MyBatis从入门到放弃七:二级缓存原理分析
前言
说起mybatis的一级缓存和二级缓存我特意问了几个身边的朋友他们平时会不会用,结果没有一个人平时业务场景中用。 好吧,那我暂且用来学习源码吧。一级缓存我个人认为也确实有些鸡肋,mybatis默认开启一级缓存,支持在同一个会话(sqlsession)同一个statement执行两次,则第二次会默认会使用第一次创建的缓存对象。
二级缓存前一篇粗略介绍了下,默认使用内存对象【PerpetualCache】内部维护一个HashMap对象来存储。
MyBatis缓存设计及二级缓存工作模式
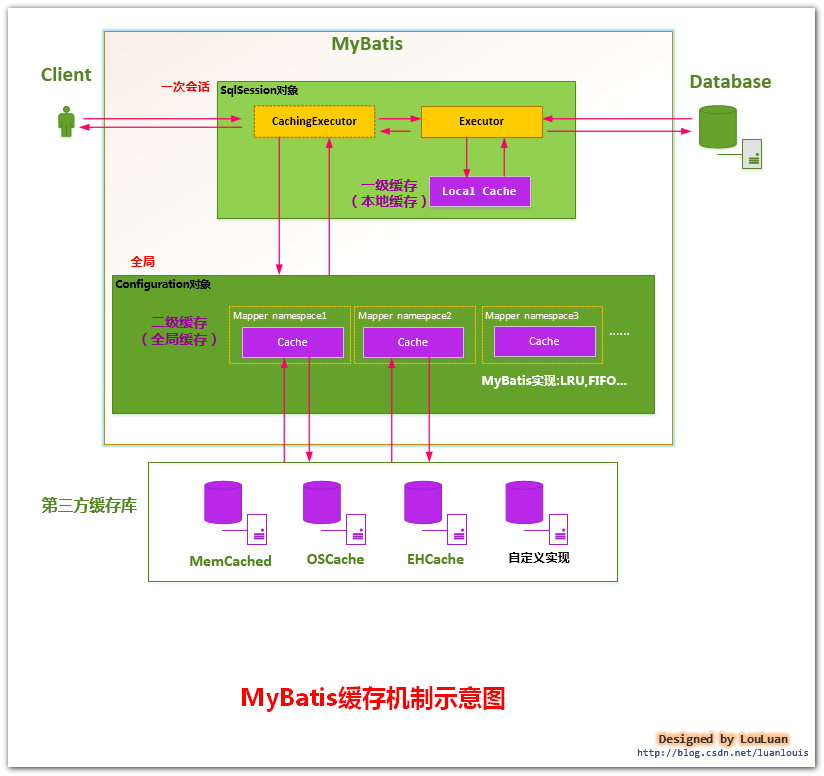
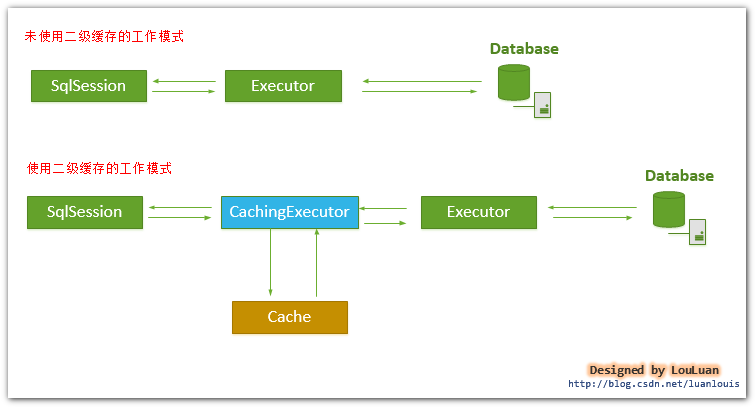
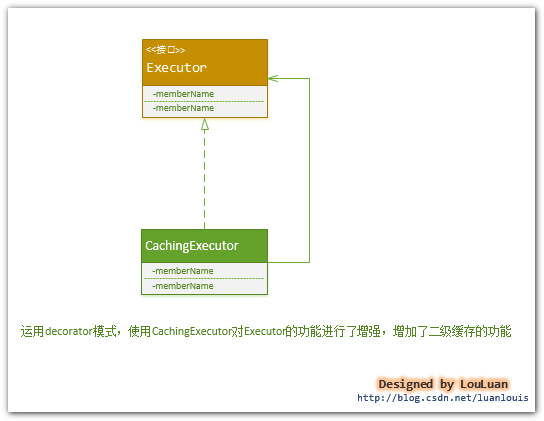
从上面三张图中我们得出结论,一级缓存是sqlsession级别、二级缓存是Mapper级别。mybatis定义了【Cache】接口,支持自定义缓存,同时还支持集成第三方缓存库,现在为了更细粒度的控制缓存,更多的集成【ehcache】、【redis】。
那么mybatis的二级缓存主要是在Executor对象上来做文章,当mybatis发现你在mybatis.xml配置文件中设置了cacheEnabled=true时,mybatis在创建sqlsession时创建Executor对象,同时会对Executor加上装饰者【CacheExecutor】。CacheExecutor对于查询请求,会判断application级别的二级缓存是否有缓存结果,如果有查询结果则直接返回,如果没有再交给查询器Executor实现类,也就是【SimpleExecutor】来执行查询。再就是缓存结果,返回给用户。
贴出SmpleExecutor源码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
|
/** * Copyright 2009-2016 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */package org.apache.ibatis.executor;import org.apache.ibatis.cursor.Cursor;import org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.StatementHandler;import org.apache.ibatis.logging.Log;import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.BoundSql;import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement;import org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration;import org.apache.ibatis.session.ResultHandler;import org.apache.ibatis.session.RowBounds;import org.apache.ibatis.transaction.Transaction;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.SQLException;import java.sql.Statement;import java.util.Collections;import java.util.List;/** * @author Clinton Begin */public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor { public SimpleExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) { super(configuration, transaction); } @Override public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null); stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); return handler.update(stmt); } finally { closeStatement(stmt); } } @Override public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler); } finally { closeStatement(stmt); } } @Override protected <E> Cursor<E> doQueryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, null, boundSql); Statement stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); return handler.<E>queryCursor(stmt); } @Override public List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) throws SQLException { return Collections.emptyList(); } private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException { Statement stmt; Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog); stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout()); handler.parameterize(stmt); return stmt; }} |
那么,缓存起来的数据怎么过期呢,这也是我这篇文章重点关心的。一般流量不大的站点,数据由后台维护,使用二级缓存足够了。先来看全局配置文件,配置只关心一点:cacheEnabled=true。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<settings>
<!--开启二级缓存-->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias alias="User" type="com.autohome.model.User" />
</typeAliases>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper/UserMapper.xml" />
</mappers>
</configuration>
Mapper.xml
这里配置Cache对象。这里的eviction参数提到几个算法策略:
LRU:(Least Recently Used),最近最少使用算法,即如果缓存中容量已经满了,会将缓存中最近做少被使用的缓存记录清除掉,然后添加新的记录;
FIFO:(First in first out),先进先出算法,如果缓存中的容量已经满了,那么会将最先进入缓存中的数据清除掉;
Scheduled:指定时间间隔清空算法,该算法会以指定的某一个时间间隔将Cache缓存中的数据清空;
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--命名空间和接口保持一致-->
<mapper namespace="com.autohome.dao.UserMapper">
<!--
eviction LRU
flushInterval缓存时间,以毫秒为单位
size缓存大小
readOnly如果为false的话,缓存对象必须是可序列化的-->
<cache eviction="LRU"
type="org.apache.ibatis.cache.impl.PerpetualCache"
flushInterval="120000"
size="1024"
readOnly="true"/>
<select id="listAllUser" resultType="User">
select * from t_userinfo
</select>
</mapper>
配图看demo
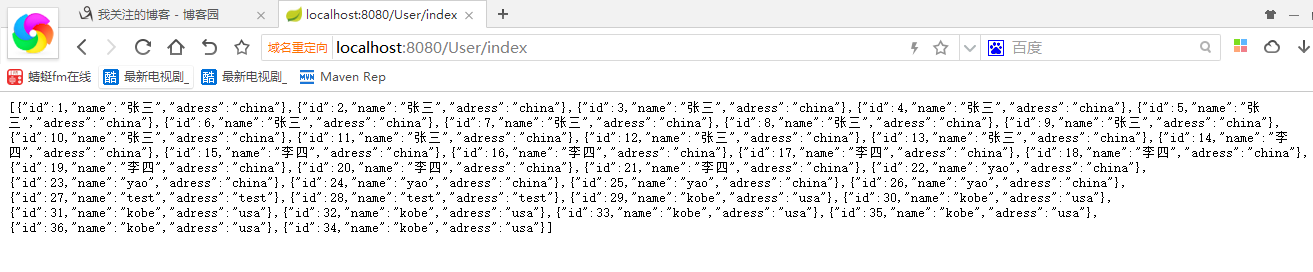
第一次查询是36条数据,我配置缓存是2分钟。然后再insert一条,你再刷新页面数据不变。等两分钟。。。。

总结
OK,所谓的存在即合理吧,适合不适合取决于你的业务场景。mybatis也提供了接口以便扩展。小流量、数据量小使用mybatis二级缓存足以。
