一、内容
二、练习
练习1
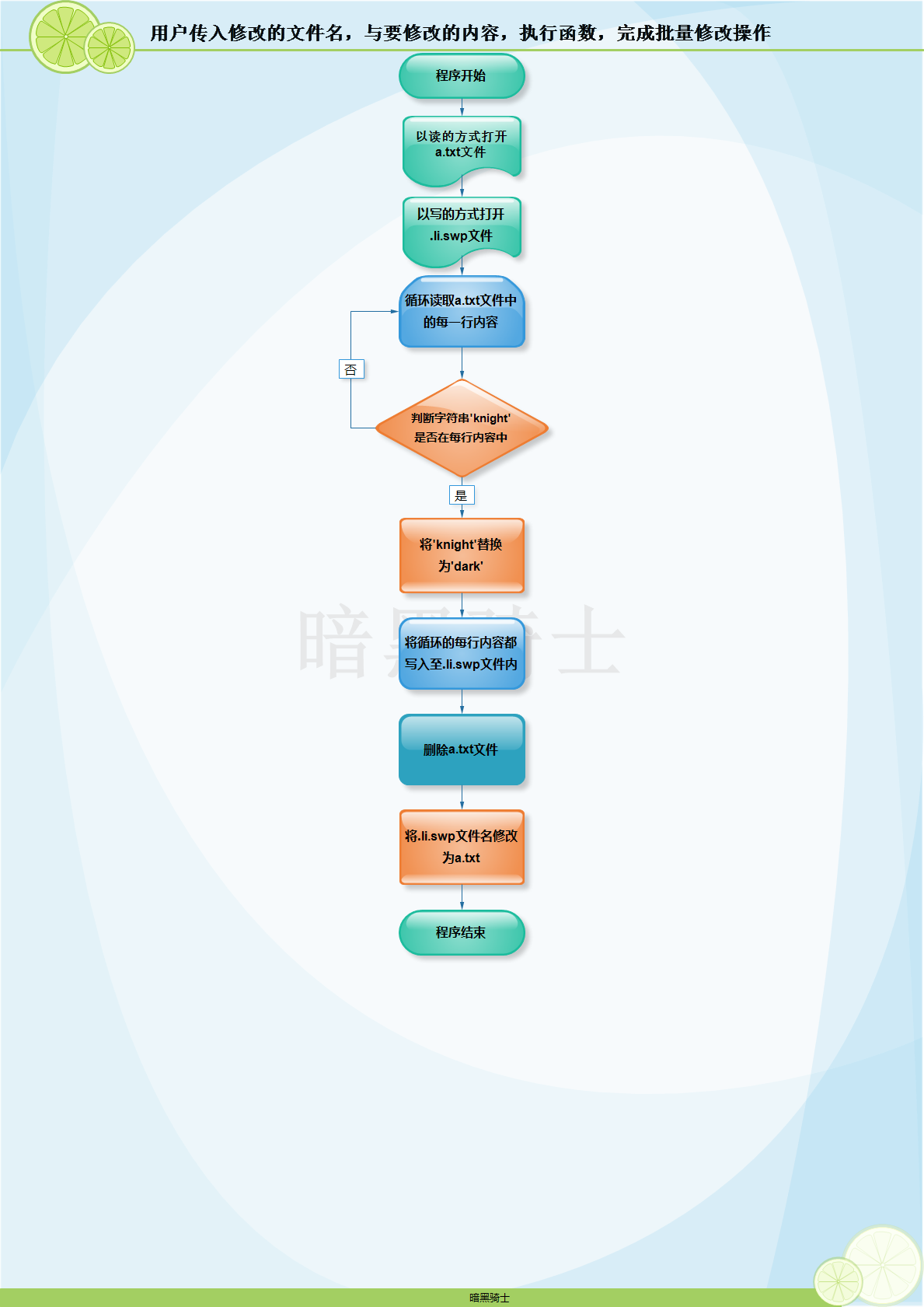
题目:写函数,用户传入修改的文件名,与要修改的内容,执行函数,完成批量修改操作
图示:
代码:
import os
def revise(f,r,x):
with open(f,'r',encoding='utf-8') as read_f,
open('.li.swp','w',encoding='utf-8') as write_f:
for line in read_f:
if r in line:
line = line.replace(r,x)
write_f.write(line)
os.remove(f)
os.rename('.li.swp',f)
revise('a.txt','knight','dark')
输出结果:
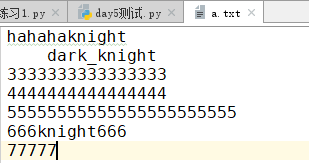
a.txt原文件内容:
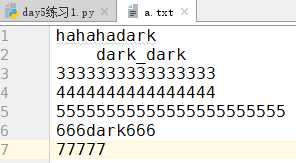
运行该程序后,a.txt文件的内容:
练习2
题目:写函数,计算传入字符串中【数字】、【字母】、【空格】 以及 【其他】的个数
图示:
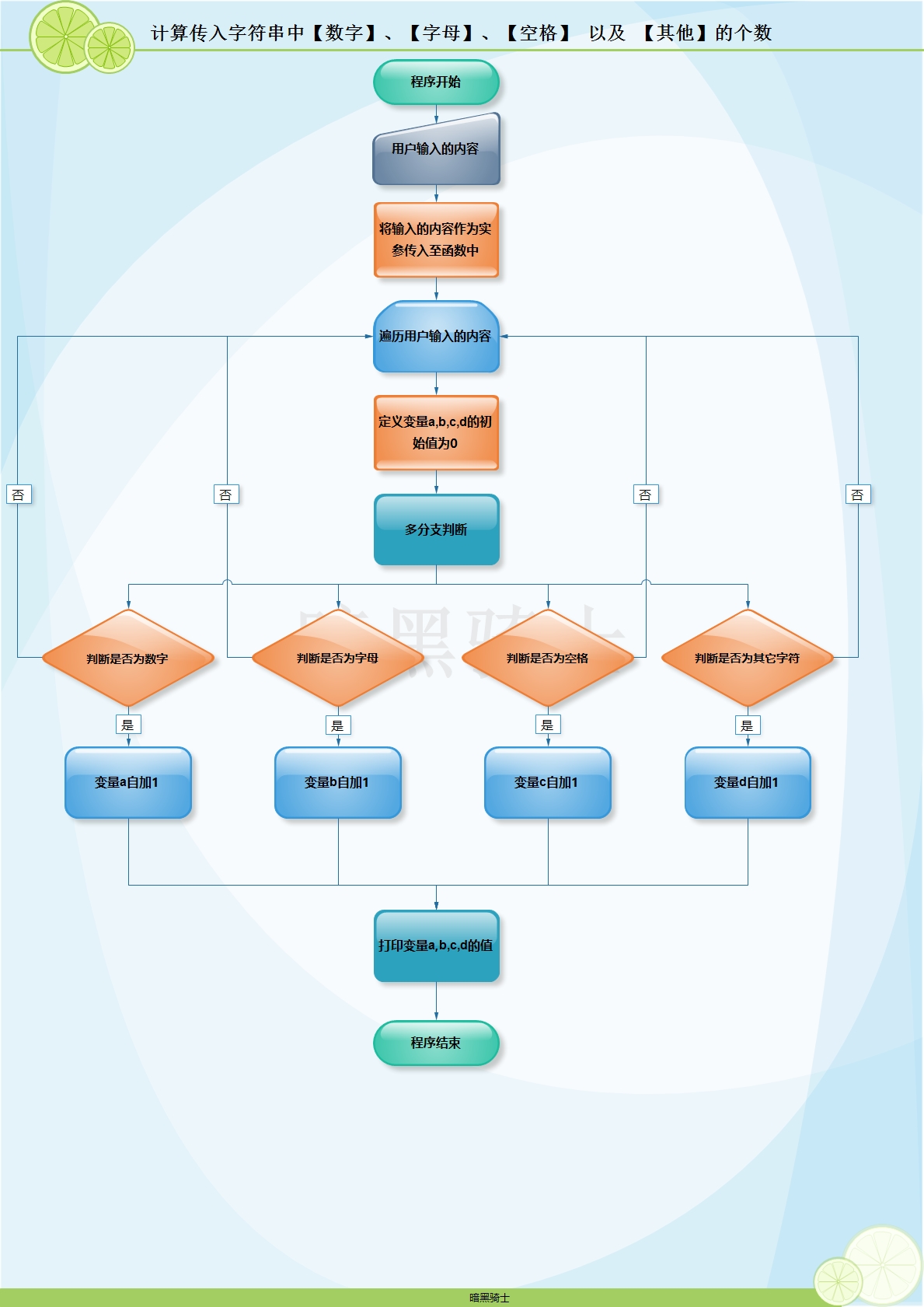
代码:
user_input = input('Please enter:')
def count(w):
a = 0
b = 0
c = 0
d = 0
for i in w:
if i.isdigit():
a += 1
elif i.isalpha():
b += 1
elif i.isspace():
c += 1
else:
d += 1
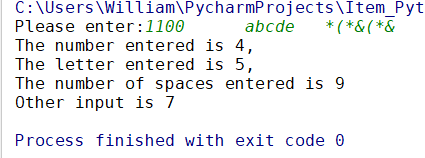
print('The number entered is %s,
The letter entered is %s,
The number of spaces entered is %s
Other input is %s'%(a,b,c,d))
count(user_input)
输出结果:
例:
练习3
题目:写函数,判断用户传入的对象(字符串、列表、元组)长度是否大于5。
图示:
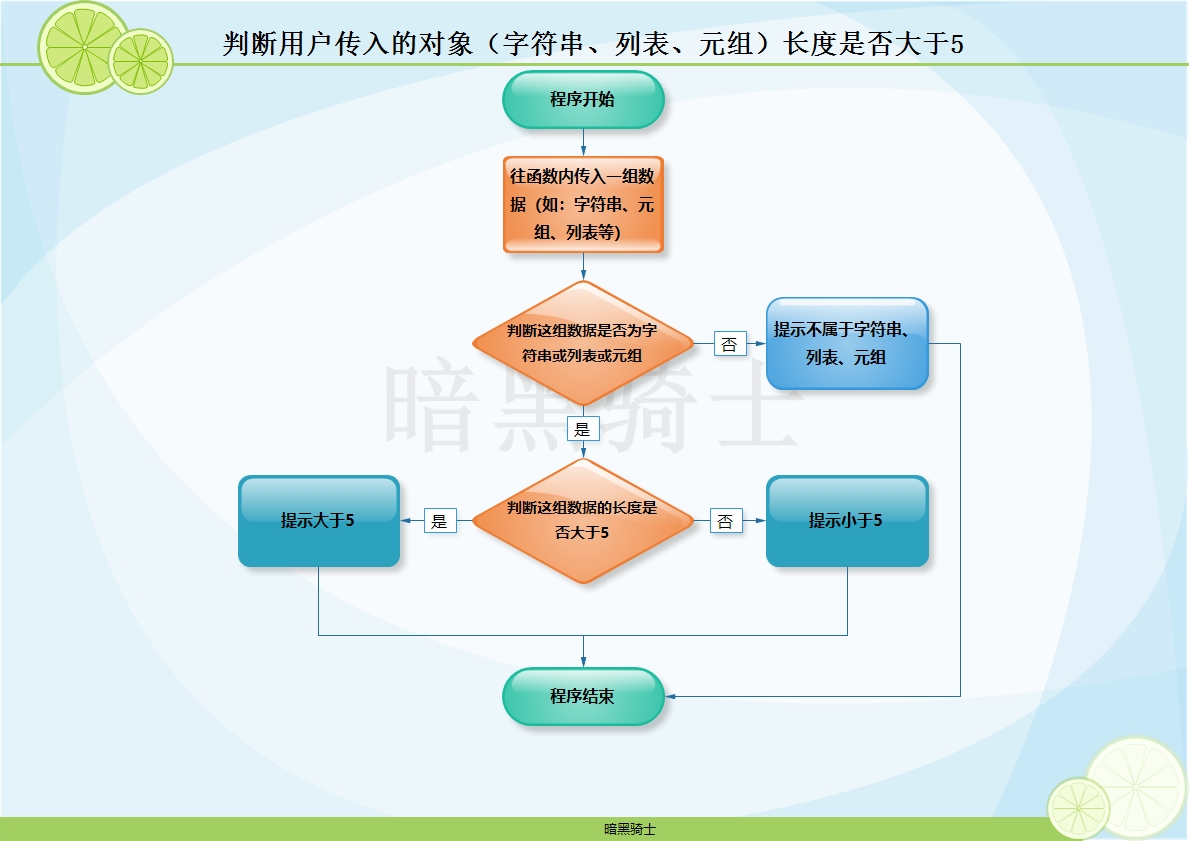
代码:
def func_len(w):
if isinstance(w,str) or isinstance(w,tuple) or isinstance(w,list):
# isinstance是Python中的一个内建函数。是用来判断一个对象的变量类型。
if len(w)>5:
print('length>5')
else:
print('length<5')
else:
print('not str,not list,not tuple.')
func_len('knight')
func_len([1,2,3,4,5,6,7])
func_len((1,2,3))
# 当用户输入的不是字符串、元组、列表时
func_len({'a':1,'b':2})
输出结果:

length>5 length>5 length<5 not str,not list,not tuple.
练习4
题目:写函数,检查用户传入的对象(字符串、列表、元组)的每一个元素是否含有空内容。
图示:
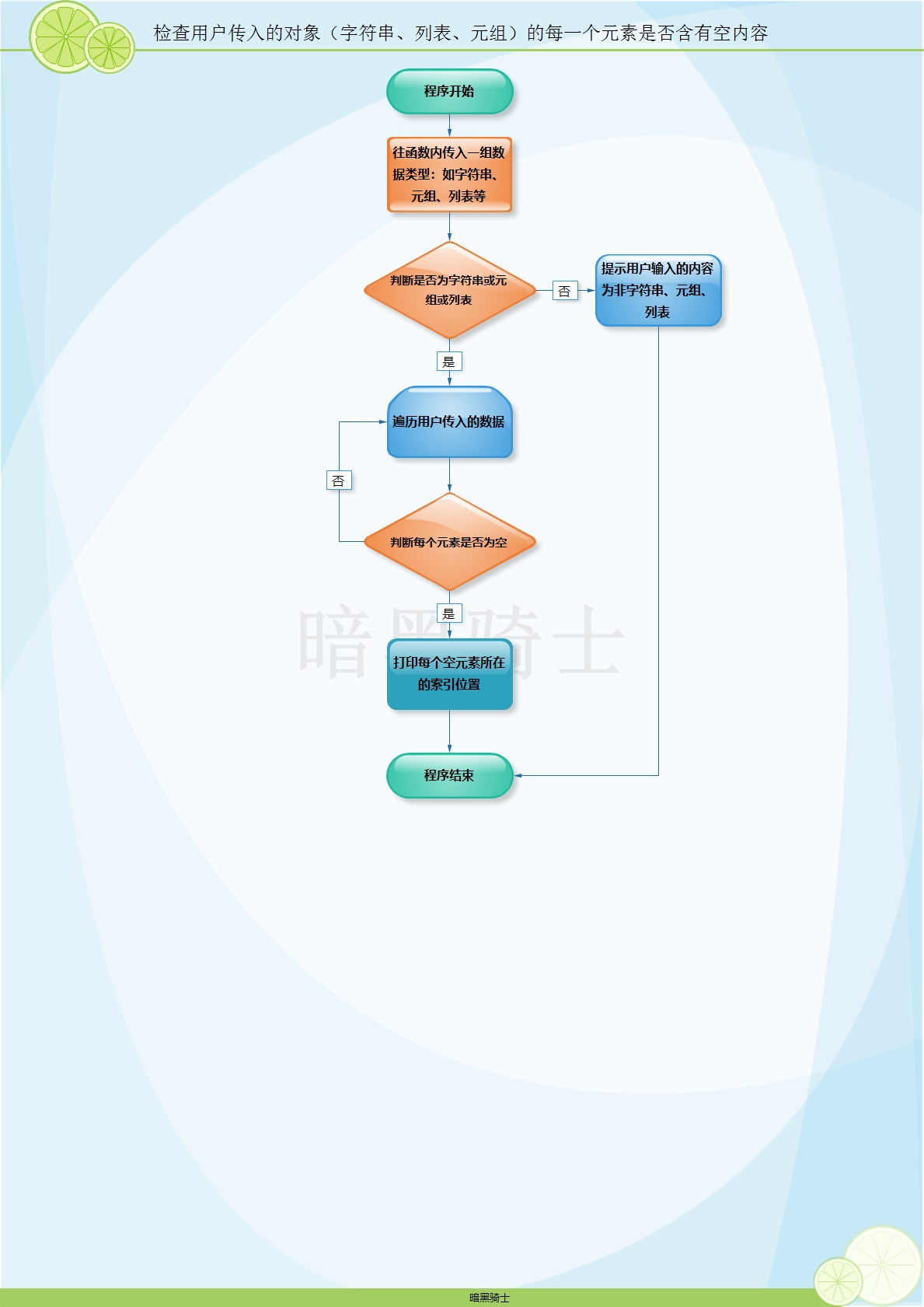
代码:
def foo(func):
if isinstance(func,str) or isinstance(func,list) or isinstance(func,tuple):
for i,j in enumerate(func,0):
if not str(j).strip():
print('The No.%s element is empty'%i)
else:
print('not str,not list,not tuple')
foo(['','2','knight','','lisa'])
foo(('tangbao','zhuozi','','',1,2,3))
foo({'x':1,'y':2})
输出结果:

The No.0 element is empty The No.3 element is empty The No.2 element is empty The No.3 element is empty not str,not list,not tuple
练习5
题目:写函数,检查传入列表的长度,如果大于2,那么仅保留前两个长度的内容,并将新内容返回给调用者。
图示:
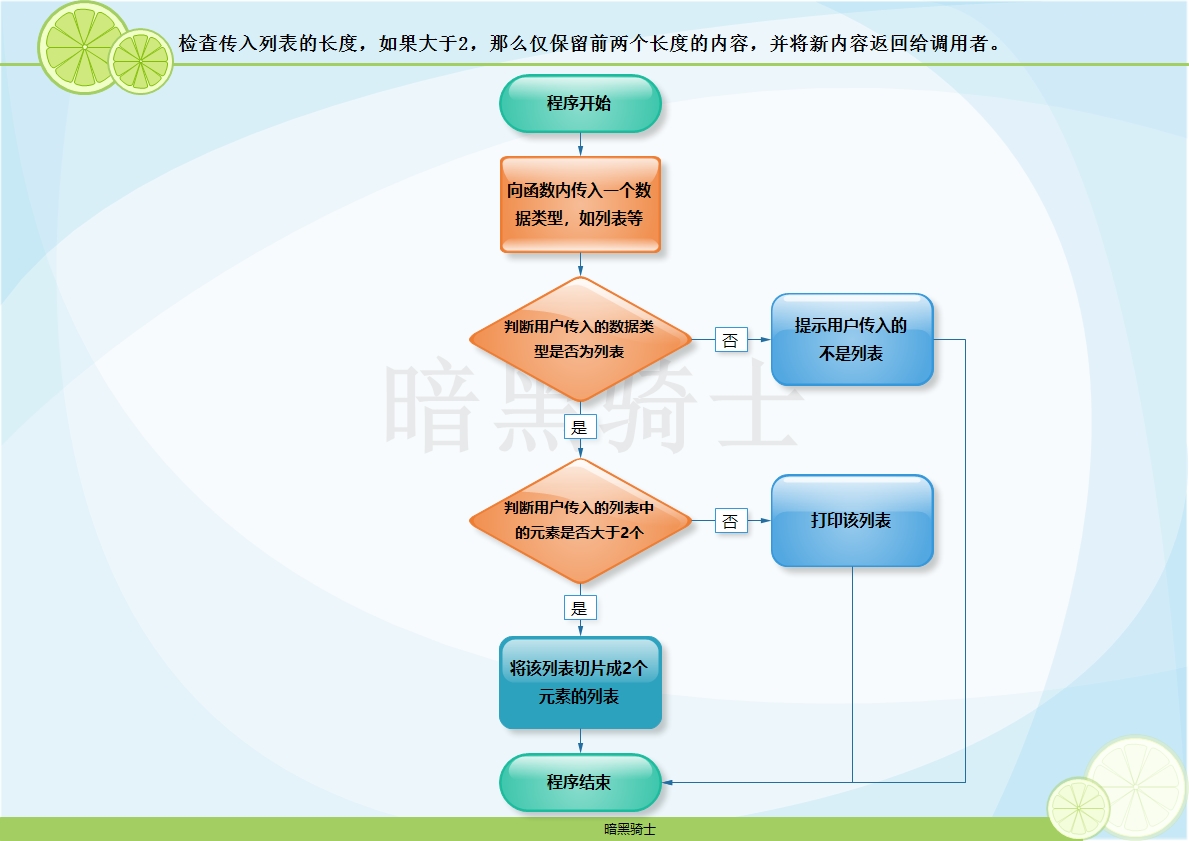
代码:
def foo(func):
if isinstance(func,list):
if len(func) > 2:
return func[0:2]
else:
return func
return 'not a list'
print(foo({'x':1,'y':2}))
print(foo(['knight','lisa','zhuozi','tangbao']))
print(foo(['haha']))
输出结果:

not a list ['knight', 'lisa'] ['haha']
练习6
题目:写函数,检查获取传入列表或元组对象的所有奇数位索引对应的元素,并将其作为新列表返回给调用者。
图示:
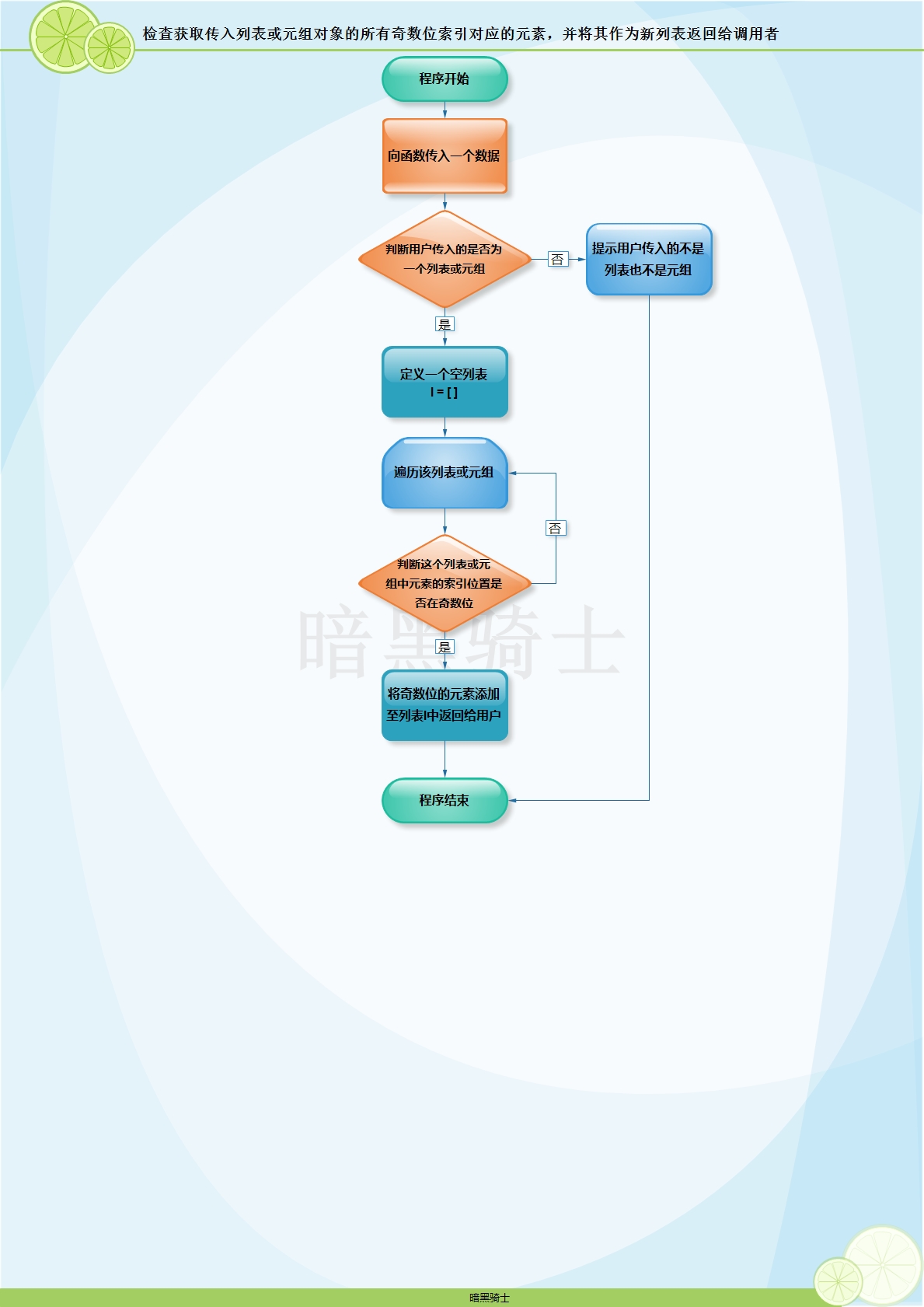
代码:
def foo(func):
if isinstance(func,list) or isinstance(func,tuple):
l = []
for i in func:
if func.index(i) % 2 != 0:
l.append(i)
return l
return 'not list or not tuple.'
print(foo([0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]))
print(foo({'x':1,'y':2}))
print(foo('knight'))
输出结果:

[1, 3, 5, 7] not list or not tuple. not list or not tuple.
练习7
题目:写函数,检查传入字典的每一个value的长度,如果大于2,那么仅保留前两个长度的内容,并将新内容返回给调用者。
图示:
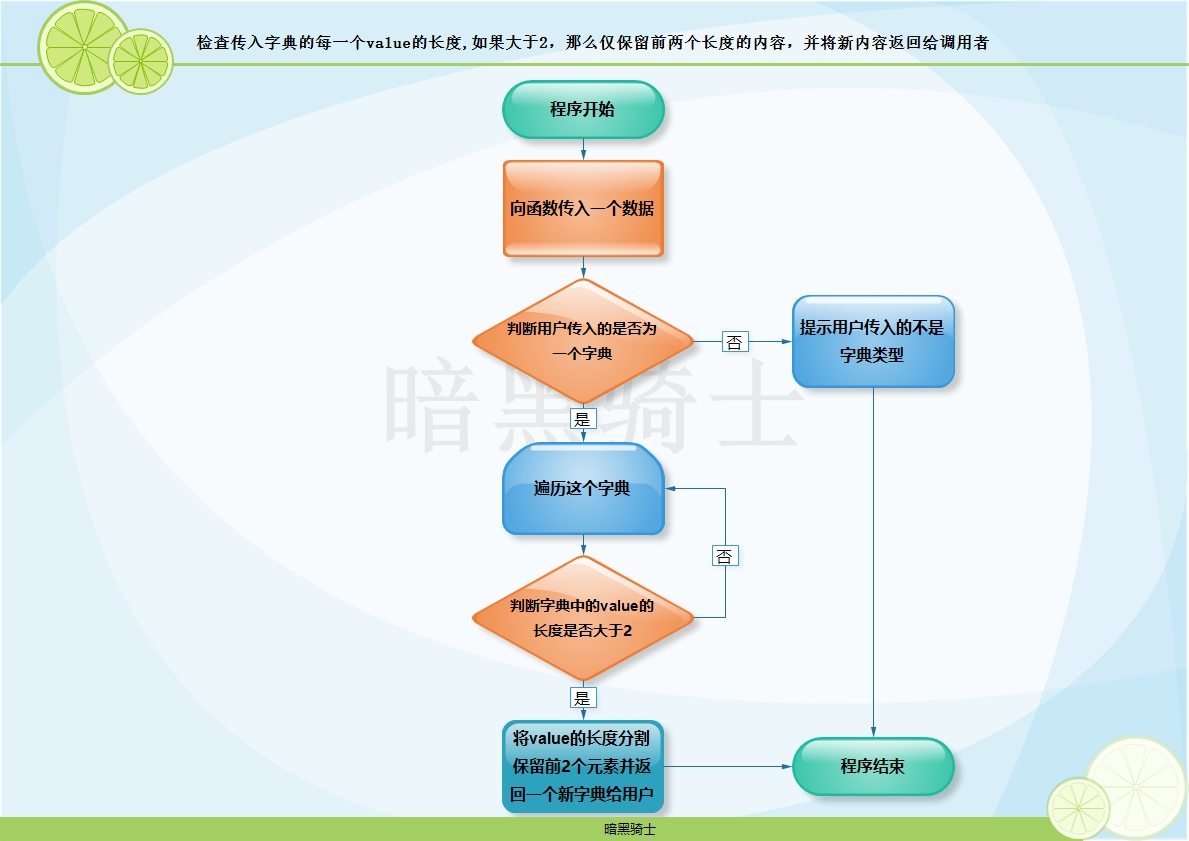
代码:
def foo(dic):
if isinstance(dic,dict):
for i in dic:
if len(dic[i]) > 2:
dic[i] = dic[i][:2]
return dic
return 'not dic'
print(foo({"k1": "value1", "k2": [11,22,33,44],"k3":"value3"}))
print(foo(['knight','lisa',1,2,3,4]))
输出结果:

{'k1': 'va', 'k2': [11, 22], 'k3': 'va'}
not dic
三、英语
1、instance
['ɪnstəns] n.实例
2、return
[rɪ'tɝn] vt.返回
3、encode
[ɪn'kod] vt.编码
4、decode
[‚diː'kəʊd] vt.解码
5、read
[rid; rɛd] vi.读
6、write
[raɪt] vi.写
