译者按: 简洁的代码可以避免写出过多的BUG。
本文采用意译,版权归原作者所有
引文
作为一个开发者,如果你关心代码质量,除了需要认真测试代码能否正确执行以外,还要注重代码的整洁(clean code)。一个专业的开发者会从将来自己或则他人方便维护的角度考虑如何写代码,而不仅仅是机器能够读懂。你写的任何代码有很大几率会被再次重构,希望未来重构代码的那个人不会觉得这是一场灾难。
代码的简洁之道可以被理解为:代码自我解释(且注释少),开发者友好(易于理解,修改和扩展)。
想想之前阅读别人的代码的时候,说过多少次下面的话?
"WTF is that?"
"WTF did you do here?"
"WTF is this for?"
下面这张图很形象地描述了这个情况:
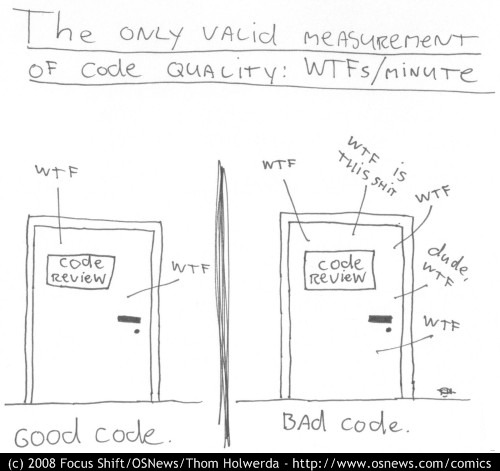
《Clean Code》的作者Robert C. Martin (Uncle Bob) 说过这样的话.
虽然烂代码可以运行,但是它不够整洁,它会把整个开发团队给整跪了
本文主要讲 JavaScript 代码的整洁之道。
1. 强类型检查
建议使用 === 而不是 == 来判断是否相等
// 如果没有妥善处理的话,可能会出现和预想不一样的结果
0 == false; // true
0 === false; // false
2 == "2"; // true
2 === "2"; // false
const value = "500";
if (value === 500) {
// 不会执行
console.log(value);
}
if (value === "500") {
// 会执行
console.log(value);
}
2. 变量命名
变量命名尽量直观易懂,方便查找;而且其他开发者也容易理解。
不好的命名方式:
let daysSLV = 10;
let y = new Date().getFullYear();
let ok;
if (user.age > 30) {
ok = true;
}
好的命名方式:
const MAX_AGE = 30;
let daysSinceLastVisit = 10;
let currentYear = new Date().getFullYear();
...
const isUserOlderThanAllowed = user.age > MAX_AGE;
不要使用多余的无意义的单词来组合命名
坏的命名方式:
let nameValue;
let theProduct;
好的命名方式:
let name;
let product;
不要使用无意义的字符/单词来命名,增加额外的记忆负担
坏的命名方式:
const users = ["John", "Marco", "Peter"];
users.forEach(u => {
doSomething();
doSomethingElse();
// ...
// ...
// ...
// ...
// 这里u到底指代什么?
register(u);
});
好的命名方式:
const users = ["John", "Marco", "Peter"];
users.forEach(user => {
doSomething();
doSomethingElse();
// ...
// ...
// ...
// ...
register(user);
});
在某些环境下,不用添加冗余的单词来组合命名。比如一个对象叫user,那么其中的一个名字的属性直接用name,不需要再使用username了。
坏的命名方式:
const user = {
userName: "John",
userSurname: "Doe",
userAge: "28"
};
...
user.userName;
好的命名方式:
const user = {
name: "John",
surname: "Doe",
age: "28"
};
...
user.name;
3. 函数
请使用完整的声明式的名字来给函数命名。比如一个函数实现了某个行为,那么函数名可以是一个动词或则一个动词加上其行为的被作用者。名字就应该表达出函数要表达的行为。
坏的命名方式:
function notif(user) {
// implementation
}
好的命名方式:
function notifyUser(emailAddress) {
// implementation
}
避免使用过多参数。最好一个函数只有 2 个甚至更少的参数。参数越少,越容易做测试。
坏的使用方式:
function getUsers(fields, fromDate, toDate) {
// implementation
}
好的使用方式:
function getUsers({ fields, fromDate, toDate }) {
// implementation
}
getUsers({
fields: ["name", "surname", "email"],
fromDate: "2019-01-01",
toDate: "2019-01-18"
});
为函数参数设置默认值,而不是在代码中通过条件判断来赋值。
坏的写法:
function createShape(type) {
const shapeType = type || "cube";
// ...
}
好的写法:
function createShape(type = "cube") {
// ...
}
一个函数应该只做一件事情。避免将多个事情塞到一个函数中。
坏的写法:
function notifyUsers(users) {
users.forEach(user => {
const userRecord = database.lookup(user);
if (userRecord.isVerified()) {
notify(user);
}
});
}
好的写法:
function notifyVerifiedUsers(users) {
users.filter(isUserVerified).forEach(notify);
}
function isUserVerified(user) {
const userRecord = database.lookup(user);
return userRecord.isVerified();
}
使用Objecg.assign来设置默认对象值。
坏的写法:
const shapeConfig = {
type: "cube",
200,
height: null
};
function createShape(config) {
config.type = config.type || "cube";
config.width = config.width || 250;
config.height = config.width || 250;
}
createShape(shapeConfig);
好的写法:
const shapeConfig = {
type: "cube",
200
// Exclude the 'height' key
};
function createShape(config) {
config = Object.assign(
{
type: "cube",
250,
height: 250
},
config
);
...
}
createShape(shapeConfig);
不要使用 true/false 的标签(flag),因为它实际上让函数做了超出它本身的事情。
坏的写法:
function createFile(name, isPublic) {
if (isPublic) {
fs.create(`./public/${name}`);
} else {
fs.create(name);
}
}
好的写法:
function createFile(name) {
fs.create(name);
}
function createPublicFile(name) {
createFile(`./public/${name}`);
}
不要污染全局。如果你需要对现有的对象进行扩展,不要在对象的原型链上定义函数。请使用 ES 的类和继承。
坏的写法:
Array.prototype.myFunc = function myFunc() {
// implementation
};
好的写法:
class SuperArray extends Array {
myFunc() {
// implementation
}
}
好的代码风格可以避免不小心写出有BUG的代码,以防万一,推荐使用Fundebug做线上实时BUG监控!
4. 判断条件
避免使用否定的条件。
坏的写法:
function isUserNotBlocked(user) {
// implementation
}
if (!isUserNotBlocked(user)) {
// implementation
}
好的写法:
function isUserBlocked(user) {
// implementation
}
if (isUserBlocked(user)) {
// implementation
}
使用简短的条件。这个要求看上去简单,但是值得提醒。
坏的写法:
if (isValid === true) {
// do something...
}
if (isValid === false) {
// do something...
}
好的写法:
if (isValid) {
// do something...
}
if (!isValid) {
// do something...
}
如果你很确定它的值不是undefined或则null,我建议你这么做。
尽量避免使用判断条件,推荐说那个多态(polymorphism)或则继承。
坏的写法:
class Car {
// ...
getMaximumSpeed() {
switch (this.type) {
case "Ford":
return this.someFactor() + this.anotherFactor();
case "Mazda":
return this.someFactor();
case "McLaren":
return this.someFactor() - this.anotherFactor();
}
}
}
好的写法:
class Car {
// ...
}
class Ford extends Car {
// ...
getMaximumSpeed() {
return this.someFactor() + this.anotherFactor();
}
}
class Mazda extends Car {
// ...
getMaximumSpeed() {
return this.someFactor();
}
}
class McLaren extends Car {
// ...
getMaximumSpeed() {
return this.someFactor() - this.anotherFactor();
}
}
5. ES 类
类是 JavaScript 新推出的语法糖。建议使用类而不是用老式的直接定义函数的写法。
坏的写法:
const Person = function(name) {
if (!(this instanceof Person)) {
throw new Error("Instantiate Person with `new` keyword");
}
this.name = name;
};
Person.prototype.sayHello = function sayHello() {
/**/
};
const Student = function(name, school) {
if (!(this instanceof Student)) {
throw new Error("Instantiate Student with `new` keyword");
}
Person.call(this, name);
this.school = school;
};
Student.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype);
Student.prototype.constructor = Student;
Student.prototype.printSchoolName = function printSchoolName() {
/**/
};
好的写法:
class Person {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
sayHello() {
/* ... */
}
}
class Student extends Person {
constructor(name, school) {
super(name);
this.school = school;
}
printSchoolName() {
/* ... */
}
}
使用函数调用链。像 jQuery,Lodash 都使用这个模式。你只需要在每一个函数的末尾返回this,之后的代码会更加的简洁。
坏的写法:
class Person {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
setSurname(surname) {
this.surname = surname;
}
setAge(age) {
this.age = age;
}
save() {
console.log(this.name, this.surname, this.age);
}
}
const person = new Person("John");
person.setSurname("Doe");
person.setAge(29);
person.save();
好的写法:
class Person {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
setSurname(surname) {
this.surname = surname;
// Return this for chaining
return this;
}
setAge(age) {
this.age = age;
// Return this for chaining
return this;
}
save() {
console.log(this.name, this.surname, this.age);
// Return this for chaining
return this;
}
}
const person = new Person("John")
.setSurname("Doe")
.setAge(29)
.save();
6. 其它
总的来说,你不能写重复代码,不能留下一堆不再使用的函数,永远不会执行的代码(死代码)。
在很多情况下,你可能搞出重复代码。比如你要实现两个略微不同的功能,他们有很多相通的地方,但是由于项目截止时间快到了,你不得不快速复制黏贴再稍微修改修改来实现。
对于死代码,最好的做法就是你决定不再使用它的那一刻就把它删掉。时间过去太久,你甚至会忘记自己当初为什么定义它。下面这幅图很形象地描述了这个情况:

关于Fundebug
Fundebug专注于JavaScript、微信小程序、微信小游戏、支付宝小程序、React Native、Node.js和Java线上应用实时BUG监控。 自从2016年双十一正式上线,Fundebug累计处理了10亿+错误事件,付费客户有Google、360、金山软件、百姓网等众多品牌企业。欢迎大家免费试用!

版权声明
转载时请注明作者Fundebug以及本文地址:
https://blog.fundebug.com/2019/06/11/javascript-clean-code/