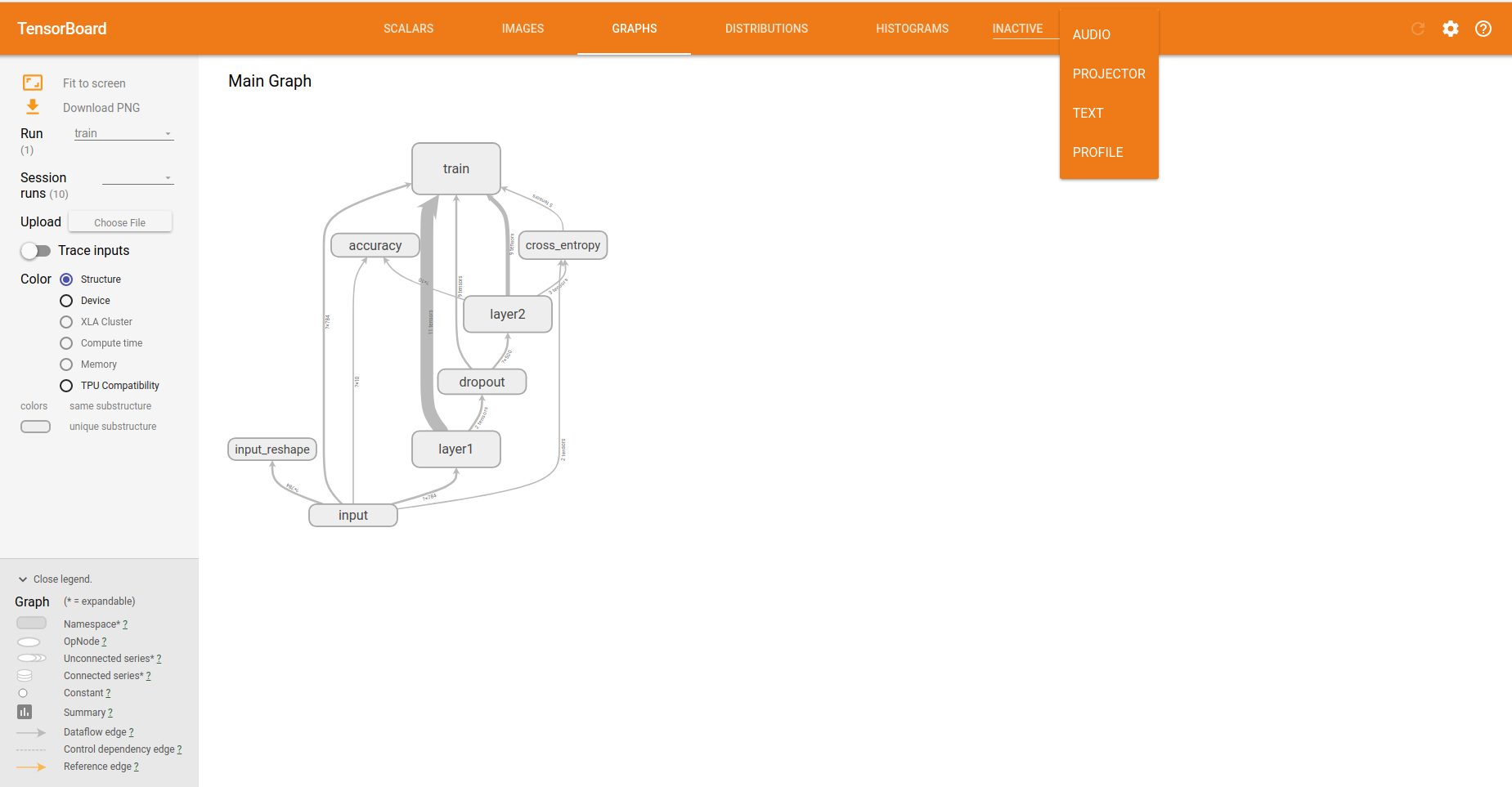
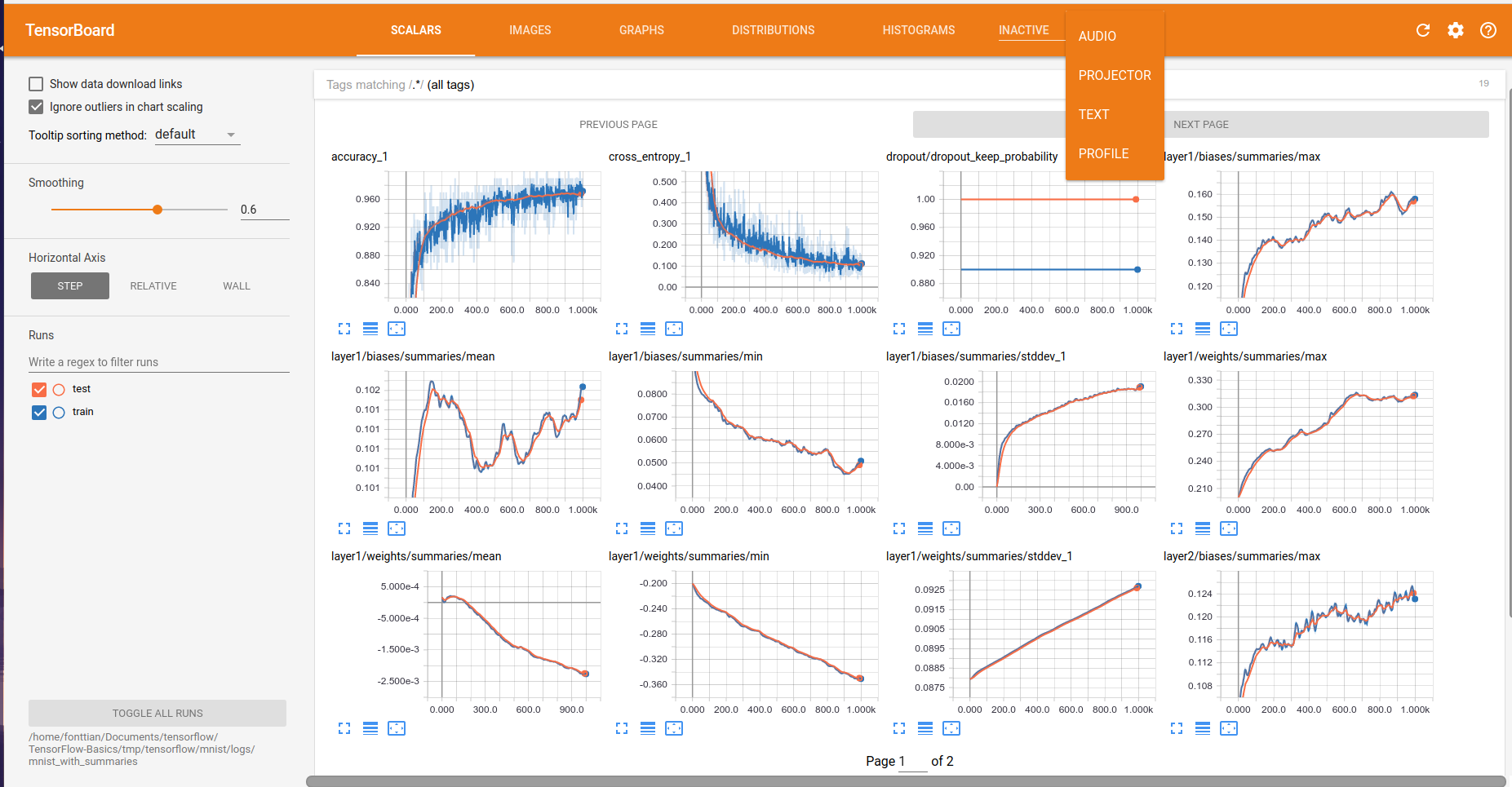
tensorboard tensorflow中的可视化组件
在新版本的tensorflow 中tensorboard已经被整合,无需下载.其执行是利用了一个封装的内置服务器,性能不错.
我们可以将神经网络运行时的各类数据存储下来进行可视化展示,我首先展示其功能,然后再分解代码.本处例子源自tensorflow的官方源码,如果你需要了解更多,建议直接阅读官方文档
展示
最重要的网络结构的展示
基本数据的展示
在本例子中获取了,mean,stddev,max,min等数据.其他部分还包括images,图片本例子中展示的则是,mnist的展示图.
更多部分建议你运行源码自己体验一下
CODE
- tf.summary使我们需要的 用来想tensorboard写入数据的方法
- tf.summary.scalar(‘accuracy’, accuracy) 如代码,scalar可以将数据传入,并在tensorboard中最终以表格的形式展示
- tf.summary.image(‘input’, image_shaped_input, NUM_CLASSES) image方法则是前面图片中image模块的数据传入方法
引用,定义基本参数
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import argparse
import os
import sys
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
FLAGS = None
# The MNIST dataset has 10 classes, representing the digits 0 through 9.
NUM_CLASSES = 10
# The MNIST images are always 28x28 pixels.
IMAGE_SIZE = 28
IMAGE_PIXELS = IMAGE_SIZE * IMAGE_SIZE官方文档的代码写的咋一看非常复杂,不过结构上并不复杂.
读取数据,定义定义可视化节点
# Import data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("/home/fonttian/Data/MNIST_data/",
one_hot=True,
fake_data=FLAGS.fake_data)
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
# Create a multilayer model.
# Input placeholders
with tf.name_scope('input'): # 此处定义了input可视化节点,下面则是占位符的声明,在tensorflow中的函数一个共有的name,就是声明的节点的name(名字),该部分可以在上面的图片中展示
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, IMAGE_PIXELS], name='x-input')
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, NUM_CLASSES], name='y-input')
with tf.name_scope('input_reshape'):
image_shaped_input = tf.reshape(x, [-1, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, 1])
tf.summary.image('input', image_shaped_input, NUM_CLASSES)
# tf.summary 是将数据传入tensorboard的,image将会展示在我们刚刚展示的images部分.
``` 抽取代码部分内容,封装为函数
<div class="se-preview-section-delimiter"></div>
# We can't initialize these variables to 0 - the network will get stuck.
def weight_variable(shape):
"""Create a weight variable with appropriate initialization."""
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def bias_variable(shape):
"""Create a bias variable with appropriate initialization."""
initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial)
“`
# We can't initialize these variables to 0 - the network will get stuck.
def weight_variable(shape):
"""Create a weight variable with appropriate initialization."""
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def bias_variable(shape):
"""Create a bias variable with appropriate initialization."""
initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def variable_summaries(var):
"""Attach a lot of summaries to a Tensor (for TensorBoard visualization)."""
with tf.name_scope('summaries'):
mean = tf.reduce_mean(var)
tf.summary.scalar('mean', mean)
with tf.name_scope('stddev'):
stddev = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(var - mean)))
tf.summary.scalar('stddev', stddev)
tf.summary.scalar('max', tf.reduce_max(var))
tf.summary.scalar('min', tf.reduce_min(var))
tf.summary.histogram('histogram', var)
def feed_dict(train):# 需要feed_dict参数
"""Make a TensorFlow feed_dict: maps data onto Tensor placeholders."""
if train or FLAGS.fake_data:
xs, ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100, fake_data=FLAGS.fake_data)
k = FLAGS.dropout
else:
xs, ys = mnist.test.images, mnist.test.labels
k = 1.0
return {x: xs, y_: ys, keep_prob: k}定义我们的神经网络
def nn_layer(input_tensor, input_dim, output_dim, layer_name, act=tf.nn.relu):
"""Reusable code for making a simple neural net layer.
It does a matrix multiply, bias add, and then uses ReLU to nonlinearize.
It also sets up name scoping so that the resultant graph is easy to read,
and adds a number of summary ops.
"""
# Adding a name scope ensures logical grouping of the layers in the graph.
with tf.name_scope(layer_name):
# This Variable will hold the state of the weights for the layer
with tf.name_scope('weights'):
weights = weight_variable([input_dim, output_dim])
variable_summaries(weights)
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
biases = bias_variable([output_dim])
variable_summaries(biases)
with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'):
preactivate = tf.matmul(input_tensor, weights) + biases
tf.summary.histogram('pre_activations', preactivate)
activations = act(preactivate, name='activation')
tf.summary.histogram('activations', activations)
return activations
hidden1 = nn_layer(x, IMAGE_PIXELS, FLAGS.hidden1_units, 'layer1')
with tf.name_scope('dropout'): # 定义dropout的可视化节点,dropout避免过拟合的方法
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
tf.summary.scalar('dropout_keep_probability', keep_prob)
dropped = tf.nn.dropout(hidden1, keep_prob)
# Do not apply softmax activation yet, see below.
y = nn_layer(dropped, FLAGS.hidden1_units, NUM_CLASSES, 'layer2', act=tf.identity)定义损失函数和优化算法,准确率
with tf.name_scope('cross_entropy'):
# The raw formulation of cross-entropy,
#
# tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(tf.softmax(y)),
# reduction_indices=[1]))
#
# can be numerically unstable.
#
# So here we use tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits on the
# raw outputs of the nn_layer above, and then average across
# the batch.
diff = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_, logits=y)
with tf.name_scope('total'):
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(diff)
tf.summary.scalar('cross_entropy', cross_entropy)
with tf.name_scope('train'):
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(FLAGS.learning_rate).minimize(
cross_entropy)
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
with tf.name_scope('correct_prediction'):
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
tf.summary.scalar('accuracy', accuracy)写入数据
# Merge all the summaries and write them out to
# /tmp/tensorflow/mnist/logs/mnist_with_summaries (by default)
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
train_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(FLAGS.log_dir + '/train', sess.graph)
test_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(FLAGS.log_dir + '/test')
tf.global_variables_initializer().run()回话设计
for i in range(FLAGS.max_steps):
if i % 10 == 0: # Record summaries and test-set accuracy
summary, acc = sess.run([merged, accuracy], feed_dict=feed_dict(False))
test_writer.add_summary(summary, i)
print('Accuracy at step %s: %s' % (i, acc))
else: # Record train set summaries, and train
if i % 100 == 99: # Record execution stats
run_options = tf.RunOptions(trace_level=tf.RunOptions.FULL_TRACE)
run_metadata = tf.RunMetadata()
summary, _ = sess.run([merged, train_step],
feed_dict=feed_dict(True),
options=run_options,
run_metadata=run_metadata)
train_writer.add_run_metadata(run_metadata, 'step%03d' % i)
train_writer.add_summary(summary, i)
print('Adding run metadata for', i)
else: # Record a summary
summary, _ = sess.run([merged, train_step], feed_dict=feed_dict(True))
train_writer.add_summary(summary, i)
# 停止writer
train_writer.close()
test_writer.close()执行CODE
def main(_):
if tf.gfile.Exists(FLAGS.log_dir):
tf.gfile.DeleteRecursively(FLAGS.log_dir)
tf.gfile.MakeDirs(FLAGS.log_dir)
train()
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--fake_data', nargs='?', const=True, type=bool,
default=False,
help='If true, uses fake data for unit testing.')
parser.add_argument('--max_steps', type=int, default=1000,
help='Number of steps to run trainer.')
parser.add_argument('--hidden1_units', type=float, default=500,
help='The number of neurons in the first hidden.')
parser.add_argument('--learning_rate', type=float, default=0.001,
help='Initial learning rate')
parser.add_argument('--dropout', type=float, default=0.9,
help='Keep probability for training dropout.')
parser.add_argument(
'--data_dir',
type=str,
default='/home/fonttian/Data/MNIST_data/',
help='Directory for storing input data')
parser.add_argument(
'--log_dir',
type=str,
default='/home/fonttian/Documents/tensorflow/TensorFlow-Basics/tmp/tensorflow/mnist/logs/mnist_with_summaries',
help='Summaries log directory')
FLAGS, unparsed = parser.parse_known_args()
tf.app.run(main=main, argv=[sys.argv[0]] + unparsed)
tensorboard的运行
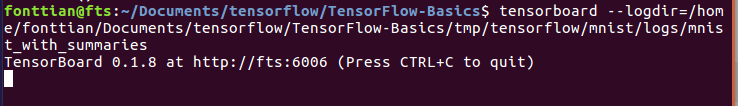
建议你运行该代码,进行更深入的尝试,