持续更新中---
一、定义:以下均使用括号中的简称
工作区:workspace (W)
暂存区:index (I)
本地仓库:local repository (L)
远程仓库:remote repository (R)
二、常用命令:
git init
2.常用配置信息
(如果不使用--global,则只设置当前项目的配置信息)
查看.gitconfig文件在哪里:
git config --list --show-origin
直接改全局代理文件:
git config --global --edit
设置代理:
git config --global http.proxy http://xxx.com:port
取消代理:
git config --global --unset http.proxy
设置用户名:
git config --global user.name "[name]"
设置邮箱:
git config --global user.email "[email address]"
设置命令行颜色:
git config --global color.ui auto
查看用户名:
git config --global user.name
配置crlf:
git config --global core.autocrlf [true/false/input]
(在windows下设置为true,则提交的内容是LF,本地是CRLF)
配置文件名大小写敏感:(git默认不区分文件名大小写)
(可以新增文件,但是之前文件还没有删除) git config core.ignorecase false
(可以尝试) git mv --force myfile myFile
3.添加--从工作区W到暂存区I
添加单个文件/多个文件/目录:
git add [file1] [file2] [directory]
添加新增和修改的文件,不做删除操作:
git add .
添加修改和删除的文件,不做新增操作:
git add -u
添加增删改的文件:等于git add .;git add -u;
git add -A
4.提交:
(1)从暂存区I到本地仓库L
git commit -m [提交信息]
(2)
5.撤销
(1)从暂存区I到工作区W
git rm --cached <file> ...
(2)恢复到HEAD版本
git reset --hard HEAD
(3)修改提交的用户名信息
git commit --amend --author="Author Name <email@address.com>"
6.远程
(1)更改远程仓库地址
git remote set-url origin http://xxx.xx.com/x.git
(2)查看远程仓库地址
git remote show origin
(2)查看远程仓库日志
git log origin/master
(3)比较本地分支和远程分支
git diff master origin/master
(4)查看远程分支
git branch -r
(5)拉取远程
方法1:拉取并合并
git pull
方法2:先拉取后合并
git fetch origin
git merge origin/master
(6)查看本地分支和远程分支的差异
git diff master origin/master
(7)基于远程分支创建本地分支
git checkout -b feature origin/feature
7.分支
查看分支:git branch
查看远程分支的本地copies:git branch -r
查看远程分支: git ls-remote
查看所有分支: git branch -a
创建分支:git branch <name> <origin/name>
切换分支:git checkout <name>
创建+切换分支:git checkout -b <name> <origin/name>
合并某分支到当前分支:git merge <name>
删除分支:git branch -d <name>
删除远程分支: git push origin --delete <name>
获取远程分支: git fetch
更新远程分支的本地copies: git fetch --prune origin
删除不存在的远程分支的信息:git remote prune origin
8.储藏
保存:git stash
查看stash列表:git stash list
恢复:git stash apply
恢复特定版本:git stash apply stash@{2}
清除某个stash记录:git stash drop stash@{0}
9.引用
(1)查看提交的哈希字串
git log
git log --pretty=oneline
git log --pretty=format:"%an %h %s" // 作者/hash/commit message
查看历史中有xxx的
git log -G"删除掉的内容" -p
git log -S"删除掉的内容" -p
git log --grep "删除掉的内容"
git log -p | grep "删除掉的内容"
查看某个目录(eg: txv)的提交记录
git log -- txv
git log -p -- txv (有详细的内容)
(2)查看某个提交
git show 0c708f(哈希)
(3)查看分支、标签或间接引用的哈希
git rev-parse master
(4)查看引用
在.git/refs目录下
git show refs/heads/some-feature
在.git目录下还有一些引用:
- HEAD – 当前所在的提交或分支。
- FETCH_HEAD – 远程仓库中fetch到的最新一次提交。
- ORIG_HEAD – HEAD的备份引用,避免损坏。
- MERGE_HEAD – 你通过
git merge并入当前分支的引用(们)。 - CHERRY_PICK_HEAD – 你
cherry pick使用的引用。
(5)refspec
refspec的定义是这样的:[+]<src>:<dst>。<src>参数是本地的源分支,<dst>是远程的目标分支。可选的+号强制远程仓库采用非快速向前的更新策略。
(6)相对引用
git show HEAD~2 祖父节点
git show HEAD^2 第二个父节点(分支合并时,原所在分支是第一个父节点)
git show HEAD^2^1 可以多层
(7)引用日志
git reflog
git checkout HEAD@{1}
10.代码回滚
reset checkout revert的选择
reset checkout 可以指定文件或某次提交,revert只针对提交,不针对文件
checkout revert 有可能会重写文件,在使用前要提交或缓存工作目录的修改
(1)reset(仅仅用在私有分支上,一般只用HEAD)
git checkout feature
git reset HEAD (末端两个提交变成悬挂提交,git垃圾回收时会被删除)
git reset --hard HEAD
- --soft – 缓存区和工作目录都不会被改变
- --mixed – 默认选项。缓存区和你指定的提交同步,但工作目录不受影响
- --hard – 缓存区和工作目录都同步到你指定的提交
git reset HEAD file1.js 将HEAD提交中的该文件加入到缓存区,针对文件没有--mixed之类的参数,相当于撤销 git add 操作(验证过这个作用)
(2)checkout
git checkout feature 切换分支
git checkout HEAD~2 把HEAD移动到特定提交,但会造成HEAD分离,非常危险,如果你接着添加新的提交,然后切换到别的分支之后就没办法回到之前添加的这些提交。因此,在为分离的HEAD添加新的提交的时候你应该创建一个新的分支。
git checkout HEAD~2 file1.js 将工作目录的该文件同步到HEAD~2
(和git reset HEAD --hard很像,但只影响特定文件)
(3)revert(可以用在公共分支,不会影响历史,创建一个新的提交来撤销某个提交的修改)
git checkout feature
git revert HEAD~2
revert多个提交生成多个commit:git revert old-commitId^..new-commitId
如果我们想把这三个revert不自动生成三个新的commit,而是用一个commit完成,可以这样:git revert -n old-commitId^..new-commitId
然后确认无误后,执行git revert --continue
11.打标签
(1)查看当前标签
git tag
(2)打标签
git tag -a v1.0.0 -m "my version v1.0.0"
(3)查看某个tag
git show v1.0.0
(4)删除某个tag
git tag -d v1.0.0
(4)把tag推送到远程
git push origin --tags
12.比较
git diff 工作区(W)跟暂存区(I)的区别(使用 f 翻下一页,使用b 翻上一页)
git diff HEAD 工作区(W)跟本地仓库(L)的区别
git diff --staged 暂存区(I)跟本地仓库(L)的区别
(后边跟上文件名则只对比某个文件)
提交前比较某个文件
git diff -- myfile.js 工作区(W)跟暂存区(I)的区别
git diff HEAD -- myfile.js 工作区(W)跟本地仓库(L)的区别
git diff --cached myfile.js 暂存区(I)与本地仓库(L)的区别
比较时忽略空格变化
git diff -w (--ignore-all-space)
使用图形化工具查看比较
gitk &
设置图形化工具的编码
13.打包
git archive --format zip --output /path/to/file.zip master
14.分支的衍合
(1)分支rebase
git checkout feature
git rebase master
解决冲突后 git add .
git rebase --continue
(2)合并多个提交:
git rebase -i [startpoint] [endpoint]
git rebase -i HEAD~3
https://juejin.im/entry/5ae9706d51882567327809d0
https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/896043488029600/1216289527823648
eg:如果要把最近两次提交合并则:
git rebase -i HEAD~2
将除第一行的pick外的改成s或者squash
:wq保存
删掉commit msg 只留下一个commit msg
:wq 保存
git push -f // 强制push到远端
(3)减少merge次数
git pull --rebase
当远端分支有其他人的提交时,本地执行git pull通常会生成一个merge节点。可以使用git pull --rebase来避免这类merge节点
15.只合并某个提交或者某个文件
git cherry-pick <commit id> 合并某一个提交
git cherry-pick -x <commit id> 合并某一个提交,并保留原提交的信息
git cherry-pick <start commit id>..<end commit id> 合并某个区间的提交,左开右闭
git cherry-pick <start commit id>^..<end commit id> 合并某个区间的提交,闭区间
git checkout branchname -- <paths>
git merge --no-ff --no-commit branchname (不快速向前,不提交)
16.git 免重复登录方式
git本身支持SSH方式,在此不具体介绍了。
git支持credential的方式,在win7下可以设置credential helper为wincred,可以在"控制面板"--"用户账户"--"凭据管理器" 里查看凭据。在mac可以设置osxkeychain,可以在keychain access钥匙串工具里的login凭据里查看。
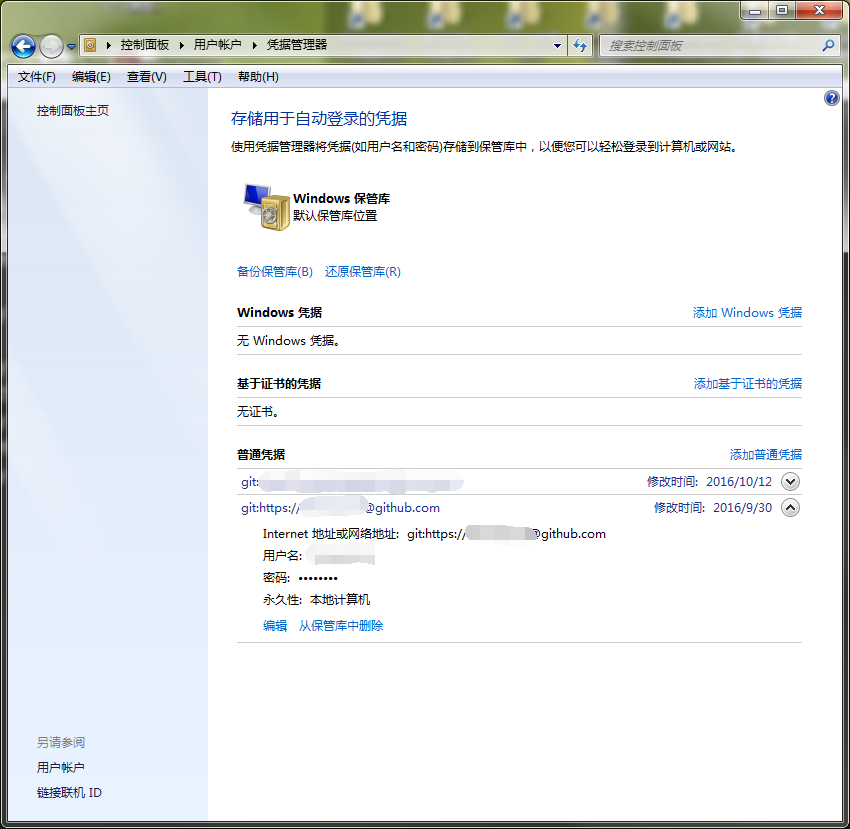
设置和取消凭证管理的方式:
git config --global --unset credential.helper
git config --global credential.helper wincred
17.git 设置命令别名
git config --global alias.co checkout
git config --global alias.ci commit
git config --global alias.br branch
git config --global alias.lg "log --color --gragh --pretty=format:'%Cred%h%Creset -%C(yellow)%d%Creset %s %Cgreen(%cr) %C(blod blue)<%an>%Creset' --abbrev-commit"
参考地址:http://blog.csdn.net/zhang31jian/article/details/41011313
18.git 判断代码最初是由谁提交的
git blame <filename>
git blame -L 100,100 <filenname>
git blame -L 100,+10 <filename>
19.冲突解决
(1)merge之后冲突,如果保留当前版本用--ours,如果保留合并版本用--theirs
eg: git checkout --theirs webpack.config.js
(2)取消合并
git merge --abort
(3)强制branchA与branchB完全一样
git checkout branchA
git reset --hard branchB
git push -f origin branchA
20.fork项目以后如何同步源项目的更新内容
git remote -v //查看远程状态
git remote add upstream https://github.com/ORIGINAL_OWNER/ORIGINAL_REPOSITORY.git //确定一个将被同步给 fork 远程的上游仓库
git remote -v //查看状态确认是否配置成功
git fetch upstream //更新本地upsteam/master
git checkout master
git merge upstream/master
git push origin master
21.git bisect
是一个很有用的命令,用来查找哪一次代码提交引入了错误 http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2018/12/git-bisect.html
git log --pretty=oneline // 查看日志
git bisect start HEAD 4d83cf // [终点] [起点]
git bisect good // 这个commit的时候是正常的
git bisect bad // 这个commit的时候是不正常的
git bisect reset // 退出查错
22.git submodule vs subtree
git submodule类似于引用,而git subtree类似于拷贝
https://www.xianmin.org/post/git-submodule/
| submodule | subtree | |
| 修改代码并提交 | 默认在detached HEAD,需要先切换分支,push跟正常git一样 | push会比较慢 |
| 更新到最新版本 | 需要递归更新git submodule foreach git submodule update | 所有子模块单独更新 |
| 远程仓库空间占用 | 只是引用,基本不占什么地方,只有.gitmodules和一个目录文件 | 子模块copy,会占用较大的额外空间 |
| 本地占用空间 | 需要详细文件 | 需要详细文件 |
| 仓库clone | 除了clone还需要init和更新,稍微复杂 | clone后即可使用,简单一下 |
submodule官方文档 https://git-scm.com/book/zh/v2/Git-%E5%B7%A5%E5%85%B7-%E5%AD%90%E6%A8%A1%E5%9D%97
submodule的坑 https://blog.devtang.com/2013/05/08/git-submodule-issues/
(1)添加子模块到指定路径:git submodule add https://github.com/chaconinc/DbConnector <本地目录名eg: DbConnector>
(2)虽然 DbConnector 是工作目录中的一个子目录,但 Git 还是会将它视作一个子模块。当你不在那个目录中时,Git 并不会跟踪它的内容, 而是将它看作子模块仓库中的某个具体的提交。
看更漂亮的差异输出: git diff --cached --submodule
(3)克隆含有子模块的项目
方法1:
git clone https://github.com/chaconinc/MainProject
git submodule init 初始化本地配置文件
git submodule update 从该项目中抓取所有数据并检出父项目中列出的合适的提交
备注: git submodule update --init 可以将将git submodule init 和 git submodule update 合并成一步,
如果还要初始化、抓取并检出任何嵌套的子模块, 请使用简明的 git submodule update --init --recursive
方法2:
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/chaconinc/MainProject
(4)从子模块的远端拉取上游修改(更新主项目对子模块的引用情况)
cd DbConnector
git fetch
git merge origin/master
如果你现在返回到主项目并运行 git diff --submodule,就会看到子模块被更新的同时获得了一个包含新添加提交的列表。 如果你不想每次运行 git diff 时都输入 --submodle,那么可以将 diff.submodule 设置为 “log” 来将其作为默认行为。
git config --global diff.submodule log
git diff
如果你不想在子目录中手动抓取与合并,那么还有种更容易的方式。 运行 git submodule update --remote,Git 将会进入子模块然后抓取并更新。
(5)使用子模块的指定分支
git config -f .gitmodules submodule.DbConnector.branch stable
如果不用 -f .gitmodules 选项,那么它只会为你做修改。但是在仓库中保留跟踪信息更有意义一些,因为其他人也可以得到同样的效果。
如果你设置了配置选项 status.submodulesummary(git config status.submodulesummary 1),Git 也会显示你的子模块的更改摘要(git status的时候)
查看日志 git log -p --submodule
(6) 从MainProject项目远端拉取上游更改
默认情况下,git pull 命令会递归地抓取子模块的更改,如上面第一个命令的输出所示。 然而,它不会 更新 子模块,可以使用git submodule update --init --recursive
如果你想自动化此过程,那么可以为 git pull 命令添加 --recurse-submodules 选项(从 Git 2.14 开始)。 这会让 Git 在拉取后运行 git submodule update,将子模块置为正确的状态。 此外,如果你想让 Git 总是以 --recurse-submodules 拉取,可以将配置选项 submodule.recurse 设置为 true (从 Git 2.15 开始可用于 git pull)。此选项会让 Git 为所有支持 --recurse-submodules 的命令使用该选项(除 clone 以外)。
在为父级项目拉取更新时,还会出现一种特殊的情况:在你拉取的提交中, 可能 .gitmodules 文件中记录的子模块的 URL 发生了改变。 比如,若子模块项目改变了它的托管平台,就会发生这种情况。 此时,若父级项目引用的子模块提交不在仓库中本地配置的子模块远端上,那么执行 git pull --recurse-submodules 或 git submodule update 就会失败。 为了补救,git submodule sync 命令需要:
# 将新的 URL 复制到本地配置中
$ git submodule sync --recursive
# 从新 URL 更新子模块
$ git submodule update --init --recursive
git push 命令接受可以设置为 “check” 或 “on-demand” 的 --recurse-submodules 参数。 push 操作失败:git push --recurse-submodules=check , 可以通过设置 git config push.recurseSubmodules check 让它成为默认行为。如果任何提交的子模块改动没有推送那么 “on-demand” 选项会直接帮你先push子模块: git push --recurse-submodules=on-demand 可以通过设置 git config push.recurseSubmodules on-demand 让它成为默认行为。git submodule foreach 'git stash'git submodule foreach 'git checkout -b featureA'$ git config alias.sdiff '!'"git diff && git submodule foreach 'git diff'"
$ git config alias.spush 'push --recurse-submodules=on-demand'
$ git config alias.supdate 'submodule update --remote --merge'23.将子文件夹拆分成新仓库
我理解是一次性的拆分,能保留该子文件夹的提交记录保留下来,之后就各自维护了吧(使用场景不多)
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/7430717/git-filter-branch-on-all-branches
三、常用场景:
1.创建新的库
mkdir tutorial
cd tutorial
git init
touch README.md
git add README.md
git commit -m "first commit"
git remote add origin http://xxx.xx.com/x.git
git push -u origin master
2.push已经存在的库
cd existing_repo
git remote add origin http://xxx.xx.com/x.git
git push -u origin master
3.merge request
git fetch origin
git checkout -b request-branch origin/request-branch
git checkout master
git merge --no-ff request-branch
git push origin master
默认情况下,Git执行"快进式合并"(fast-farward merge),会直接将Master分支指向Develop分支。
使用--no-ff参数后,会执行正常合并,在Master分支上生成一个新节点。为了保证版本演进的清晰,我们希望采用这种做法。
4.github quick setup
(1)https://github.com/username/gittest.git
git@github.com:username/gittest.git
(2)create a new repository on the command line:
echo "# gittest" >> README.md
git init
git add REAME.md
git commit -m "first commit"
git remote add origin git@github.com:username/gittest.git
git push -u origin master
(3)push an existing repository from the command line
git remote add origin git@github.com:username/gittest.git
git push -u origin master
(4)import code from another repository
You can initialize the repository with code from a Subversion,Mercurial, or TFS project.
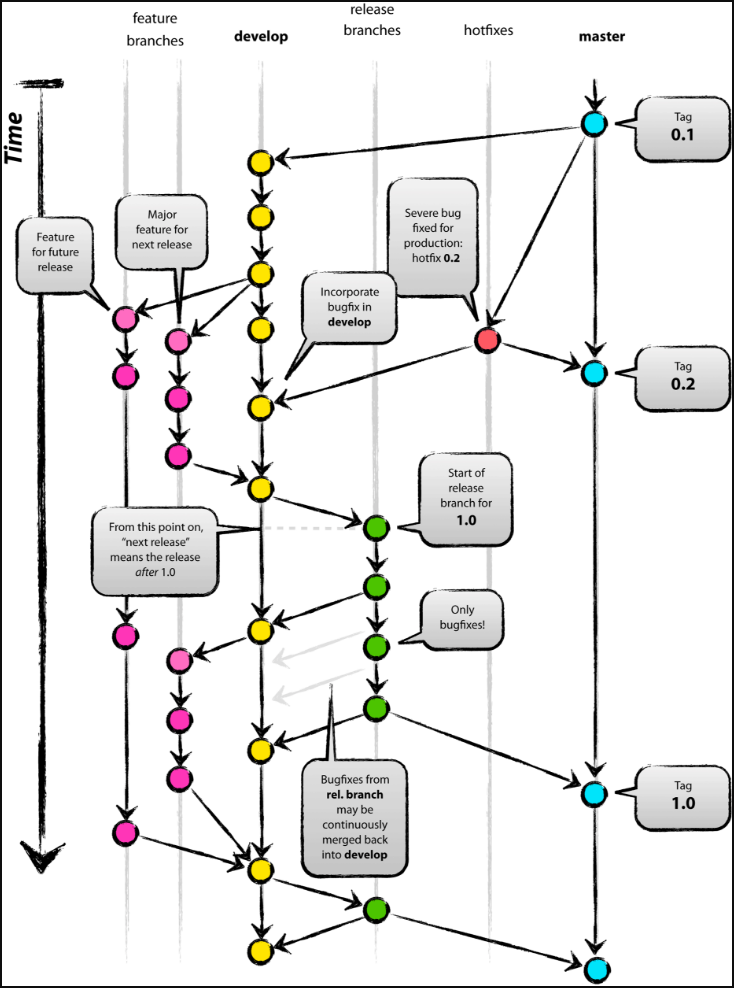
5.gitflow
参考链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/cnblogsfans/p/5075073.html
可以使用GUI工具SourceTree(http://blog.csdn.net/victor_barnett/article/details/51211282)
git flow init之后,配置文件和hooks分别在.git/config .git/hooks/
-
初始化: git flow init
-
开始新Feature: git flow feature start MYFEATURE
-
Publish一个Feature(也就是push到远程): git flow feature publish MYFEATURE
-
获取Publish的Feature: git flow feature pull origin MYFEATURE
-
完成一个Feature: git flow feature finish MYFEATURE
-
开始一个Release: git flow release start RELEASE [BASE]
- Publish一个Release: git flow release publish RELEASE
-
发布Release: git flow release finish RELEASE
别忘了git push --tags -
开始一个Hotfix: git flow hotfix start VERSION [BASENAME]
-
发布一个Hotfix: git flow hotfix finish VERSION