NetworkEnvironment 是一个TaskManager对应一个,而不是一个task对应一个
其中最关键的是networkBufferPool,
operator产生的中间结果,ResultPartition,或是input数据,InputGate
都是需要memory来暂存的,这就需要networkBufferPool来管理这部分内存
/** * Network I/O components of each {@link TaskManager} instance. The network environment contains * the data structures that keep track of all intermediate results and all data exchanges. * * When initialized, the NetworkEnvironment will allocate the network buffer pool. * All other components (netty, intermediate result managers, ...) are only created once the * environment is "associated" with a TaskManager and JobManager. This happens as soon as the * TaskManager actor gets created and registers itself at the JobManager. */ public class NetworkEnvironment { private final NetworkEnvironmentConfiguration configuration; private final NetworkBufferPool networkBufferPool; private ConnectionManager connectionManager; private ResultPartitionManager partitionManager; private ResultPartitionConsumableNotifier partitionConsumableNotifier; /** * ExecutionEnvironment which is used to execute remote calls with the * {@link JobManagerResultPartitionConsumableNotifier} */ private final ExecutionContext executionContext; /** * Initializes all network I/O components. */ public NetworkEnvironment( ExecutionContext executionContext, FiniteDuration jobManagerTimeout, NetworkEnvironmentConfiguration config) throws IOException { // create the network buffers - this is the operation most likely to fail upon // mis-configuration, so we do this first try { networkBufferPool = new NetworkBufferPool(config.numNetworkBuffers(), config.networkBufferSize(), config.memoryType()); } catch (Throwable t) { throw new IOException("Cannot allocate network buffer pool: " + t.getMessage(), t); } } }
NetworkBufferPool
先看看networkBufferPool,
首先,它管理了一堆的BufferPool,而不是buffer,因为一个task manager只有一个networkBufferPool,所以对于每个task,需要分配一个buffer pool
再者,它的内存管理和memory manager一样的模式,从heap或off-heap申请相应数量的segments放入availableMemorySegments中
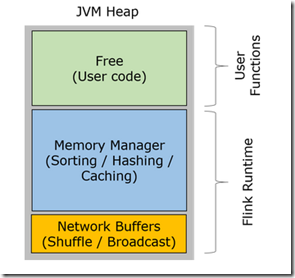
可以看到底下黄色部分,就是分配给networkBufferPool的heap
/** * The NetworkBufferPool is a fixed size pool of {@link MemorySegment} instances * for the network stack. * * The NetworkBufferPool creates {@link LocalBufferPool}s from which the individual tasks draw * the buffers for the network data transfer. When new local buffer pools are created, the * NetworkBufferPool dynamically redistributes the buffers between the pools. */ public class NetworkBufferPool implements BufferPoolFactory { private final int totalNumberOfMemorySegments; //该Pool所管理的所有MemorySegment的数量 private final int memorySegmentSize; //memorySegment的大小,size private final Queue<MemorySegment> availableMemorySegments; //可用的MemorySegment队列 private final Set<LocalBufferPool> managedBufferPools = new HashSet<LocalBufferPool>(); //管理一组LocalBufferPool,每个task需要分配一个 public final Set<LocalBufferPool> allBufferPools = new HashSet<LocalBufferPool>(); private int numTotalRequiredBuffers; /** * Allocates all {@link MemorySegment} instances managed by this pool. */ public NetworkBufferPool(int numberOfSegmentsToAllocate, int segmentSize, MemoryType memoryType) { this.totalNumberOfMemorySegments = numberOfSegmentsToAllocate; this.memorySegmentSize = segmentSize; final long sizeInLong = (long) segmentSize; try { this.availableMemorySegments = new ArrayBlockingQueue<MemorySegment>(numberOfSegmentsToAllocate); //availableMemorySegments按totalNumberOfMemorySegments分配 } catch (OutOfMemoryError err) { } try { if (memoryType == MemoryType.HEAP) { //可以选择是从heap或off-heap分配 for (int i = 0; i < numberOfSegmentsToAllocate; i++) { byte[] memory = new byte[segmentSize]; availableMemorySegments.add(MemorySegmentFactory.wrapPooledHeapMemory(memory, null)); } } else if (memoryType == MemoryType.OFF_HEAP) { for (int i = 0; i < numberOfSegmentsToAllocate; i++) { ByteBuffer memory = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(segmentSize); availableMemorySegments.add(MemorySegmentFactory.wrapPooledOffHeapMemory(memory, null)); } } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown memory type " + memoryType); } } } public MemorySegment requestMemorySegment() { return availableMemorySegments.poll(); //request就是从availableMemorySegments里面取一个 } // This is not safe with regard to destroy calls, but it does not hurt, because destroy happens // only once at clean up time (task manager shutdown). public void recycle(MemorySegment segment) { availableMemorySegments.add(segment); //而回收就是放回availableMemorySegments } @Override public BufferPool createBufferPool(int numRequiredBuffers, boolean isFixedSize) throws IOException { // It is necessary to use a separate lock from the one used for buffer // requests to ensure deadlock freedom for failure cases. synchronized (factoryLock) { // Ensure that the number of required buffers can be satisfied. // With dynamic memory management this should become obsolete. if (numTotalRequiredBuffers + numRequiredBuffers > totalNumberOfMemorySegments) { //确定已经required的加上这次require的没有超过总量 throw new IOException(String.format("Insufficient number of network buffers: " + "required %d, but only %d available. The total number of network " + "buffers is currently set to %d. You can increase this " + "number by setting the configuration key '%s'.", numRequiredBuffers, totalNumberOfMemorySegments - numTotalRequiredBuffers, totalNumberOfMemorySegments, ConfigConstants.TASK_MANAGER_NETWORK_NUM_BUFFERS_KEY)); } this.numTotalRequiredBuffers += numRequiredBuffers; //增加numTotalRequiredBuffers // We are good to go, create a new buffer pool and redistribute // non-fixed size buffers. LocalBufferPool localBufferPool = new LocalBufferPool(this, numRequiredBuffers); //创建LocalBufferPool,这时并不会把segement给他,request是lazy的 // The fixed size pools get their share of buffers and don't change // it during their lifetime. if (!isFixedSize) { //如果不是Fixed,可以动态把多的segment分配出去 managedBufferPools.add(localBufferPool); } allBufferPools.add(localBufferPool); //管理localBufferPool redistributeBuffers(); return localBufferPool; } } // Must be called from synchronized block //目的就是把多余的segement也分配出去,利用起来 private void redistributeBuffers() throws IOException { int numManagedBufferPools = managedBufferPools.size(); if (numManagedBufferPools == 0) { return; // necessary to avoid div by zero when no managed pools } // All buffers, which are not among the required ones int numAvailableMemorySegment = totalNumberOfMemorySegments - numTotalRequiredBuffers; //多的Segments // Available excess (not required) buffers per pool int numExcessBuffersPerPool = numAvailableMemorySegment / numManagedBufferPools; //多的平均到每个bufferpool // Distribute leftover buffers in round robin fashion int numLeftoverBuffers = numAvailableMemorySegment % numManagedBufferPools; //余数 int bufferPoolIndex = 0; for (LocalBufferPool bufferPool : managedBufferPools) { int leftoverBuffers = bufferPoolIndex++ < numLeftoverBuffers ? 1 : 0; //余数可能是1或0 bufferPool.setNumBuffers(bufferPool.getNumberOfRequiredMemorySegments() + numExcessBuffersPerPool + leftoverBuffers); //在getNumberOfRequiredMemorySegments的基础上加上多余的 } }
可看到,当一个task需要申请buffer pool时,要先createBufferPool
即,在从availableMemorySegments中取出相应数量的segement,封装成LocalBufferPool,返回
这里有个managedBufferPools,表示bufferpool的size是可以动态变化的,
redistributeBuffers会平均将现有可用的segments分配到所有当前的managedBufferPools上去
LocalBufferPool
class LocalBufferPool implements BufferPool { private final NetworkBufferPool networkBufferPool; //总的bufferPool // The minimum number of required segments for this pool private final int numberOfRequiredMemorySegments; //要求申请的MemorySegments的个数,最小个数 // The current size of this pool private int currentPoolSize; //实际的MemorySegments的个数,如果不是fixed,可能会多 // The currently available memory segments. These are segments, which have been requested from // the network buffer pool and are currently not handed out as Buffer instances. private final Queue<MemorySegment> availableMemorySegments = new ArrayDeque<MemorySegment>(); //缓存MemorySegment的队列 // Buffer availability listeners, which need to be notified when a Buffer becomes available. // Listeners can only be registered at a time/state where no Buffer instance was available. private final Queue<EventListener<Buffer>> registeredListeners = new ArrayDeque<EventListener<Buffer>>(); // Number of all memory segments, which have been requested from the network buffer pool and are // somehow referenced through this pool (e.g. wrapped in Buffer instances or as available segments). private int numberOfRequestedMemorySegments; //已经分配的MemorySegments的个数 private boolean isDestroyed; private BufferPoolOwner owner; //owner复杂去释放networkBufferPool的buffer LocalBufferPool(NetworkBufferPool networkBufferPool, int numberOfRequiredMemorySegments) { this.networkBufferPool = networkBufferPool; this.numberOfRequiredMemorySegments = numberOfRequiredMemorySegments; //初始化的时候,numberOfRequiredMemorySegments,currentPoolSize相等 this.currentPoolSize = numberOfRequiredMemorySegments; } @Override public int getMemorySegmentSize() { return networkBufferPool.getMemorySegmentSize(); //MemorySegment本身的size } @Override public int getNumBuffers() { synchronized (availableMemorySegments) { return currentPoolSize; //当前local pool的size } } private Buffer requestBuffer(boolean isBlocking) throws InterruptedException, IOException { synchronized (availableMemorySegments) { returnExcessMemorySegments(); //把多申请的MemorySegment还回去,如果动态的情况下,是可能的 boolean askToRecycle = owner != null; while (availableMemorySegments.isEmpty()) { //如果availableMemorySegments中没有现成的 if (numberOfRequestedMemorySegments < currentPoolSize) { //只有在numberOfRequestedMemorySegments小于currentPoolSize,才能继续申请 final MemorySegment segment = networkBufferPool.requestMemorySegment(); //从networkBufferPool中申请一块 if (segment != null) { numberOfRequestedMemorySegments++; availableMemorySegments.add(segment); continue; //如果申请到继续 } } if (askToRecycle) { //如果申请不到,说明networkBufferPool也没有buffer了 owner.releaseMemory(1); //试图让owner去让networkBufferPool释放一块 } if (isBlocking) { availableMemorySegments.wait(2000); } else { return null; } } return new Buffer(availableMemorySegments.poll(), this); } } @Override public void recycle(MemorySegment segment) { synchronized (availableMemorySegments) { if (isDestroyed || numberOfRequestedMemorySegments > currentPoolSize) { returnMemorySegment(segment); //直接还回networkBufferPool } else { EventListener<Buffer> listener = registeredListeners.poll(); if (listener == null) { //如果没有listen,直接把segment放回availableMemorySegments availableMemorySegments.add(segment); availableMemorySegments.notify(); //触发通知availableMemorySegments有新的segment } else { try { listener.onEvent(new Buffer(segment, this)); //如果有listener,触发onEvent让listener去处理这个segment } catch (Throwable ignored) { availableMemorySegments.add(segment); availableMemorySegments.notify(); } } } } } @Override public void setNumBuffers(int numBuffers) throws IOException { synchronized (availableMemorySegments) { checkArgument(numBuffers >= numberOfRequiredMemorySegments, "Buffer pool needs at least " + numberOfRequiredMemorySegments + " buffers, but tried to set to " + numBuffers + "."); currentPoolSize = numBuffers; returnExcessMemorySegments(); // If there is a registered owner and we have still requested more buffers than our // size, trigger a recycle via the owner. if (owner != null && numberOfRequestedMemorySegments > currentPoolSize) { owner.releaseMemory(numberOfRequestedMemorySegments - numBuffers); } } } }
associateWithTaskManagerAndJobManager
NetworkEnvironment首先需要做的是associate,然后才能用
NetworkEnvironment 中有很多组件,是需要在绑定TaskManagerAndJobManager时,才需要去初始化的
/** * This associates the network environment with a TaskManager and JobManager. * This will actually start the network components. * * @param jobManagerGateway Gateway to the JobManager. * @param taskManagerGateway Gateway to the TaskManager. * * @throws IOException Thrown if the network subsystem (Netty) cannot be properly started. */ public void associateWithTaskManagerAndJobManager( ActorGateway jobManagerGateway, ActorGateway taskManagerGateway) throws IOException { synchronized (lock) { if (this.partitionConsumableNotifier == null && this.partitionManager == null && this.taskEventDispatcher == null && this.connectionManager == null) { // good, not currently associated. start the individual components LOG.debug("Starting result partition manager and network connection manager"); this.partitionManager = new ResultPartitionManager(); this.taskEventDispatcher = new TaskEventDispatcher(); this.partitionConsumableNotifier = new JobManagerResultPartitionConsumableNotifier( executionContext, jobManagerGateway, taskManagerGateway, jobManagerTimeout); this.partitionStateChecker = new JobManagerPartitionStateChecker( jobManagerGateway, taskManagerGateway); // ----- Network connections ----- final Option<NettyConfig> nettyConfig = configuration.nettyConfig(); connectionManager = nettyConfig.isDefined() ? new NettyConnectionManager(nettyConfig.get()) : new LocalConnectionManager(); try { LOG.debug("Starting network connection manager"); connectionManager.start(partitionManager, taskEventDispatcher, networkBufferPool); } catch (Throwable t) { throw new IOException("Failed to instantiate network connection manager: " + t.getMessage(), t); } } else { throw new IllegalStateException( "Network Environment is already associated with a JobManager/TaskManager"); } } }
主要是初始化一系列组件,TaskEventDispatcher,ConnectionManager, ResultPartitionManager
JobManagerResultPartitionConsumableNotifier, JobManagerPartitionStateChecker
对于ConnectionManager,这里如果定义了netty,会创建NettyConnectionManager
这里面,主要是初始化Netty client和Netty server
否则是创建LocalConnectionManager
而对于ResultPartitionManager, 主要就是用于track所有的result partitions,
核心结构为, Table<ExecutionAttemptID, IntermediateResultPartitionID, ResultPartition> registeredPartitions = HashBasedTable.create();
这个会记录所有的ResultPartition
/** * The result partition manager keeps track of all currently produced/consumed partitions of a * task manager. */ public class ResultPartitionManager implements ResultPartitionProvider { private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ResultPartitionManager.class); public final Table<ExecutionAttemptID, IntermediateResultPartitionID, ResultPartition> registeredPartitions = HashBasedTable.create(); private boolean isShutdown; public void registerResultPartition(ResultPartition partition) throws IOException { synchronized (registeredPartitions) { checkState(!isShutdown, "Result partition manager already shut down."); ResultPartitionID partitionId = partition.getPartitionId(); ResultPartition previous = registeredPartitions.put(partitionId.getProducerId(), partitionId.getPartitionId(), partition); } } }
JobManagerResultPartitionConsumableNotifier,比较关键,通知JobMananger,ResultPartition已经ready,可以开始consume
private static class JobManagerResultPartitionConsumableNotifier implements ResultPartitionConsumableNotifier { /** * {@link ExecutionContext} which is used for the failure handler of {@link ScheduleOrUpdateConsumers} * messages. */ private final ExecutionContext executionContext; private final ActorGateway jobManager; private final ActorGateway taskManager; private final FiniteDuration jobManagerMessageTimeout; @Override public void notifyPartitionConsumable(JobID jobId, final ResultPartitionID partitionId) { final ScheduleOrUpdateConsumers msg = new ScheduleOrUpdateConsumers(jobId, partitionId); //通知jobmanager,去deployconsumer Future<Object> futureResponse = jobManager.ask(msg, jobManagerMessageTimeout); //等JobManager的回复 futureResponse.onFailure(new OnFailure() { //失败,即无法deploy consumer @Override public void onFailure(Throwable failure) { LOG.error("Could not schedule or update consumers at the JobManager.", failure); // Fail task at the TaskManager FailTask failMsg = new FailTask( partitionId.getProducerId(), new RuntimeException("Could not notify JobManager to schedule or update consumers", failure)); taskManager.tell(failMsg); } }, executionContext); } }
RegisterTask
在NetworkEnvironment中比较重要的操作,是注册task,需要为task的resultpartition和inputgate分配bufferpool
public void registerTask(Task task) throws IOException { final ResultPartition[] producedPartitions = task.getProducedPartitions(); final ResultPartitionWriter[] writers = task.getAllWriters(); ResultPartitionConsumableNotifier jobManagerNotifier; synchronized (lock) { for (int i = 0; i < producedPartitions.length; i++) { final ResultPartition partition = producedPartitions[i]; final ResultPartitionWriter writer = writers[i]; // Buffer pool for the partition BufferPool bufferPool = null; try { bufferPool = networkBufferPool.createBufferPool(partition.getNumberOfSubpartitions(), false); //创建LocalPool,注意Reqired的segment数目是Subpartitions的数目,即一个subP一个segment partition.registerBufferPool(bufferPool); //把localPool注册到ResultPartition partitionManager.registerResultPartition(partition); //注册到partitionManager } // Register writer with task event dispatcher taskEventDispatcher.registerWriterForIncomingTaskEvents(writer.getPartitionId(), writer); } // Setup the buffer pool for each buffer reader final SingleInputGate[] inputGates = task.getAllInputGates(); for (SingleInputGate gate : inputGates) { BufferPool bufferPool = null; try { bufferPool = networkBufferPool.createBufferPool(gate.getNumberOfInputChannels(), false); gate.setBufferPool(bufferPool); } // Copy the reference to prevent races with concurrent shut downs jobManagerNotifier = partitionConsumableNotifier; } for (ResultPartition partition : producedPartitions) { // Eagerly notify consumers if required. if (partition.getEagerlyDeployConsumers()) { //如果是eager的方式,通知jobmanager,可以deploy consumer了 jobManagerNotifier.notifyPartitionConsumable( partition.getJobId(), partition.getPartitionId()); } } }