linux进程间通信的4种方式:
(1)管道pipe
(2)消息队列message queue
(3)共享内存 share memory
(4)网络套接字 socket
pipe 是linux操作系统提供的一个消息传递机制.
在linux中 很多东西都被抽象为文件,它把所有的设备都抽象为文件.操作这个文件就是操作设备.
进程间通信,是一种新的文件类型,管道.不是一个普通的文件.
接下来就管道通信过程介绍如下:
1.创建一个pipe的文件夹
mkdir pipe
2.mkfifo ~/project/message
cd pipe
pipe message #创建管道
创建了一个管道对象, 在进程A中 open管道文件,向文件中write 数据,在进程B中,打开管道文件,从文件中read数据.于是数据从进程A传递到了进程B.显然管道文件不是普通的文件.
3.创建write.cpp文件
touch write.cpp
内容:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
int main()
{
int fd=open("message",O_WRONLY);
if(fd<0)
{
printf("failed to open pipe
");
return -1;
}
printf("open ok.
");
char data[12]="hello";
write(fd,data,5);
printf("press enter to exit..
");
getchar();
close(fd);
return 0;
}
4.创建read.cpp文件
touch read.cpp
内容:
#include<unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int fd=open("message",O_RDONLY);
if(fd<0)
{
printf("failed to open pipe!
");
return -1;
}
printf("open ok.
");
char data[12];
int n=read(fd,data,12);
printf("get %d bytes
",n);
printf("press enter to exit..
");
getchar();
close(fd);
return 0;
}
5.打开一个终端编译write.cpp ,生成可执行文件write
g++ write.cpp -o write
6.再打开一个终端编译read.cpp,生成可执行文件read
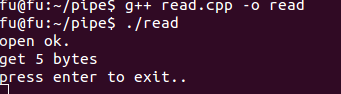
g++ read.cpp -o read
7.执行write
./write
8.执行read
./read
执行结果: