linux 启动流程
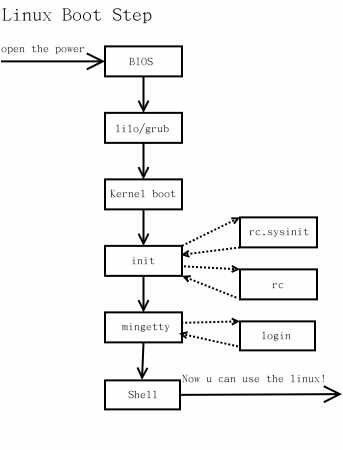
系统启动主要顺序就是:
1. 加载内核
2. 启动初始化进程
3. 确定运行级别
4. 加载开机启动程序
5. 用户登录
启动流程的具体细节可以看看Linux 的启动流程
第4步加载启动程序其实是两步:
- init进程逐一加载开机启动程序,其实就是运行指定目录里的启动脚本。
- 在运行完指定目录里面的程序后init进程还会去执行/etc/rc.local 这个脚本。
ps:“指定目录”是指在第3步中设置的运行级别对应的目录。
要完成我们的需求,我们使用第4步中的任意一种方式都可以。
方式一,chkconfig
以supervisord服务脚本为例:

#!/bin/sh ## ## /etc/rc.d/init.d/supervisord ## #supervisor is a client/server system that # allows its users to monitor and control a # number of processes on UNIX-like operating # systems. # # chkconfig: - 64 36 # description: Supervisor Server # processname: supervisord # Source init functions . /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions prog="supervisord" prefix="/usr/" exec_prefix="${prefix}" PIDFILE="/var/run/supervisord.pid" CONFIG="/etc/supervisord.conf" prog_bin="${exec_prefix}bin/supervisord -c $CONFIG " function log_success_msg() { echo "$@" "[ OK ]" } function log_failure_msg() { echo "$@" "[ OK ]" } start() { #echo -n $"Starting $prog: " #daemon $prog_bin --pidfile $PIDFILE #[ -f $PIDFILE ] && success $"$prog startup" || failure $"$prog failed" #echo if [ ! -r $CONFIG ]; then log_failure_msg "config file doesn't exist (or you don't have permission to view)" exit 4 fi if [ -e $PIDFILE ]; then PID="$(pgrep -f $PIDFILE)" if test -n "$PID" && kill -0 "$PID" &>/dev/null; then # If the status is SUCCESS then don't need to start again. log_failure_msg "$NAME process is running" exit 0 fi fi log_success_msg "Starting the process" "$prog" daemon $prog_bin --pidfile $PIDFILE log_success_msg "$prog process was started" } stop() { echo -n $"Shutting down $prog: " [ -f $PIDFILE ] && killproc $prog || success $"$prog shutdown" echo } case "$1" in start) start ;; stop) stop ;; status) status $prog ;; restart) stop start ;; *) echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop|restart|status}" ;; esac
第1步:把上面的脚本放在/etc/init.d/文件夹下。
ln -s ./supervisord /etc/init.d/supervisord
第2步:将启动脚本权限改为可执行。
chmod a+x /etc/init.d/supervisord第3步:添加启动项。
chkconfig --add supervisordchkconfig supervisord on第4步:检查是否设置成功。
chkconfig --list | grep supervisord supervisord 0:关闭 1:关闭 2:启用 3:启用 4:启用 5:启用 6:关闭
方式二,修改/etc/rc.local脚本
1 #!/bin/sh 2 # 3 # This script will be executed *after* all the other init scripts. 4 # You can put your own initialization stuff in here if you don't 5 # want to do the full Sys V style init stuff. 6 7 #touch /var/lock/subsys/local 8 echo "hello linux" >> /tmp/hello2.log 9 10 influxd > /tmp/influxd.log 2>&1 & 11 12 echo "hello linux" >> /tmp/hello3.log
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/ouruola863/p/8573374.html
