背景:
笔者最近这几天在思考,为什么要学习设计模式,学些设计模式无非是提高自己的开发技能,但是通过这一段时间来看,其实我也学习了一些设计模式,但是都是一些demo,没有具体的例子,学习起来不深刻,所以我感觉我可能要换一条路走,所以我现在想法是看一些源码的东西,一方面是因为自己大部分的源码其实没有看过,另一方面源码中可能会涉及到一些编码风格和设计模式的东西,我也可以学习。
使用jdk版本:1.7.0_80
先从最简单的开始:
public static void main(String[] args) { Map map = new HashMap(); }
然后走到了这个方法:
/** * Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the default initial capacity * (16) and the default load factor (0.75). */ public HashMap() { this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR); }
这个是什么意思呢?我们看这个方法的注释:构建一个空的HashMap,使用默认的初始空间16和 装载因子0.75
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16 是默认的初始空间
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; 默认的装载因子的大小,
具体这两个是干什么的我们下面再看
/** * Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the specified initial * capacity and load factor. * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity * @param loadFactor the load factor * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative * or the load factor is nonpositive */ public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { //如果初始空间小于0,抛出异常 if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity); //若是初始空间大于1 << 30,1左移30位:1073741824 if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; //这里判断装载因子是否小于0,以及判断是否非值,这里额外说明一下 //Float.isNaN 有几种情况 /** Float f1 =new Float(-1.0/0.0); //-Infinity (负无穷) Float f2 =new Float(0.0/0.0); // Infinity (正无穷) Float f3 =new Float(1.0/0.0); // NAN 只有这种调用isNaN 是true */ if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor); this.loadFactor = loadFactor; //目前设置的值是容器大小的值,后面还有作用 threshold = initialCapacity; //这个init方法在hashMap中为空,但在LinkedHashMap中有重写 init(); }
我看在new的时候,HashMap并没有创建数组和存储,所以我思考可能是在put的时候进行数组的初始化
所以我们来深究以下put方法
/** * 这里是HashMap的put方法,hashMap是由数组和链表组成的 */ public V put(K key, V value) { //如果是空数组的话,就初始化一个 // static final Entry<?,?>[] EMPTY_TABLE = {}; if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) { //从上面那个步骤我们可以知道,threshold=16,这个步骤应该是初始化数组 inflateTable(threshold); } //我们知道hashMap的key是可以存null的,这里应该是对key为null的时候做的逻辑处理 if (key == null) return putForNullKey(value); // ok 那这个方法我们一会再看 int hash = hash(key);//hashMap的hash运算 int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); //hash值与表长度 按位与计算 //根据运算得到的是数组的索引, //下面for循环中的e就是数组中的一个索引,这个索引对应的值是一个链表 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; //如果hash值相同且key值也相等,则只是保存value,然后返回老的值 //如果多个线程对hashMap操作,这里不是线程安全的 if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; //recordAccess hashMap没有操作,LinkedHashMap有重写 e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } // transient int modCount; 默认值为0,记录hashMap结构修改的次数 modCount++; //增加数组中的索引 addEntry(hash, key, value, i); return null; }
然后 继续看put方法中的 inflateTable 方法,它传入的值是设置的默认空间大小 16
/** * Inflates the table. 初始化数组,一开始toSize传入为16 */ private void inflateTable(int toSize) { // Find a power of 2 >= toSize //roundUpToPowerOf2 在下面 int capacity = roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize); //Math.min() 返回这两个数的小的一个 threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1); //初始化数组,注意这里取得是capacity table = new Entry[capacity]; //初始化hash掩码值 initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity); } private static int roundUpToPowerOf2(int number) { // assert number >= 0 : "number must be non-negative"; //判断传入的值是否大于最大值,看到若是number不大于1 直接返回1 return number >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : (number > 1) ? Integer.highestOneBit((number - 1) << 1) : 1; //number - 1 然后左移一位 相当于 (number - 1)*2 } // Integer.highestOneBit 这个是干啥的呢, //传入一个int参数i,返回其二进制最高位1的权值。( //比如说 使用hashMap默认的构建方法,这里传入的是值也就是i是 30 public static int highestOneBit(int i) { // HD, Figure 3-1 i |= (i >> 1);//经过第一步,i成为31 i |= (i >> 2);//还是31 i |= (i >> 4);//还是31 i |= (i >> 8);//还是31 i |= (i >> 16);//还是31 //使用i 无符号右移一位 return i - (i >>> 1); } //笔者尝试使用 System.out.println(Integer.highestOneBit((16-1) <<1)); 发现打印出来还是16 //求a 和 b 的最小值,使用默认构造函数的HashMap这里传入的是12,以及1 << 30 + 1 public static float min(float a, float b) { if (a != a) return a; // a is NaN if ((a == 0.0f) && (b == 0.0f) && (Float.floatToIntBits(b) == negativeZeroFloatBits)) { return b; } return (a <= b) ? a : b; } // 然后构建了16空间的数组 table = new Entry[capacity]; //Entry中包括: final K key; V value; Entry<K,V> next; // 这里应该是传说中的数组中的链表 int hash; //通过每个hash值判断 //然后我们再看下这个在做什么 initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity); /** * Initialize the hashing mask value. We defer initialization until we * really need it. * //翻译:初始化哈希掩码值。我们推迟初始化直到我们真正的需要,传入的参数就是 hashMAP的数组大小, */ final boolean initHashSeedAsNeeded(int capacity) { // 这里默认的hashSeed 为 0 ,currentAltHashing 为false boolean currentAltHashing = hashSeed != 0; //sun.misc.VM.isBooted() 默认为 false 然后debug 出来 结果是 true //useAltHashing 结果是 false boolean useAltHashing = sun.misc.VM.isBooted() && (capacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD); // currentAltHashing 、useAltHashing异或操作,得到结果false boolean switching = currentAltHashing ^ useAltHashing; if (switching) { hashSeed = useAltHashing ? sun.misc.Hashing.randomHashSeed(this) : 0; } return switching; } //到这里,我们可以看到初始化数组已经完成
inflateTable 方法分析完了,然后我们再看下 putForNullKey 方法:这个方法只有当key是null的时候才会进入
/** * Offloaded version of put for null keys */ private V putForNullKey(V value) { //取数组的第一位,若是key为空,则把现在的value放进去,把之前的value返回出来 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) { if (e.key == null) { V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } //modCount 标识 hashMap结构修改的次数 modCount++; //增加数组节点 addEntry(0, null, value, 0); return null; } /** * Adds a new entry with the specified key, value and hash code to * the specified bucket. It is the responsibility of this * method to resize the table if appropriate. * * Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of put method. */ //这里的hash,key,bucketIndex值在hashMap都是写死的,value代表着你传入的value值
//若是putForNullKey则,hash和bucketIndex是0
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { /** The number of key-value mappings contained in this map. transient int size; map的数量 */ //开始的时候这个size是0,然后当size大于(需要扩容的数值),并且当前非空 if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) { //重新扩大数组大小 resize(2 * table.length); hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0; bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length); } //扩建节点 createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex); }
/** //创建 * Like addEntry except that this version is used when creating entries * as part of Map construction or "pseudo-construction" (cloning, * deserialization). This version needn't worry about resizing the table. * * Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of HashMap(Map), * clone, and readObject. */ void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { //数组链表 Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex]; table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e); size++; }
/** * Rehashes the contents of this map into a new array with a * larger capacity. This method is called automatically when the * number of keys in this map reaches its threshold. * * If current capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY, this method does not * resize the map, but sets threshold to Integer.MAX_VALUE. * This has the effect of preventing future calls. * * @param newCapacity the new capacity, MUST be a power of two; * must be greater than current capacity unless current * capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY (in which case value * is irrelevant). */ //这个方法很重要 void resize(int newCapacity) { Entry[] oldTable = table; int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; //若是数组的大小是最大值,则不处理 if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return; } //新的数组 Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity]; //防止新的数组节点 transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity)); table = newTable;//覆盖老的数组 threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);// 空间大小*0.75 }
好了,大概hashMap就说到这里吧,要是继续说的话,我自己也不太清楚了,稍微看了下remove方法,里面主要调用了removeEntryForKey方法,且里面没有对数组大小的改变,也就是这个数组只是增加的
下面是一张类图,作为参考
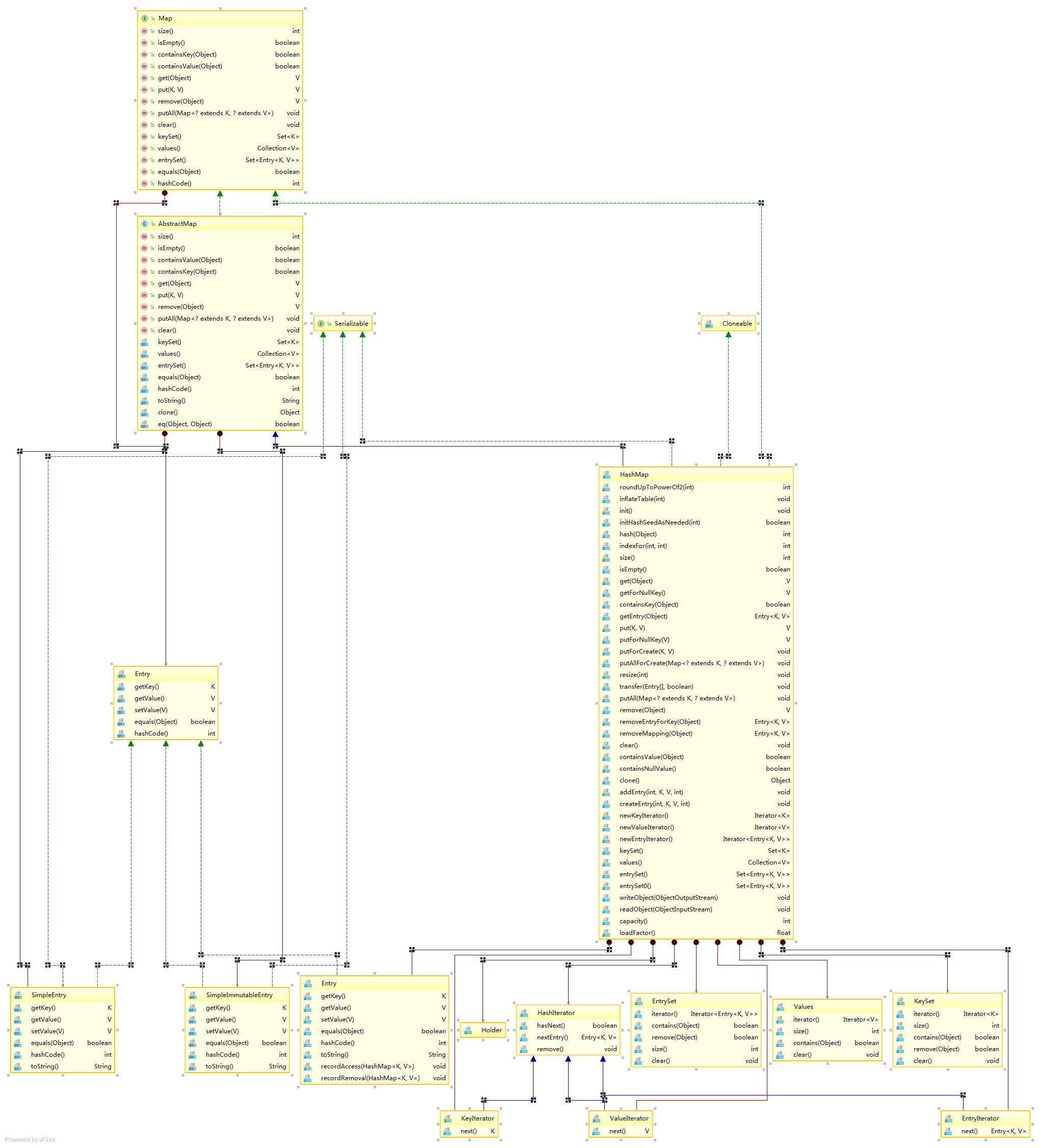
先到这里了,感觉没有整体上的了解,希望以后更加努力!