洛谷 SP14932 LCA - Lowest Common Ancestor
题目描述
A tree is an undirected graph in which any two vertices are connected by exactly one simple path. In other words, any connected graph without cycles is a tree. - Wikipedia
The lowest common ancestor (LCA) is a concept in graph theory and computer science. Let T be a rooted tree with N nodes. The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes v and w as the lowest node in T that has both v and w as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself). - Wikipedia
Your task in this problem is to find the LCA of any two given nodes v and w in a given tree T.
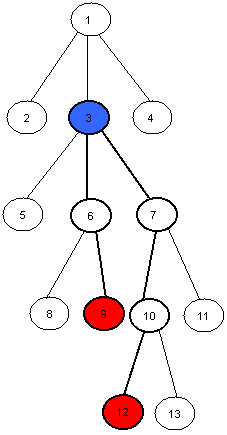
For example the LCA of nodes 9 and 12 in this tree is the node number 3.
Input
The first line of input will be the number of test cases. Each test case will start with a number N the number of nodes in the tree, 1 <= N <= 1,000. Nodes are numbered from 1 to N. The next N lines each one will start with a number M the number of child nodes of the Nth node, 0 <= M <= 999 followed by M numbers the child nodes of the Nth node. The next line will be a number Q the number of queries you have to answer for the given tree T, 1 <= Q <= 1000. The next Q lines each one will have two number v and w in which you have to find the LCA of v and w in T, 1 <= v, w <= 1,000.
Input will guarantee that there is only one root and no cycles.
Output
For each test case print Q + 1 lines, The first line will have “Case C:” without quotes where C is the case number starting with 1. The next Q lines should be the LCA of the given v and w respectively.
Example
Input:
1
7
3 2 3 4
0
3 5 6 7
0
0
0
0
2
5 7
2 7
Output:
Case 1:
3
1
输入格式
无
输出格式
无
题意翻译
Description:
一棵树是一个简单无向图,图中任意两个节点仅被一条边连接,所有连通无环无向图都是一棵树。-Wikipedia
最近公共祖先(LCA)是……(此处省去对LCA的描述),你的任务是对一棵给定的树TT以及上面的两个节点u,vu,v求出他们的LCALCA。
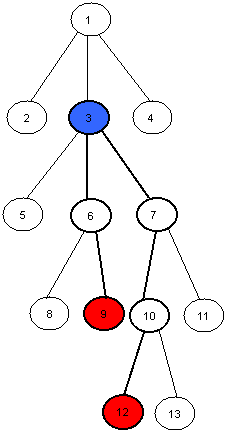
例如图中99和1212号节点的LCA*L*C*A*为33号节点
Input:
输入的第一行为数据组数TT,对于每组数据,第一行为一个整数N(1leq Nleq1000)N(1≤N≤1000),节点编号从11到NN,接下来的NN行里每一行开头有一个数字M(0leq Mleq999)M(0≤M≤999),MM为第ii个节点的子节点数量,接下来有MM个数表示第ii个节点的子节点编号。下面一行会有一个整数Q(1leq Qleq1000)Q(1≤Q≤1000),接下来的QQ行每行有两个数u,vu,v,输出节点u,vu,v在给定树中的LCALCA。
输入数据保证只有一个根节点并且没有环。
Output:
对于每一组数据输出Q+1Q+1行,第一行格式为"Case i:"(没有双引号),i表示当前数据是第几组,接下来的QQ行每一行一个整数表示一对节点u,vu,v的LCALCA。
Sample Input:
1
7
3 2 3 4
0
3 5 6 7
0
0
0
0
2
5 7
2 7
Sample Output:
Case 1:
3
1
Translated by @yxl_gl
输入输出样例
无
题解:
LCA模板题目双倍经验~~
点进来的小伙伴肯定还不太会LCA...
请参考蒟蒻的这篇博客:
(这里介绍了倍增求LCA,其实求LCA还有好多方式,比如离线Tarjan和树链剖分等,有兴趣的巨佬可以自己涉及,如果只求LCA的话,还是这种倍增法更快一些)
当然,本题还有一些小细节,比如多组数据数据要清空,以及比较奇葩的读入边的方式。
代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1010;
char *p1,*p2,buf[100000];
#define nc() (p1==p2&&(p2=(p1=buf)+fread(buf,1,100000,stdin),p1==p2)?EOF:*p1++)
int read()
{
int x=0,f=1;
char ch=nc();
while(ch<48){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=nc();}
while(ch>47) x=(((x<<2)+x)<<1)+ch-48,ch=nc();
return x*f;
}
int n,m,q;
int tot,head[maxn],nxt[maxn<<1],to[maxn<<1];
int deep[maxn],fa[maxn][21];
void add(int x,int y)
{
to[++tot]=y;
nxt[tot]=head[x];
head[x]=tot;
}
void dfs(int x,int f)
{
deep[x]=deep[f]+1;
fa[x][0]=f;
for(int i=1;(1<<i)<=deep[x];i++)
fa[x][i]=fa[fa[x][i-1]][i-1];
for(int i=head[x];i;i=nxt[i])
{
int y=to[i];
if(y==f)
continue;
dfs(y,x);
}
}
int lca(int x,int y)
{
int ret;
if(deep[x]<deep[y])
swap(x,y);
for(int i=20;i>=0;i--)
if(deep[fa[x][i]]>=deep[y])
x=fa[x][i];
if(x==y)
return y;
for(int i=20;i>=0;i--)
{
if(fa[x][i]!=fa[y][i])
{
x=fa[x][i];
y=fa[y][i];
}
else
ret=fa[x][i];
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
int t;
t=read();
for(int k=1;k<=t;k++)
{
tot=0;
memset(head,0,sizeof(head));
memset(nxt,0,sizeof(nxt));
memset(to,0,sizeof(to));
memset(deep,0,sizeof(deep));
memset(fa,0,sizeof(fa));
n=read();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
m=read();
if(!m)
continue;
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)
{
int u=read();
add(u,i);
add(i,u);
}
}
dfs(1,0);
q=read();
printf("Case %d:
",k);
while(q--)
{
int u=read();
int v=read();
printf("%d
",lca(u,v));
}
}
return 0;
}