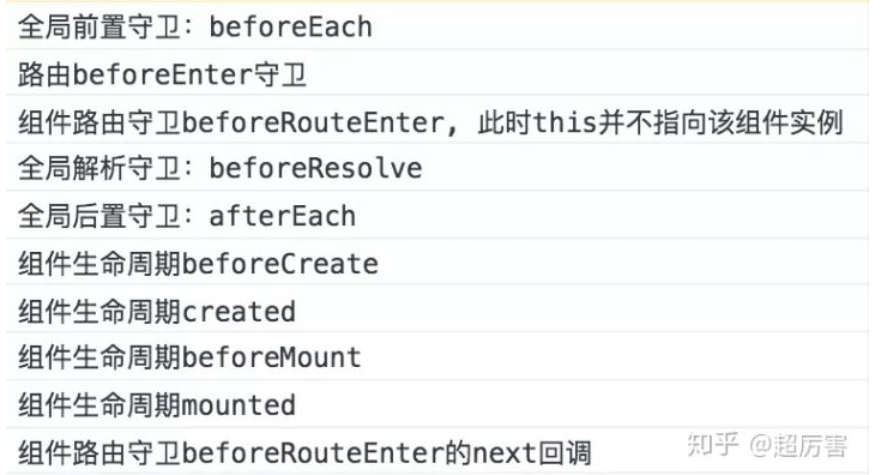
全局路由钩子:beforeEach(to,from, next)、beforeResolve(to,from, next)、afterEach(to,from);
独享路由钩子:beforeEnter(to,from, next);
组件内路由钩子:beforeRouteEnter(to,from, next)、beforeRouteUpdate(to,from, next)、beforeRouteLeave(to,from, next)
全局的:路由实例上直接操作的钩子函数
全局守卫又分全局前置守卫,全局解析守卫 和 全局后置钩子。
全局前置守卫
在一个导航被触发时调用,守卫异步解析执行,在所有守卫 resolve 前,导航一直处于等待状态。我们可以使用 router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => { //. . .}) 来注册一个全局前置守卫
// 全局路由守卫 router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => { console.log('navigation-guards'); // to: Route: 即将要进入的目标 路由对象 // from: Route: 当前导航正要离开的路由 // next: Function: 一定要调用该方法来 resolve 这个钩子。执行效果依赖 next 方法的调用参数。 //首先to和from 其实是一个路由对象,所以路由对象的属性都是可以获取到的(具体可以查看官方路由对象的api文档). //例如:我想获取获取to的完整路径就是to.path.获取to的子路由to.matched[0]. // next();//使用时,千万不能漏写next!!! //next() 表示直接进入下一个钩子. //next(false) 中断当前导航 //next('/path路径')或者对象形式next({path:'/path路径'}) 跳转到path路由地址 //next({path:'/shotcat',name:'shotCat',replace:true,query:{logoin:true}...}) 这种对象的写法,可以往里面添加很多.router-link 的 to prop 和 router.push 中的选项(具体可以查看api的官方文档)全都是可以添加进去的,再说明下,replace:true表示替换当前路由地址,常用于权限判断后的路由修改. //next(error)的用法,(需2.4.0+) const nextRoute = ['home', 'good-list', 'good-detail', 'cart', 'profile']; let isLogin = global.isLogin; // 是否登录 // 未登录状态;当路由到nextRoute指定页时,跳转至login if (nextRoute.indexOf(to.name) >= 0) { if (!isLogin) { console.log('what fuck'); router.push({ name: 'login' }) } } // 已登录状态;当路由到login时,跳转至home if (to.name === 'login') { if (isLogin) { router.push({ name: 'home' }); } } next(); }); .catch(()=>{ //跳转失败页面 next({ path: '/error', replace: true, query: { back: false }}) }) //如果你想跳转报错后,再回调做点其他的可以使用 router.onError() router.onError(callback => { console.log('出错了!', callback); });全局解析守卫
- 我们可以通过 router.beforeResolve 注册一个全局守卫。使用方法 router.beforeEach 类似,区别是在导航被确认之前,同时在所有组件内守卫和异步路由组件被解析之后,解析守卫就被调用。
全局后置钩子
全局后置钩子和全局前置守卫的区别在于没有 next,因此不会改变导航:router.afterEach((to, from, next) => { //. . .})
路由独享守卫
路由独享的守卫是在路由配置上定义 beforeEnter 的,用法与全局前置守卫一致
{ path: '/foo', component: Foo, beforeEnter: (to, from, next) => { // ... }组件内的守卫
//在组件内部进行配置,这里的函数用法也是和beforeEach一毛一样 const Foo = { template: `...`, beforeRouteEnter (to, from, next) { // 在渲染该组件的对应路由被 confirm 前调用 // 不!能!获取组件实例 `this` // 因为当守卫执行前,组件实例还没被创建 }, beforeRouteUpdate (to, from, next) { // 在当前路由改变,但是该组件被复用时调用 // 举例来说,对于一个带有动态参数的路径 /foo/:id,在 /foo/1 和 /foo/2 之间跳转的时候, // 由于会渲染同样的 Foo 组件,因此组件实例会被复用。而这个钩子就会在这个情况下被调用。 // 可以访问组件实例 `this` }, beforeRouteLeave (to, from, next) { // 导航离开该组件的对应路由时调用 // 可以访问组件实例 `this` } }
vue-router meta
在路由列表中,每个路由都有一个 meta 元数据字段, 我们可以在这里设置一些自定义信息,供页面组件或者路由钩子函数中使用。
获取meta数据
- $route.meta 获取路由元信息中的数据
- 路由钩子中获取
//全局路由改变前钩子
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
window.document.title = to.meta.title;
next();
})
//动态获取
this.$route.meta.title
还有一些太复杂我就不写了
编程式导航的写法
//字符串
this.$router.push('home')
//对象
this.$ruter.push({path:'home'})
//命名路由
this.$router.push({name:'user',params:{userId:2333}})
//带查询参数,变成/register?plan=private
this.$router.push({path:'register',query:{plan:'private'}})
注意:path和params是不能同时生效的 ,否则params会被忽略掉,使用对象写法进行params传参时,要么就是path加冒号:,要么就是像上例中的'命名路由'.通过name和params进行传参.
router.reqlace
- 用push方法,页面1跳转到页面2,你使用浏览器的后退可以回到页面1
- 用replace方法,页面1被替换成页面2,你使用浏览器的后退,此时你回不到页面1,只能回到页面1的前一页,页面0.
- 那什么时候会用到replace呢? 当你不想让用户回退到之前的页面时,常见于权限验证,验证后就不让用户回退到登录页重复验证
<router-link :to="{ name:'shotCat',params:{paramId:'hello'},query:{queryId:'world'}}">helloWorld</router-link>
<!--此时通过name匹配到路由对象shotCat.-->
<router-link :to="{ path:'/shotCat',params:{paramId:'hello'},query:{queryId:'world'}}">helloWorld</router-link>
<!--此时通过path匹配到路由对象shotCat.但是!!!!!此时`paramId`并不能添加到`$route.params`里,只有`queryId`成功添加到`$route.query`-->
{{$route.params}}和{{$route.query}}进行验证
路由嵌套和单组件多视图
嵌套路由:就是父路由嵌套子路由.url上就是/user嵌套两个子路由后就是/user/foo和/uer/bar.用一张图表示就是
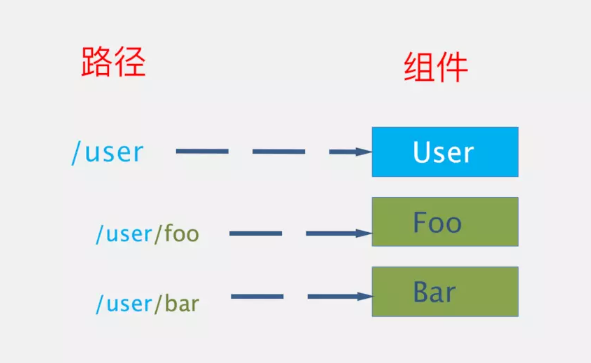
单组件多视图:就是一个组件里有多个视图进行展示.即包含有多个<router-view/>
axios
import axios from 'axios' import VueAxios from 'vue-axios' Vue.use(VueAxios,axios) this.axios.get(api).then((response) => { console.log(response.data) })
vue生命周期
beforeCreate
- el 没有
- data 没有
- 事件没有初始化
created
- el 没有
- data 数据有了
- 事件 也有了
beforeMount
- el 找到了
- data 数据有了
- 事件也有了
mounted
- el:找到了,并且数据渲染进标签了
- dta:数据有了,被监听
- 事件有了被监听了
beforeUpdate
updated
beforeDestory
VueRouter的实现原理:是通过监听a标签的描点值,来动态的显示页面的值
proxyTable
v-model.lazy
同步输出 简称 防抖
v-model.number 规定输出的数字
v-model.trim 去除空格
vue 项目问题
v-if 解决异步传参组件
` <mapBox v-if="mapData" :data="mapData"></mapBox>` 点击搜索的时候 let This=this this.mapData=false; //重要 this.$http.post('/api/show..',{参数}).then( response=>this.mapData=response.data; )还有一些强制刷新的
$forceUpdate()this.$nextTick(()=>{ }) this.$set()使用$refs调用子组件的方法
<Tree ref="Tree"></Tree> let rules = this.$refs.Tree.方法setTimeout
$set()
组件递归实现多级菜单
父组件 ` <div> <Items :msg="msg"></Items> </div> data () { return { msg: [{ text: 1, next: [{ text: '1-1', next: [{ text: '1-1-1', next: [{ text: '1-1-1-1', }], }], }, { text: '1-2', //1-2写在这儿,第二层数据数组中的a[1].text就是‘1-2’ }], }, { text: 2, }, { text: 3, }], } }, components: { Items, }, ` 子组件 <ul > <li v-for='(a,index) in msg' @click.stop.self='show=!show' :key="index"> {{a.text}} <Items :msg='a.next' v-if='show' ></Items> </li> </ul> export default { name:'Items', //这个必须写 props:['msg'],// 父组件传到子组件的数据 data(){ return { show:false } } }使用watch监听路由参数重新获取数据
// 监听,当路由发生变化的时候执行 watch: { '$route':'getPath' }, methods: { getPath(){ console.log(this.$route.path); } } Vue 为你提供了一种方式来声明“这两个元素是完全独立的——不要复用它们”。只需添加一个具有唯一值的 key 属性 <router-view :key="key"></router-view> computed: { key() { return this.$route.name !== undefined? this.$route.name +new Date(): this.$route +new Date() } }
Vue.js 内置的通信手段一般有两种:
-
ref:给元素或组件注册引用信息;
-
$parent/$children:访问父 / 子实例。 -
this.$parent.属性或者方法 this.$children[0].属性或者方法
vue 组件传值provide/inject
以允许一个祖先组件向其所有子孙后代注入一个依赖,不论组件层次有多深,并在起上下游关系成立的时间里始终生效
跟react 上下文特性相似
// A.vue 父组件
export default {
provide: {
name: 'Aresn'
}
}
// B.vue 子组件
export default {
inject: ['name'],
mounted () {
console.log(this.name); // Aresn
}
}
实例还暴露了一些有用的实例属性与方法。它们都有前缀 `### ,以便与用户定义的属性区分开
通过$event 访问原始DOM事件
<button @click.self='warn($event)'>点击我</button>
methods:{
warn(event){
event.target.innerHTML
}
}
prevent是拦截默认事件
@click.prevent.self 会阻止所有的点击
@click.self.prevent 只会阻止对元素自身的点击
按键修饰符
@keyup.enter="submit"
.enter
.tab
.delete (捕获“删除”和“退格”键)
.esc
.space
.up
.down
.left
.right
根实例可以通过 $root 属性进行访问
@click.native
监听根元素的原生事件,使用 .native 修饰符
是用来修饰点击组件的 @click.native
使用.native修饰符来操作普通HTML标签是会令事件失效的
父组件
<MyButton @click.native="equire"/>
components:{
'MyButton':{
template:'<button>点我</button>'
}
},
methods:{
equire(){
console.log(1);
}
}
如何在引用的外部js文件中获取vue页面实例
import houseColumn from '地址'
created(){
this.houseColumn=houseColumn(this)
}
.stop 阻止事件冒泡
.prevent 阻止事件的默认行为
@submit.prevent='' 提交时间不在重载页面
.once 只有一次
passive
移动端的 onscroll 事件整了一个 .lazy修饰符
@scroll.passive=""
qs
进行传参格式化
slot 插槽的深入理解
父组件
<template>
<div>
<child>
<div slot='zhangsan'>
{{msg}} <br>
<ul>
<li v-for="(i,index) of arr" :key="index">{{i}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
</child>
</div>
</template>
export default {
components:{
child,
},
data(){
return {
msg:'111',
arr:[1,2,3,4,5,6]
}
}
子组件
<slot name='zhangsan'></slot>
作用域插槽
先从子组件触发
<slot :data="data1"></slot>
data(){
return {
data1: ['zhangsan','lisi','wanwu','zhaoliu','tianqi','xiaoba']
}
}
父组件
<template slot-scope="{data}">
<li v-for="item in data">{{item}}</li>
</template>
vue更新后生命周期被$nextTick替代
$set
this.$set(this.stu,'gender','male') //添加一个属性
this.stu=Object.assign({},this.stu, { genders: 'female', height: 180 })//添加多个属性
$ attrs 和 $listeners
子触发父亲的方法
v-bind=$attrs 属性(子组件获取父亲绑定子组件的属性)
$listeners 事件 绑定所有的方法(组组建获取父亲的绑定子组件的方法)
v-on=$listeners
组件的通信
props emit v-bind=
$attrsv-on="$listeners"$parent
$child
$refs
全局vue
npm install -g @vue/cli-service-global
vue serve 文件
异步加载
defer 有序加载js async 异步 无序的
//webpack 懒加载
preload prefetch
路由钩子函数
当组件切换时
会触发离开的钩子 beforeRouteLeave()
当进入新的页面里,组件内部会触发一个 beforeRouterEnter
当属性变化时 并没有重新加载组件 会触发 beforeRouteUpdate
组件渲染完成后, 会调用当前beforeRouteEnter