启动时检查
Dubbo缺省会在启动时检查依赖的服务是否可用,不可用时会抛出异常,阻止Spring初始化完成,以便上线时,能及早发现问题,默认check=true。
如果你的Spring容器是懒加载的,或者通过API编程延迟引用服务,请关闭check,否则服务临时不可用时,会抛出异常,拿到null引用,如果check=false,总是会返回引用,当服务恢复时,能自动连上。
可以通过check="false"关闭检查,比如,测试时,有些服务不关心,或者出现了循环依赖,必须有一方先启动。
关闭某个服务的启动时检查:(没有提供者时报错)
<dubbo:reference interface="com.foo.BarService" check="false" /> |
关闭所有服务的启动时检查:(没有提供者时报错)
<dubbo:consumer check="false" /> |
关闭注册中心启动时检查:(注册订阅失败时报错)
<dubbo:registry check="false" /> |
也可以用dubbo.properties配置:
dubbo.reference.com.foo.BarService.check=false
|
也可以用-D参数:
java -Ddubbo.reference.com.foo.BarService.check=false java -Ddubbo.reference.check=false java -Ddubbo.consumer.check=false java -Ddubbo.registry.check=false |
注意区别
dubbo.reference.check=false,强制改变所有reference的check值,就算配置中有声明,也会被覆盖。
dubbo.consumer.check=false,是设置check的缺省值,如果配置中有显式的声明,如:<dubbo:reference check="true"/>,不会受影响。
dubbo.registry.check=false,前面两个都是指订阅成功,但提供者列表是否为空是否报错,如果注册订阅失败时,也允许启动,需使用此选项,将在后台定时重试。
引用缺省是延迟初始化的,只有引用被注入到其它Bean,或被getBean()获取,才会初始化。
如果需要饥饿加载,即没有人引用也立即生成动态代理,可以配置:
<dubbo:reference interface="com.foo.BarService" init="true" /> |
集群容错
在集群调用失败时,Dubbo提供了多种容错方案,缺省为failover重试。
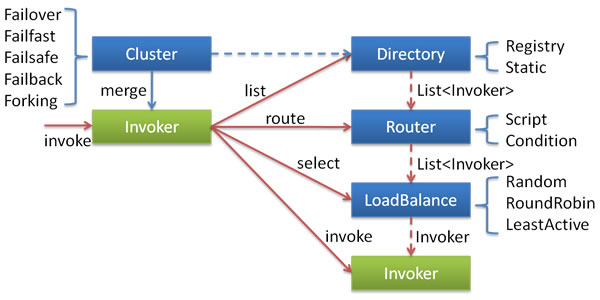
各节点关系:
这里的Invoker是Provider的一个可调用Service的抽象,Invoker封装了Provider地址及Service接口信息。
Directory代表多个Invoker,可以把它看成List<Invoker>,但与List不同的是,它的值可能是动态变化的,比如注册中心推送变更。
Cluster将Directory中的多个Invoker伪装成一个Invoker,对上层透明,伪装过程包含了容错逻辑,调用失败后,重试另一个。
Router负责从多个Invoker中按路由规则选出子集,比如读写分离,应用隔离等。
LoadBalance负责从多个Invoker中选出具体的一个用于本次调用,选的过程包含了负载均衡算法,调用失败后,需要重选。
集群容错模式:
Failover Cluster
失败自动切换,当出现失败,重试其它服务器。(缺省)
通常用于读操作,但重试会带来更长延迟。
可通过retries="2"来设置重试次数(不含第一次)。
Failfast Cluster
快速失败,只发起一次调用,失败立即报错。
通常用于非幂等性的写操作,比如新增记录。
Failsafe Cluster
失败安全,出现异常时,直接忽略。
通常用于写入审计日志等操作。
Failback Cluster
失败自动恢复,后台记录失败请求,定时重发。
通常用于消息通知操作。
Forking Cluster
并行调用多个服务器,只要一个成功即返回。
通常用于实时性要求较高的读操作,但需要浪费更多服务资源。
可通过forks="2"来设置最大并行数。
Broadcast Cluster
广播调用所有提供者,逐个调用,任意一台报错则报错。(2.1.0开始支持)
通常用于通知所有提供者更新缓存或日志等本地资源信息。
重试次数配置如:(failover集群模式生效)
|
retries="2" /> |
或:
<dubbo:reference retries="2" /> |
或:
|
name="findFoo" retries="2" /> |
集群模式配置如:
<dubbo:service cluster="failsafe" /> |
或:
<dubbo:reference cluster="failsafe" /> |
负载均衡
在集群负载均衡时,Dubbo提供了多种均衡策略,缺省为random随机调用。
Random LoadBalance
随机,按权重设置随机概率。
在一个截面上碰撞的概率高,但调用量越大分布越均匀,而且按概率使用权重后也比较均匀,有利于动态调整提供者权重。
RoundRobin LoadBalance
轮循,按公约后的权重设置轮循比率。
存在慢的提供者累积请求问题,比如:第二台机器很慢,但没挂,当请求调到第二台时就卡在那,久而久之,所有请求都卡在调到第二台上。
LeastActive LoadBalance
最少活跃调用数,相同活跃数的随机,活跃数指调用前后计数差。
使慢的提供者收到更少请求,因为越慢的提供者的调用前后计数差会越大。
ConsistentHash LoadBalance
一致性Hash,相同参数的请求总是发到同一提供者。
当某一台提供者挂时,原本发往该提供者的请求,基于虚拟节点,平摊到其它提供者,不会引起剧烈变动。
算法参见:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Consistent_hashing。
缺省只对第一个参数Hash,如果要修改,请配置<dubbo:parameter key="hash.arguments" value="0,1" />
缺省用160份虚拟节点,如果要修改,请配置<dubbo:parameter key="hash.nodes" value="320" />
配置如:
<dubbo:service interface="..." loadbalance="roundrobin" /> |
或:
<dubbo:reference interface="..." loadbalance="roundrobin" /> |
或:
<dubbo:service interface="...">
name="..." loadbalance="roundrobin"/>
|
或:
<dubbo:reference interface="...">
name="..." loadbalance="roundrobin"/>
|
线程模型
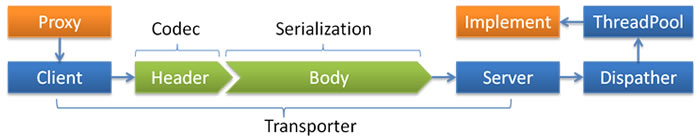
件处理线程说明
如果事件处理的逻辑能迅速完成,并且不会发起新的IO请求,比如只是在内存中记个标识,则直接在IO线程上处理更快,因为减少了线程池调度。
但如果事件处理逻辑较慢,或者需要发起新的IO请求,比如需要查询数据库,则必须派发到线程池,否则IO线程阻塞,将导致不能接收其它请求。
如果用IO线程处理事件,又在事件处理过程中发起新的IO请求,比如在连接事件中发起登录请求,会报“可能引发死锁”异常,但不会真死锁。
Dispatcher
all 所有消息都派发到线程池,包括请求,响应,连接事件,断开事件,心跳等。
direct 所有消息都不派发到线程池,全部在IO线程上直接执行。
message 只有请求响应消息派发到线程池,其它连接断开事件,心跳等消息,直接在IO线程上执行。
execution 只请求消息派发到线程池,不含响应,响应和其它连接断开事件,心跳等消息,直接在IO线程上执行。
connection 在IO线程上,将连接断开事件放入队列,有序逐个执行,其它消息派发到线程池。
ThreadPool
fixed 固定大小线程池,启动时建立线程,不关闭,一直持有。(缺省)
cached 缓存线程池,空闲一分钟自动删除,需要时重建。
limited 可伸缩线程池,但池中的线程数只会增长不会收缩。(为避免收缩时突然来了大流量引起的性能问题)。
配置如:
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" dispatcher="all" threadpool="fixed" threads="100" /> |
直连提供者
在开发及测试环境下,经常需要绕过注册中心,只测试指定服务提供者,这时候可能需要点对点直连,点对点直联方式,将以服务接口为单位,忽略注册中心的提供者列表,A接口配置点对点,不影响B接口从注册中心获取列表。
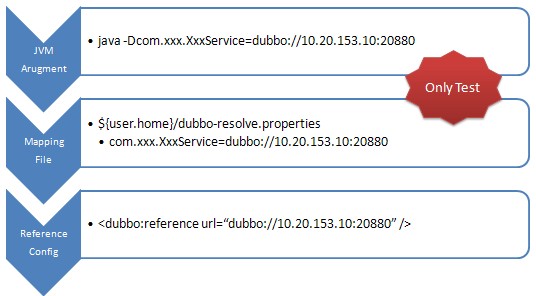
(1) 如果是线上需求需要点对点,可在<dubbo:reference>中配置url指向提供者,将绕过注册中心,多个地址用分号隔开,配置如下:(1.0.6及以上版本支持)
<dubbo:reference interface="com.alibaba.xxx.XxxService" url="dubbo://localhost:20890" /> |
(2) 在JVM启动参数中加入-D参数映射服务地址,如:
(key为服务名,value为服务提供者url,此配置优先级最高,1.0.15及以上版本支持)
java |
注意
为了避免复杂化线上环境,不要在线上使用这个功能,只应在测试阶段使用。
(3) 如果服务比较多,也可以用文件映射,如:
(用-Ddubbo.resolve.file指定映射文件路径,此配置优先级高于<dubbo:reference>中的配置,1.0.15及以上版本支持)
(2.0以上版本自动加载${user.home}/dubbo-resolve.properties文件,不需要配置)
java |
然后在映射文件xxx.properties中加入:(key为服务名,value为服务提供者url)
com.alibaba.xxx.XxxService=dubbo://localhost:20890 |
注意
为了避免复杂化线上环境,不要在线上使用这个功能,只应在测试阶段使用。
只订阅
问题
为方便开发测试,经常会在线下共用一个所有服务可用的注册中心,这时,如果一个正在开发中的服务提供者注册,可能会影响消费者不能正常运行。
解决方案
可以让服务提供者开发方,只订阅服务(开发的服务可能依赖其它服务),而不注册正在开发的服务,通过直连测试正在开发的服务。
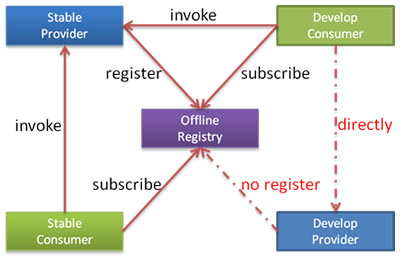
禁用注册配置:
<dubbo:registry address="10.20.153.10:9090" register="false" /> |
或者:
<dubbo:registry address="10.20.153.10:9090?register=false" /> |
只注册
问题
如果有两个镜像环境,两个注册中心,有一个服务只在其中一个注册中心有部署,另一个注册中心还没来得及部署,而两个注册中心的其它应用都需要依赖此服务,所以需要将服务同时注册到两个注册中心,但却不能让此服务同时依赖两个注册中心的其它服务。
解决方案
可以让服务提供者方,只注册服务到另一注册中心,而不从另一注册中心订阅服务。
禁用订阅配置:
<dubbo:registry id="hzRegistry" address="10.20.153.10:9090" /> id="qdRegistry" address="10.20.141.150:9090" subscribe="false" /> |
或者:
<dubbo:registry id="hzRegistry" address="10.20.153.10:9090" /> id="qdRegistry" address="10.20.141.150:9090?subscribe=false" /> |
静态服务
有时候希望人工管理服务提供者的上线和下线,此时需将注册中心标识为非动态管理模式。
<dubbo:registry address="10.20.141.150:9090" dynamic="false" /> |
或者:
<dubbo:registry address="10.20.141.150:9090?dynamic=false" /> |
服务提供者初次注册时为禁用状态,需人工启用,断线时,将不会被自动删除,需人工禁用。
如果是一个第三方独立提供者,比如memcached等,可以直接向注册中心写入提供者地址信息,消费者正常使用:(通常由脚本监控中心页面等调用)
| RegistryFactory registryFactory = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(RegistryFactory.class).getAdaptiveExtension(); Registry registry = registryFactory.getRegistry(URL.valueOf("zookeeper://10.20.153.10:2181")); registry.register(URL.valueOf ("memcached://10.20.153.11/com.foo.BarService?category=providers&dynamic=false&application=foo")); |
多协议
(1) 不同服务不同协议
比如:不同服务在性能上适用不同协议进行传输,比如大数据用短连接协议,小数据大并发用长连接协议。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> |
(2) 多协议暴露服务
比如:需要与http客户端互操作
consumer.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> |
多注册中心
(1) 多注册中心注册
比如:中文站有些服务来不及在青岛部署,只在杭州部署,而青岛的其它应用需要引用此服务,就可以将服务同时注册到两个注册中心。
consumer.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> |
(2) 不同服务使用不同注册中心
比如:CRM有些服务是专门为国际站设计的,有些服务是专门为中文站设计的。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> |
(3) 多注册中心引用
比如:CRM需同时调用中文站和国际站的PC2服务,PC2在中文站和国际站均有部署,接口及版本号都一样,但连的数据库不一样。
consumer.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> |
如果只是测试环境临时需要连接两个不同注册中心,使用竖号分隔多个不同注册中心地址:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> |
服务分组
当一个接口有多种实现时,可以用group区分。
<dubbo:service group="feedback" interface="com.xxx.IndexService" /> group="member" interface="com.xxx.IndexService" /> |
任意组:(2.2.0以上版本支持,总是只调一个可用组的实现)
<dubbo:reference id="feedbackIndexService" group="feedback" interface="com.xxx.IndexService" /> id="memberIndexService" group="member" interface="com.xxx.IndexService" /> |
多版本
当一个接口实现,出现不兼容升级时,可以用版本号过渡,版本号不同的服务相互间不引用。
在低压力时间段,先升级一半提供者为新版本
再将所有消费者升级为新版本
然后将剩下的一半提供者升级为新版本
<dubbo:service interface="com.foo.BarService" version="1.0.0" /> |
<dubbo:service interface="com.foo.BarService" version="2.0.0" /> |
<dubbo:reference id="barService" interface="com.foo.BarService" version="1.0.0" /> |
<dubbo:reference id="barService" interface="com.foo.BarService" version="2.0.0" /> |
不区分版本:(2.2.0以上版本支持)
<dubbo:reference id="barService" interface="com.foo.BarService" version="*" /> |
分组聚合
按组合并返回结果,比如菜单服务,接口一样,但有多种实现,用group区分,现在消费方需从每种group中调用一次返回结果,合并结果返回,这样就可以实现聚合菜单项。
从2.1.0版本开始支持
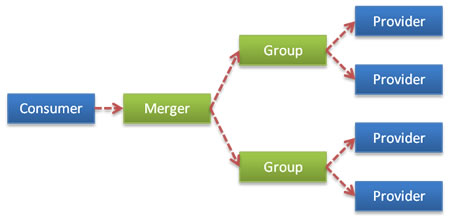
代码参见:https://github.com/alibaba/dubbo/tree/master/dubbo-test/dubbo-test-examples/src/main/java/com/alibaba/dubbo/examples/merge
配置如:(搜索所有分组)
<dubbo:reference interface="com.xxx.MenuService" group="*" merger="true" /> |
或:(合并指定分组)
<dubbo:reference interface="com.xxx.MenuService" group="aaa,bbb" merger="true" /> |
或:(指定方法合并结果,其它未指定的方法,将只调用一个Group)
<dubbo:reference interface="com.xxx.MenuService" group="*"> name="getMenuItems" merger="true" /> |
或:(某个方法不合并结果,其它都合并结果)
<dubbo:reference interface="com.xxx.MenuService" group="*" merger="true"> name="getMenuItems" merger="false" /> |
或:(指定合并策略,缺省根据返回值类型自动匹配,如果同一类型有两个合并器时,需指定合并器的名称)
参见:[合并结果扩展]
<dubbo:reference interface="com.xxx.MenuService" group="*"> name="getMenuItems" merger="mymerge" /> |
或:(指定合并方法,将调用返回结果的指定方法进行合并,合并方法的参数类型必须是返回结果类型本身)
<dubbo:reference interface="com.xxx.MenuService" group="*"> name="getMenuItems" merger=".addAll" /> |
参数验证
参数验证功能是基于JSR303实现的,用户只需标识JSR303标准的验证Annotation,并通过声明filter来实现验证。
2.1.0以上版本支持
完整示例代码参见:https://github.com/alibaba/dubbo/tree/master/dubbo-test/dubbo-test-examples/src/main/java/com/alibaba/dubbo/examples/validation
验证方式可扩展,参见:Validation扩展点
参数标注示例:
import java.io.Serializable; java.util.Date; javax.validation.constraints.Future; javax.validation.constraints.Max; javax.validation.constraints.Min; javax.validation.constraints.NotNull; javax.validation.constraints.Past; javax.validation.constraints.Pattern; javax.validation.constraints.Size; class Serializable { static // 不允许为空 String name; String email; int // 必须为一个过去的时间 Date loginDate; // 必须为一个未来的时间 Date expiryDate; String getName() { name; void String getEmail() { email; void
int age; void age) { Date getLoginDate() { loginDate; void Date getExpiryDate() { expiryDate; void 分组验证示例: public interface Save{} // save(ValidationParameter parameter); update(ValidationParameter parameter); |
分组验证示例:
import javax.validation.GroupSequence; public interface @GroupSequence(Update.class) @interface Save{}
save(ValidationParameter parameter); @interface Update{}
update(ValidationParameter parameter); } |
参数验证示例:
import javax.validation.constraints.Min; javax.validation.constraints.NotNull; interface save(@NotNull ValidationParameter parameter); // delete(@Min(1) id); // |
在客户端验证参数:
<dubbo:reference id="validationService" interface="com.alibaba.dubbo.examples.validation.api.ValidationService" validation="true" /> |
在服务器端验证参数:
<dubbo:service interface="com.alibaba.dubbo.examples.validation.api.ValidationService" ref="validationService" validation="true" /> |
验证异常信息:
import javax.validation.ConstraintViolationException; javax.validation.ConstraintViolationException; org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; com.alibaba.dubbo.examples.validation.api.ValidationParameter; com.alibaba.dubbo.examples.validation.api.ValidationService; com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcException; class static Exception {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
{ ValidationParameter(); (RpcException e) { // |
需要加入依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>javax.validation</groupId> |