说在最前面
centos 是基于redhat linux,所以最好的教程在红帽官网
https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/
ubuntu是基于debian,所以ubuntu学习最好的教程,也在debian官网
https://www.debian.org/doc/manuals/debian-faq/index.zh-cn.html
https://wiki.debian.org/zh_CN/FrontPage?action=show&redirect=首页
centos7的基本管理操作(非常推荐)
https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html/system_administrators_guide/ch-getting_started
redhat常用系统管理的一些软件(非常推荐)
https://access.redhat.com/articles/1189123
安装
去centos官网下载mini安装iso,从最基本的精简版系统一步一步配置。
联网
开始之前先做一些预习的知识点
CentOS7网卡命名
en: Ethernet 有线局域网
wl: wlan 无线局域网
ww: wwan无线广域网
——————————
o
s
x
p
联网方案 NetworkManger
安装完mini系统后,可直接通过有线网络联网,为了方便下面还是配置wifi联网。管理网络,在centos中使用的是NetworkManger,这是一个软件包,含有好几个软件工具:nmcli、nmtui、nm-connection-editor、control-center、control-center、network connection icon,详细可见 https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html/networking_guide/sec-networkmanager_tools
简单介绍下nmtui和nmcli
1、nmtui 这是一个Text User Interface类型的软件,用于连接wifi,nm的意思是NetworkManger Text User Interface,控制台输入nmtui后直接扫描可用的无线网络。
nmtui是包含在NetworkManager 软件包中的,默认NetworkManager-tui 是集成再centos7中的,如果想要手动安装可使用下面的命令:
yum install NetworkManager-tui
要使用该程序,直接在控制台输入nmtui回车即可,软件使用非常人性化,不再详细介绍。
一些截图:
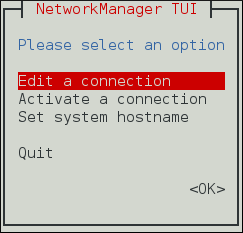
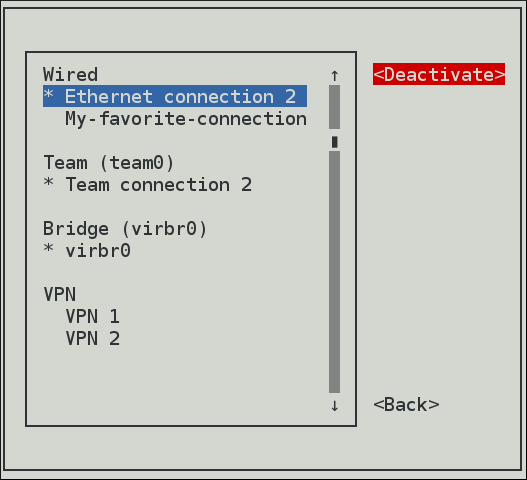
可用的一些命令
nmtui edit connection-name
nmtui connect connection-name
可参考的资料:
https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Enterprise_Linux/7/html/Networking_Guide/sec-Networking_Config_Using_nmtui.html
https://developer.gnome.org/NetworkManager/stable/nmtui.html
https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html/system_administrators_guide/sec-networking#sec-Network-access-after-installation-nmcli
2、nmcli (NetworkManager Command Line Interface)这是一个命令行连接的方案
命令详解:
常用:
nmcli connection show 查看所有连接
nmcli device status 查看已经识别的设备及其状态
nmcli dev wifi list 列出可用的网络
nmcli radio wifi [on | off ] 更改wifi状态
关于这两个工具推荐使用nmtui,图形化做的比较好,用起来方便。
你的网卡硬件正常工作了吗?
有了上面的解决方案就能准确的联网了
使用命令nmcli dev status查看当前所有网卡信息,如果能看到wl开头的网卡能正常工作那就是硬件驱动起来了,如果没有驱动起来(你确定装了无线网卡但没有找到wl开头的设备,或者其他什么提示)那么就建议,换网卡,不建议折腾驱动,linux内核对于intel或者高通的无线网卡支持非常好基本都能直接驱动起来,如果真的出现无法驱动无线网卡,直接换个内核支持的硬件是非常快速有效的办法。
使用nmcli联网
至此我就认为硬件是正常工作的,那么接下来联网吧!
列出可用的wifi网络
nmcli dev wifi list
连接网络
nmcli dev wifi connect <name> password <password> 不指定网卡连接wifi
nmcli dev wifi connect <name> password <password> ifname wlan1 [profile_name] 指定网卡
测试网络是否正常工作
ping 8.8.8.8如果能ping通,说明已经联网,但是别着急,你可能还需要配置dns,试着yum update一下,可能会遇到could not retrieve mirrorlist报错,一般就是dns没有配置的原因。
添加dns,依然可以使用nmcli命令nmcli con mod eno1 ipv4.dns "8.8.8.8",这就设置了8.8.8.8为dns,重新执行yum update一般就没什么问题了。
其他方案
不使用NetworkManger配置网络的一些方案
使用ip命令
使用内核命令
网络配置的总结
关于网络配置这部分知识多数翻译自红帽手册,其他对于Route(ip、netmask、Gateway等)、DNS、HostName等可参考原链接:
https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html/networking_guide/index
上面涉及到的知识Redhat的网络管理,如果是Ubuntu等Debian系列的系统可参考这个链接:
https://wiki.debian.org/zh_CN/Network#A.2Bf1F.2B3JFNf24-
安装桌面环境
正式安装桌面环境之前 yum的一点说明
1、yum仓库配置
yum有一个全局的配置文件,文件目录是 /etc/yum.conf,该文件中会有一个名为main的小节,在该小节中我们可以设置一些yum的选项来对全局有效。比如可以手动添加新的仓库到main中,但是推荐的是在/etc/yum.repos.d/目录下创建一个新以.repo为结尾的文件,来添加新的仓库。
下面示例添加一个新的仓库来安装该仓库中的软件(chrome)
vi /etc/yum.repos.d/google-chrome.repo
在文件中写入:
[google-chrome]
name=google-chrome
baseurl=http://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/rpm/stable/x86_64
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://dl.google.com/linux/linux_signing_key.pub
然后去终端中执行:
yum install google-chrome-stable
一路选择y就可以了。
2、yum的一些常用操作
yum search term…
yum search vim gvim emacs
yum list all
yum list installed glob_expression…
yum repolist
yum info package_name…
yum install package_name
yum install package_name package_name…
yum localinstall path 安装本地rpm包
yum remove package_name…
3、yum group操作
作开发的时候要用到好多开发工具,如果能用一条命令安装所有常用的开发工具该有多好!
于是centos为了方便,为yum添加了group的功能,使用yum grouplist列出可用的软件包(包含一系列软件的名称)
下面是常用的命令
yum grouplist
yum groupinfo
yum groupinstall
yum groupremove
yum groupupdate
比如安装"Development Tools"就可以执行:
yum groupinstall "Development Tools"
参考 https://www.unixmen.com/yum-groupinstall-a-quick-introduction/
安装gnome桌面环境
yum groupinstall "X Window System"
yum groupinstall "GNOME Desktop" "Graphical Administration Tools" 这里顺带安装了一些工具
等待执行完成就可以了,但是有一点问题,那就是安装之后重启系统还是会进入命令行模式,使用startx命令之后才能进入图形界面。
参考 https://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2018-04/152000.htm
设置默认启动图形环境
开始之前,国际惯例,先介绍预备知识点。
1、软连接和硬连接
网上搜去吧,比较容易理解。
2、Linux系统启动流程
bios -> Kernel -> hardware driver-> systemd -> default.target
整个流程大体上是上面的意思。
关于硬件驱动:
Linux中把硬件驱动与一些其他的东西看作modules,每一个硬件的驱动就算一个module,有个默认的配置文件说明默认加载哪些modules,详细的日后再补充吧。
一些可能有用的资料
https://www.thegeekdiary.com/centos-rhel-how-to-disable-and-blacklist-linux-kernel-module-to-prevent-it-from-loading-automatically/
https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/6/html/deployment_guide/blacklisting_a_module (推荐)
https://www.debian.org/releases/buster/s390x/ch05s02.en.html
https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Kernel_module_(简体中文)
关于systemd:
systemd是一个守护服务,官网 https://freedesktop.org/wiki/Software/systemd/ ,github 代码 https://github.com/systemd/systemd ,archwiki的解释 https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Systemd_(简体中文)
简单来说,systemd会加载一些单元,这些单元有:系统服务(.service)、挂载点(.mount)、sockets(.sockets) 、系统设备(.device)、交换分区(.swap)、文件路径(.path)、启动目标(.target)、计时器(.timer),目前我们关心的是.target。
systemd的执行流程是按照/etc/systemd/system/default.target的规划进行的,到/etc/systemd/system/目录里能看到很多.target文件,这些分别是systemd可以执行的流程,有的是执行多用户命令行界面、有的是执行图形界面,详细介绍如下:
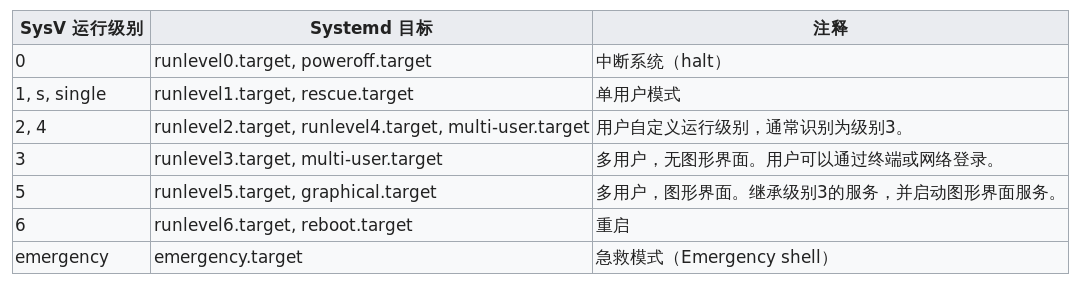
systemd会去加载default.target(/etc/systemd/system/default.target),默认default.target指向的多用户,我们手动软连接default.target到graphal.target就会默认加载图形界面。
当然也可以使用 systemctl命令来设置默认的启动target,例如 systemctl set-default multi-user.target就是设置多用户来启动。
启动流程
关于Linux系统的启动、systemd都还有很多知识点,比如管理工具systemctl、insmod、rmmod、modprobe,先留个坑,有空再补充。
可参考的资料 :
https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html/kernel_administration_guide/index
https://access.redhat.com/articles/754933
https://wiki.debian.org/systemd
https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html/system_administrators_guide/chap-managing_services_with_systemd
多语言
到目前为止,我们的系统还都是英文的,这里设置下中文。
输入法
防火墙
未完待续——