memcache 是一个分布式的缓存系统,但是本身没有提供集群功能,在大型应用的情况下容易成为瓶颈。但是客户端这个时候可以自由扩展,分两阶段实现。第一阶段:key 要先根据一定的算法映射到一台memcache服务器。第二阶段从服务器中取出缓存的值。但是有一个问题,比如其中一台服务器挂了,或者需要增加一台服务 的时候,这个时候第一阶段的算法就很重要了,怎样使得原来的数据尽可能的继续有效,减少扩展节点或缩减节点带来的冲击。下面列出想到一些解决方法:
一:hash一致性算法:
优点:
当一个节点失效的时候,其他节点的数据不会受到破坏,这个节点的数据会被分流到另外一个节点。当增加一个节点时,只会对一个节点的一分部数据有影响。
缺点:
极容易造成节点间数据量的不平衡,可能一个节点上热点非常多,一个节点上热点很少。
下面是具体介绍:(转自:http://blog.csdn.net/sparkliang/archive/2010/02/02/5279393.aspx)
consistent hashing 算法早在 1997 年就在论文 Consistent hashing and random trees 中被提出,目前在 cache 系统中应用越来越广泛;
1 基本场景
比如你有 N 个 cache 服务器(后面简称 cache ),那么如何将一个对象 object 映射到 N 个 cache 上呢,你很可能会采用类似下面的通用方法计算 object 的 hash 值,然后均匀的映射到到 N 个 cache ;
hash(object)%N
一切都运行正常,再考虑如下的两种情况;
1 一个 cache 服务器 m down 掉了(在实际应用中必须要考虑这种情况),这样所有映射到 cache m 的对象都会失效,怎么办,需要把 cache m 从 cache 中移除,这时候 cache 是 N-1 台,映射公式变成了 hash(object)%(N-1) ;
2 由于访问加重,需要添加 cache ,这时候 cache 是 N+1 台,映射公式变成了 hash(object)%(N+1) ;
1 和 2 意味着什么?这意味着突然之间几乎所有的 cache 都失效了。对于服务器而言,这是一场灾难,洪水般的访问都会直接冲向后台服务器;
再来考虑第三个问题,由于硬件能力越来越强,你可能想让后面添加的节点多做点活,显然上面的 hash 算法也做不到。
有什么方法可以改变这个状况呢,这就是 consistent hashing...
2 hash 算法和单调性
Hash 算法的一个衡量指标是单调性( Monotonicity ),定义如下:
单调性是指如果已经有一些内容通过哈希分派到了相应的缓冲中,又有新的缓冲加入到系统中。哈希的结果应能够保证原有已分配的内容可以被映射到新的缓冲中去,而不会被映射到旧的缓冲集合中的其他缓冲区。
容易看到,上面的简单 hash 算法 hash(object)%N 难以满足单调性要求。
3 consistent hashing 算法的原理
consistent hashing 是一种 hash 算法,简单的说,在移除 / 添加一个 cache 时,它能够尽可能小的改变已存在 key 映射关系,尽可能的满足单调性的要求。
下面就来按照 5 个步骤简单讲讲 consistent hashing 算法的基本原理。
3.1 环形hash 空间
考虑通常的 hash 算法都是将 value 映射到一个 32 为的 key 值,也即是 0~2^32-1 次方的数值空间;我们可以将这个空间想象成一个首( 0)尾( 2^32-1 )相接的圆环,如下面图 1 所示的那样。
图 1 环形 hash 空间
3.2 把对象映射到hash 空间
接下来考虑 4 个对象 object1~object4 ,通过 hash 函数计算出的 hash 值 key 在环上的分布如图 2 所示。
hash(object1) = key1;
… …
hash(object4) = key4;
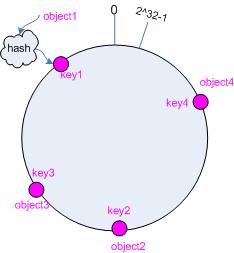
图 2 4 个对象的 key 值分布
3.3 把cache 映射到hash 空间
Consistent hashing 的基本思想就是将对象和 cache 都映射到同一个 hash 数值空间中,并且使用相同的 hash 算法。
假设当前有 A,B 和 C 共 3 台 cache ,那么其映射结果将如图 3 所示,他们在 hash 空间中,以对应的 hash 值排列。
hash(cache A) = key A;
… …
hash(cache C) = key C;
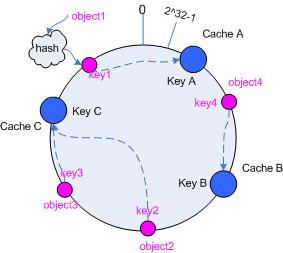
图 3 cache 和对象的 key 值分布
说到这里,顺便提一下 cache 的 hash 计算,一般的方法可以使用 cache 机器的 IP 地址或者机器名作为 hash 输入。
3.4 把对象映射到cache
现在 cache 和对象都已经通过同一个 hash 算法映射到 hash 数值空间中了,接下来要考虑的就是如何将对象映射到 cache 上面了。
在这个环形空间中,如果沿着顺时针方向从对象的 key 值出发,直到遇见一个 cache ,那么就将该对象存储在这个 cache 上,因为对象和 cache 的 hash 值是固定的,因此这个 cache 必然是唯一和确定的。这样不就找到了对象和 cache 的映射方法了吗?!
依然继续上面的例子(参见图 3 ),那么根据上面的方法,对象 object1 将被存储到 cache A 上; object2 和 object3 对应到 cache C ; object4 对应到 cache B ;
3.5 考察cache 的变动
前面讲过,通过 hash 然后求余的方法带来的最大问题就在于不能满足单调性,当 cache 有所变动时, cache 会失效,进而对后台服务器造成巨大的冲击,现在就来分析分析 consistent hashing 算法。
3.5.1 移除 cache
考虑假设 cache B 挂掉了,根据上面讲到的映射方法,这时受影响的将仅是那些沿 cache B 逆时针遍历直到下一个 cache ( cache C )之间的对象,也即是本来映射到 cache B 上的那些对象。
因此这里仅需要变动对象 object4 ,将其重新映射到 cache C 上即可;参见图 4 。
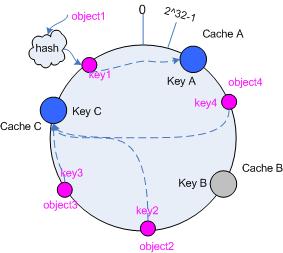
图 4 Cache B 被移除后的 cache 映射
3.5.2 添加 cache
再考虑添加一台新的 cache D 的情况,假设在这个环形 hash 空间中, cache D 被映射在对象 object2 和 object3 之间。这时受影响的将仅是那些沿 cache D 逆时针遍历直到下一个 cache ( cache B )之间的对象(它们是也本来映射到 cache C 上对象的一部分),将这些对象重新映射到 cache D 上即可。
因此这里仅需要变动对象 object2 ,将其重新映射到 cache D 上;参见图 5 。
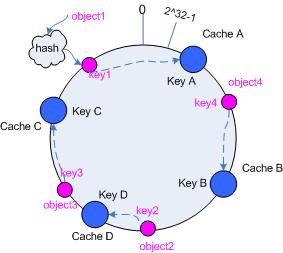
图 5 添加 cache D 后的映射关系
4 虚拟节点
考量 Hash 算法的另一个指标是平衡性 (Balance) ,定义如下:
平衡性
平衡性是指哈希的结果能够尽可能分布到所有的缓冲中去,这样可以使得所有的缓冲空间都得到利用。
hash 算法并不是保证绝对的平衡,如果 cache 较少的话,对象并不能被均匀的映射到 cache 上,比如在上面的例子中,仅部署 cache A 和 cache C 的情况下,在 4 个对象中, cache A 仅存储了 object1 ,而 cache C 则存储了 object2 、 object3 和 object4 ;分布是很不均衡的。
为了解决这种情况, consistent hashing 引入了“虚拟节点”的概念,它可以如下定义:
“虚拟节点”( virtual node )是实际节点在 hash 空间的复制品( replica ),一实际个节点对应了若干个“虚拟节点”,这个对应个数也成为“复制个数”,“虚拟节点”在 hash 空间中以 hash 值排列。
仍以仅部署 cache A 和 cache C 的情况为例,在图 4 中我们已经看到, cache 分布并不均匀。现在我们引入虚拟节点,并设置“复制个数”为 2 ,这就意味着一共会存在 4 个“虚拟节点”, cache A1, cache A2 代表了 cache A ; cache C1, cache C2 代表了 cache C ;假设一种比较理想的情况,参见图 6 。
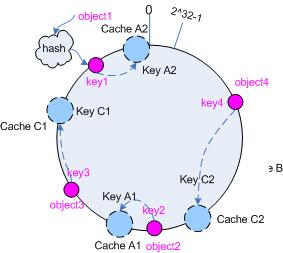
图 6 引入“虚拟节点”后的映射关系
此时,对象到“虚拟节点”的映射关系为:
objec1->cache A2 ; objec2->cache A1 ; objec3->cache C1 ; objec4->cache C2 ;
因此对象 object1 和 object2 都被映射到了 cache A 上,而 object3 和 object4 映射到了 cache C 上;平衡性有了很大提高。
引入“虚拟节点”后,映射关系就从 { 对象 -> 节点 } 转换到了 { 对象 -> 虚拟节点 } 。查询物体所在 cache 时的映射关系如图 7 所示。
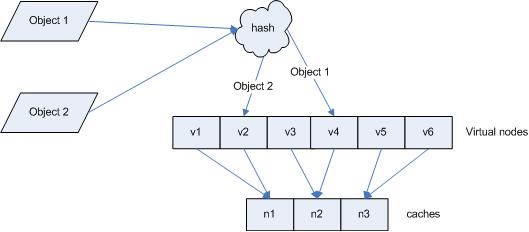
图 7 查询对象所在 cache
“虚拟节点”的 hash 计算可以采用对应节点的 IP 地址加数字后缀的方式。例如假设 cache A 的 IP 地址为 202.168.14.241 。
引入“虚拟节点”前,计算 cache A 的 hash 值:
Hash(“202.168.14.241”);
引入“虚拟节点”后,计算“虚拟节”点 cache A1 和 cache A2 的 hash 值:
Hash(“202.168.14.241#1”); // cache A1
Hash(“202.168.14.241#2”); // cache A2
5 小结
Consistent hashing 的基本原理就是这些,具体的分布性等理论分析应该是很复杂的,不过一般也用不到。
http://weblogs.java.net/blog/2007/11/27/consistent-hashing 上面有一个 java 版本的例子,可以参考。
http://blog.csdn.net/mayongzhan/archive/2009/06/25/4298834.aspx 转载了一个 PHP 版的实现代码。
http://www.codeproject.com/KB/recipes/lib-conhash.aspx C语言版本
一些参考资料地址:
http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=258660
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Consistent_hashing
http://www.spiteful.com/2008/03/17/programmers-toolbox-part-3-consistent-hashing/
http://weblogs.java.net/blog/2007/11/27/consistent-hashing
http://tech.idv2.com/2008/07/24/memcached-004/
http://blog.csdn.net/mayongzhan/archive/2009/06/25/4298834.aspx
此文章转载于:
http://www.open-open.com/lib/view/open1340337319596.html
php对一致性hash分布不均,使用虚拟节点,看了http://bbs.phpchina.com/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=233897这个之后,自己对查找算法进行了修改:
<?php
class memcacheHashMap{
private $_node = array();
private $_nodeData = array();
private $_keyNode = 0;
private $_memcache = null;
// 每个物理服务器生成虚拟节点的个数
private $_virtualNodeNum = 200;
private function __construct(){
// 配置文件
$config = array(
"127.0.0.1:11211",
"127.0.0.1:11212",
"127.0.0.1:11213",
"127.0.0.1:11214",
"127.0.0.1:11215"
);
if (!$config){
throw new Exception("cache config null");
}
// 设置虚拟节点
foreach($config as $key=>$value){
for ($i = 0; $i < $this->_virtualNodeNum; $i++){
$this->_node[sprintf("%u", crc32($value."#".$i))] = $value."#".$i;
}
}
// 排序
ksort($this->_node);
// print_r($this->_node);
}
// 单例模式
static public function getInstance(){
static $memcacheObj = null;
if (!is_object($memcacheObj)) {
$memcacheObj = new self();
}
return $memcacheObj;
}
private function _connectMemcache($key){
$this->_nodeData = array_keys($this->_node);
// echo "all node:\n";
// print_r($this->_nodeData);
$this->_keyNode = sprintf("%u", crc32($key));
// $this->_keyNode = 1803717635;
// var_dump($this->_keyNode);
// 获取key值对应的最近的节点
$nodeKey = $this->_findServerNode(0, count($this->_nodeData)-1);
// var_dump($nodeKey);
// echo "$this->_keyNode :search node:$nodeKey IP:{$this->_node[$nodeKey]}\n";
//获取对应的真实ip
list($config, $num) = explode("#", $this->_node[$nodeKey]);
if (empty($config)){
throw new Exception("serach ip config error");
}
if (!isset($this->_memcache[$config])){
$this->_memcache[$config] = new Memcache;
list($host, $port) = explode(":", $config);
$this->_memcache[$config]->connect($host, $port);
}
return $this->_memcache[$config];
}
/**
* 采用二分法从虚拟memcache节点中查找最近的节点
* @param int $low 开始位置
* @param int $high 结束位置
*
*/
private function _findServerNode($low, $high){
// 开始下标小于结束下标
if ($low < $high){
$avg = intval(($low+$high)/2);
if ($this->_nodeData[$avg] == $this->_keyNode){
return $this->_nodeData[$avg];
}elseif ($this->_keyNode < $this->_nodeData[$avg]){
return $this->_findServerNode($low, $avg-1);
}else{
return $this->_findServerNode($avg+1, $high);
}
}else if(($low == $high)){
// 大于平均值
if ($low ==0 || $low == count($this->_nodeData)-1){
return $this->_nodeData[$low];
}
// var_dump($low);
if ($this->_nodeData[$low] < $this->_keyNode){
if (abs($this->_nodeData[$low] - $this->_keyNode) < abs($this->_nodeData[$low+1]-$this->_keyNode)){
return $this->_nodeData[$low];
}else{
return $this->_nodeData[$low+1];
}
}else {
if (abs($this->_nodeData[$low] - $this->_keyNode) < abs($this->_nodeData[$low-1]-$this->_keyNode)){
return $this->_nodeData[$low];
}else{
return $this->_nodeData[$low-1];
}
}
}else{
if ( ($low == 0)&&($high < 0) ){
return $this->_nodeData[$low];
}
if (abs($this->_nodeData[$low] - $this->_keyNode) < abs($this->_nodeData[$high]-$this->_keyNode)){
return $this->_nodeData[$low];
}else{
return $this->_nodeData[$high];
}
}
}
public function set($key, $value, $expire=0){
// var_dump($key);
return $this->_connectMemcache($key)->set($key, json_encode($value), 0, $expire);
}
public function add($key, $vakue, $expire=0){
return $this->_connectMemcache($key)->add($key, json_encode($value), 0, $expire);
}
public function get($key){
return $this->_connectMemcache($key)->get($key, true);
}
public function delete($key){
return $this->_connectMemcache($key)->delete($key);
}
}
$runData['BEGIN_TIME'] = microtime(true);
//测试一万次set加get
for($i=0;$i<10000;$i++) {
$key = md5(mt_rand());
// var_dump($key);
$b = memcacheHashMap::getInstance()->set($key, time(), 10);
}
echo "一致性hash:";
var_dump(number_format(microtime(true) - $runData['BEGIN_TIME'],6));
$runData['BEGIN_TIME'] = microtime(true);
$m= new Memcache;
$m->connect('127.0.0.1', 11211);
for($i=0;$i<10000;$i++) {
$key = md5(mt_rand());
$b = $m->set($key, time(), 0, 10);
}
echo "单台机器:";
var_dump(number_format(microtime(true) - $runData['BEGIN_TIME'],6)); 测试结果:
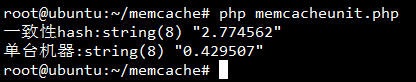
根据http://blog.csdn.net/mayongzhan/article/details/4298834进行了修改与测试
下边查找真实节点的原理是:将虚拟后的节点排序,返回第一个比key哈希后大的节点,若不存在则返回第一个
<?php
/**
* 一致性hahs实现类
*
*/
class FlexiHash{
/**
* var int
* 虚拟节点
*/
private $_replicas = 200;
/**
* 使用hash方法
*/
private $_hasher = null;
/**
* 真实节点计数器
*
*/
private $_tagertCount = 0;
/**
* 位置对应节点,用户lookup中根据位置确定要访问的节点
*/
private $_positionToTarget = array();
/**
* 节点对应位置,用于删除节点
*/
private $_targetToPositions = array();
/**
* 是否已排序
*/
private $_positionToTargetSorted = false;
/**
* @ $hasher hash方法
* @ $replicas 虚拟节点的个数
*
* 确定要使用的hash方法和虚拟的节点数,虚拟节点越多,分布越均匀,但程序的分布式运算越慢
*/
public function __construct(FlexiHash_Hasher $hasher=null, $replicas = null){
// hash方法
$this->_hasher = $hasher?$hasher: new FlexiHash_Crc32Hasher();
// 虚拟节点的个数
if (!empty($replicas)){
$this->_replicas = $replicas;
}
}
/**
* 增加节点,根据虚拟节点数,把节点分布到更多的虚拟位置上
*/
public function addTarget($target){
if (isset($this->_targetToPositions[$target])) {
throw new FlexiHash_Exception("Target $target already exists.");
}
$this->_targetToPositions[$target] = array();
for ($i = 0; $i < $this->_replicas; $i++) {
// 根据规定的方法hash
$position = $this->_hasher->hash($target.$i);
// 虚拟节点对应的真实的节点
$this->_positionToTarget[$position] = $target;
// 真实节点包含的虚拟节点
$this->_targetToPositions[$target][] = $position;
}
$this->_positionToTargetSorted = false;
// 真实节点个数
$this->_targetCount++;
return $this;
}
/**
* 添加多个节点
*
*/
public function addTargets($targets){
foreach ($targets as $target){
$this->addTarget($target);
}
return $this;
}
/**
* 移除某个节点
*
*/
public function removeTarget($target){
if (!isset($this->_targetToPositions[$target])){
throw new FlexiHash_Exception("target $target does not exist\n");
}
foreach($this->_targetToPositions[$target] as $position){
unset($this->_positionToTarget[$position]);
}
unset($this->_targetToPositions[$target]);
$this->_targetCount--;
return $this;
}
/**
* 获取所有节点
*
*/
public function getAllTargets(){
return array_keys($this->_targetToPositions);
}
/**
* 根据key查找hash到的真实节点
*
*/
public function lookup($resource){
$targets = $this->lookupList($resource, 1);
if (empty($targets)){
throw new FlexiHash_Exception("no targets exist");
}
return $targets[0];
}
/**
* 查找资源存在的节点
*
* 描述:根据要求的数量,返回与$resource哈希后数值相等或比其大并且是最小的数值对应的节点,若不存在或数量不够,则从虚拟节点排序后的前一个或多个
*/
public function lookupList($resource, $requestedCount){
if (!$requestedCount) {
throw new FlexiHash_Exception('Invalid count requested');
}
if (empty($this->_positionToTarget)) {
return array();
}
// 直接节点只有一个的时候
if ($this->_targetCount == 1 ){
return array_unique(array_values($this->_positionToTarget));
}
// 获取当前key进行hash后的值
$resourcePosition = $this->_hasher->hash($resource);
$results = array();
$collect = false;
$this->_sortPositionTargets();
// 查找与$resourcePosition 相等或比其大并且是最小的数
foreach($this->_positionToTarget as $key => $value){
if (!$collect && $key > $resourcePosition){
$collect = true;
}
if ($collect && !in_array($value, $results)){
$results[] = $value;
}
// 找到$requestedCount 或个数与真实节点数量相同
if (count($results) == $requestedCount || count($results) == $this->_targetCount){
return $results;
}
}
// 如数量不够或者未查到,则从第一个开始,将$results中不存在前$requestedCount-count($results),设置为需要的节点
foreach ($this->_positionToTarget as $key => $value){
if (!in_array($value, $results)){
$results[] = $value;
}
if (count($results) == $requestedCount || count($results) == $this->_targetCount){
return $results;
}
}
return $results;
}
/**
* 根据虚拟节点进行排序
*/
private function _sortPositionTargets(){
if (!$this->_positionToTargetSorted){
ksort($this->_positionToTarget, SORT_REGULAR);
$this->_positionToTargetSorted = true;
}
}
}// end class
/**
* hash方式
*/
interface FlexiHash_Hasher{
public function hash($string);
}
class FlexiHash_Crc32Hasher implements FlexiHash_Hasher{
public function hash($string){
return sprintf("%u",crc32($string));
}
}
class FlexiHash_Md5Hasher implements FlexiHash_Hasher{
public function hash($string){
return substr(md5($string), 0, 8);
}
}
class FlexiHash_Exception extends Exception{
}
$runData['BEGIN_TIME'] = microtime(true);
for($i=0;$i<10000;$i++) {
$targetsArray = array(
"127.0.0.1:11211",
"127.0.0.1:11212",
"127.0.0.1:11213",
"127.0.0.1:11214",
"127.0.0.1:11215"
);
$flexiHashObj = new FlexiHash(new FlexiHash_Crc32Hasher(),1);
$result = $flexiHashObj->addTargets($targetsArray);
$key = md5(mt_rand());
$targets = $flexiHashObj->lookup($key);
// var_dump($targets);
}
echo "一致性hash:";
var_dump(number_format(microtime(true) - $runData['BEGIN_TIME'],6));
$runData['BEGIN_TIME'] = microtime(true);
$m= new Memcache;
$m->connect('127.0.0.1', 11211);
for($i=0;$i<10000;$i++) {
$key = md5(mt_rand());
$b = $m->set($key, time(), 0, 10);
}
echo "单台机器:";
var_dump(number_format(microtime(true) - $runData['BEGIN_TIME'],6));
?>
测试结果:
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/xinguan1267/article/details/7870308