soundtouch变速主要采用WSOLA算法来进行变速。
http://www.surina.net/soundtouch/
https://blog.csdn.net/suhetao/article/details/5863477
The principle of WSOLA refer to following figure:
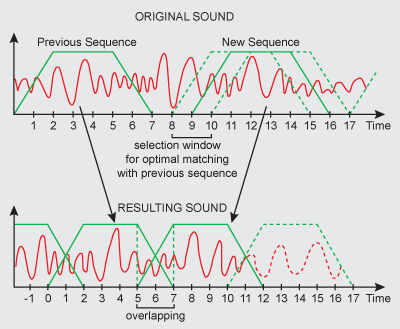
There are three important parameter: SequenceMs, overlapMs, seekWindowMs.
These parameters affect to the time-stretch algorithm as follows:
- DEFAULT_SEQUENCE_MS: This is the default length of a single processing sequence in milliseconds which determines the how the original sound is chopped in the time-stretch algorithm. Larger values mean fewer sequences are used in processing. In principle a larger value sounds better when slowing down the tempo, but worse when increasing the tempo and vice versa.
By default, this setting value is calculated automatically according to tempo value. - DEFAULT_SEEKWINDOW_MS: The seeking window default length in milliseconds is for the algorithm that seeks the best possible overlapping location. This determines from how wide a sample "window" the algorithm can use to find an optimal mixing location when the sound sequences are to be linked back together.
The bigger this window setting is, the higher the possibility to find a better mixing position becomes, but at the same time large values may cause a "drifting" sound artifact because neighboring sequences can be chosen at more uneven intervals. If there's a disturbing artifact that sounds as if a constant frequency was drifting around, try reducing this setting.
By default, this setting value is calculated automatically according to tempo value. - DEFAULT_OVERLAP_MS: Overlap length in milliseconds. When the sound sequences are mixed back together to form again a continuous sound stream, this parameter defines how much the ends of the consecutive sequences will overlap with each other.
This shouldn't be that critical parameter. If you reduce the DEFAULT_SEQUENCE_MS setting by a large amount, you might wish to try a smaller value on this.
function out = check_limits(in, min, max)
if in < min
out = min;
else if in > max
out = max;
else
out = in;
end
end
function [seekWindowLength, seekLength, overlapLength] = calcSeqParams(fs, tempo)
overlapMs = 8;
autoseq_tempo_low = 0.5;
autoseq_tempo_top = 2.0;
autoseq_at_min = 90;
autoseq_at_max = 40;
autoseq_k =(autoseq_at_max - autoseq_at_min) / (autoseq_temp_top - auto_temp_low);
autoseq_c = autoseq_at_min -autoseq_k * autoseq_temp_low;
autoseek_at_min = 20;
autoseek_at_max = 15;
autoseek_k =(autoseek_at_max - autoseek_at_min) / (autoseq_temp_top - auto_temp_low);
autoseek_c = autoseek_at_min -autoseek_k * autoseq_temp_low;
%calc sequenceMs
seq = autoseq_c + autoseq_k * tempo;
seq = check_limits(seq, autoseq_at_max, autoseq_at_min);
sequenceMs = round(seq);
seek= autoseek_c + autoseek_k * tempo;
seek= check_limits(seek, autoseek_at_max, autoseek_at_min);
seekMs = round(seek)
seekWindowLength = sequenceMs * fs / 1000;
seekLength = seekMs * fs /1000;
overlapLength = overlapMs * fs / 1000;
overlapLength = overlapLength - mod(overlapLength, 8);
end
function corr = calcCrossCorr(mixingSeg, compareSeg)
len = length(compareSeg(:,1));
corr = 0;
norm = 0;
for i = 1: 1 : len
corr = corr + mixingSeg(i) * compareSeg(i);
norm = norm + mixingSeg(i) * mixingSeg(i);
end
corr = corr / sqrt(norm);
end
function offset = seekBestOverlapPosition(seekWindow, compareSeg, overlapLength, seekLength)
bestCorr = calcCrossCorr(seekWindow(1:overlapLength, 1), compareSeg);
offset = 1;
for i = 2 : 1 : seekLength
corr = calcCrossCorr(seekWindow(i:i + overlapLength, 1), compareSeg);
if corr > bestCorr
bestCorr = corr;
offset = i;
end
end
end
function output = overlap(rampUp, rampDown)
len=length(rampDown);
for i = 1:1:len
output(i,1) = rampUp(i) * i / len + rampDown(i) * (len - i) / len;
end
end
function [output, outpos, lastCompare, inpos] = processSamples(input, inputLen, expectOutputLen, compareSeg, overlapLength, seekLength, seekWindowLength, tempo, isBeginning)
nominalSkip = tempo * (seekWindowLength - overlapLength);
sampleReq = max(round(nominalSkip) + overlapLength, seekWindow);
inpos = 1;
outpos = 1;
offset = 0;
skipFract = 0;
while inputLen - inpos >= sampleReq
if isBeginning == 0
offset = seekBestOverlapPosition(input(inpos : inpos + overlapLength + seekLength - 1, 1), compareSeg, overlapLength, seekLength);
output(outpos:outpos + overlapLength - 1, 1) = overlap(input(inpos + offset : inpos + offset + overlapLength - 1, 1), compareseg);
ouputpos = outpos + overlapLength;
offset = offset + overlapLength;
else
isBeginning = 0;
skip = round(tempo * overlapLength);
skipFract = skipFract - skip;
end
temp = (seekWindowLength - 2 * overlapLength);
if outpos + tmep < expectOutputLen
output(outpos : outpos + temp - 1, 1) = input (inpos + offset : inpos + offset + temp - 1, 1);
outpos = outpos + temp;
else
output(outpos : expectOutputLen, 1) = input (inpos + offset : inpos + offset + expectOutputLen- outpos, 1);
outpos = expectOutputLen;
beak;
end
compareSeg = input (inpos + offset + temp: inpos + offset + temp +overlapLength - 1, 1);
skipFract = skipFract + nominalSkip;
ovlSkip = floor(skipFract);
skipFract = skipFract - ovlSkip;
inpos = inpos + ovlSkip;
end
lastCompare = compareSeg;
end
function output = changeTempo(input, fs, tempo)
inputLen = length(input(:,1));
outputLen = round(inputLen / tempo);
output = zeros(outputLen, 1);
[seekWindowLength, seekLength, overlapLength] = calcSeqParams(fs, tempo);
isBeginning = 1;
compareBuf = zeros(overlapLength, 1);
expectOutLen = outputLen;
[output, outpos, compareBuf, inpos] = processSamples(input, inputLen, expectOutLen, compareBuf, overlapLength, seekLength, seekWindowLength, tempo, isBeginning);
remainningSamples = inputLen - inpos;
%append zeros to the remainning data
remainningLen = remainningSamples + 200 * 128;
remainningInput = zeros(remainningLen, 1);
remainningInput(1:remainningSamples, 1) = input(inpos:inpos + remainningSamples - 1, 1);
if outputLen > outpos
expectOutLen = outputLen - outpos + 1;
isBeginning = 0;
[tempOutput, tempOutpos, compareBuf, inpos] = processSamples(remainingInput, remainingInputLen, expectOutLen, compareBuf, overlapLength, seekLength, seekWindowLength, tempo, isBeginning);
output(outpos:outputLen, 1) = tempOutput(1: tempOutpos);
end
end
main.m:
clc;
clear all;
[input fs] = wavread('test.wav');
tempo = 2;
output = changeTempo(input, fs, tempo);
wavwrite(output, fs, 'output.wav');