在上一遍博客中,我们已经分析了actor创建的大致过程,但只是涉及到了Dipatcher/Mailbox/ActorCell/InternalActorRef等对象的创建,并没有介绍我们自定义的继承Actor特质的类如何完成初始化。这篇文章对这一部分内容进行简单的补充。
在akka.actor.dungeon.init代码中,有一段代码我们当时没有分析,此处对此代码进行深入分析,然后才能找到Actor子类完成创建的真实过程。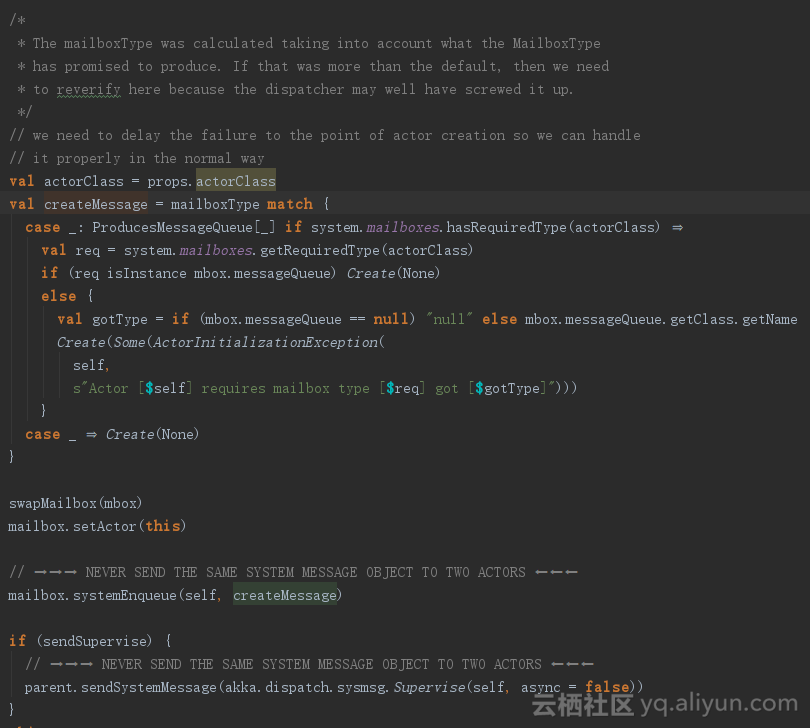
上面是init的代码片段,其中有一个局部变量createMessage,根据前后分析,它的值应该是Create这个case
class。最后mailbox.systemEnqueue(self,
createMessage)这个代码给actor对应的邮箱发送了该消息。
/**
* INTERNAL API
*/
@SerialVersionUID(1L)
private[akka] final case class Create(failure: Option[ActorInitializationException]) extends SystemMessage // sent to self from Dispatcher.register根据Create类名以及前后上下文分析,这应该是指示Actor完成初始化的。那么我们要分析一下actor是如何对该消息响应的。那么究竟是哪段代码对这个消息进行响应的呢?
如果读过之前的文章,你肯定能想起来Mailbox在循环处理消息时,有一个processAllSystemMessages方法,这个方法里面调用了actor的systemInvoke方法。具体源码如下:
/**
* Will at least try to process all queued system messages: in case of
* failure simply drop and go on to the next, because there is nothing to
* restart here (failure is in ActorCell somewhere …). In case the mailbox
* becomes closed (because of processing a Terminate message), dump all
* already dequeued message to deadLetters.
*/
final def processAllSystemMessages() {
var interruption: Throwable = null
var messageList = systemDrain(SystemMessageList.LNil)
while ((messageList.nonEmpty) && !isClosed) {
val msg = messageList.head
messageList = messageList.tail
msg.unlink()
if (debug) println(actor.self + " processing system message " + msg + " with " + actor.childrenRefs)
// we know here that systemInvoke ensures that only "fatal" exceptions get rethrown
actor systemInvoke msg
if (Thread.interrupted())
interruption = new InterruptedException("Interrupted while processing system messages")
// don’t ever execute normal message when system message present!
if ((messageList.isEmpty) && !isClosed) messageList = systemDrain(SystemMessageList.LNil)
}
/*
* if we closed the mailbox, we must dump the remaining system messages
* to deadLetters (this is essential for DeathWatch)
*/
// 忽略剩余源码
}我们来研究一下systemInvoke的代码
/*
* MESSAGE PROCESSING
*/
//Memory consistency is handled by the Mailbox (reading mailbox status then processing messages, then writing mailbox status
final def systemInvoke(message: SystemMessage): Unit = {
/*
* When recreate/suspend/resume are received while restarting (i.e. between
* preRestart and postRestart, waiting for children to terminate), these
* must not be executed immediately, but instead queued and released after
* finishRecreate returns. This can only ever be triggered by
* ChildTerminated, and ChildTerminated is not one of the queued message
* types (hence the overwrite further down). Mailbox sets message.next=null
* before systemInvoke, so this will only be non-null during such a replay.
*/
def calculateState: Int =
if (waitingForChildrenOrNull ne null) SuspendedWaitForChildrenState
else if (mailbox.isSuspended) SuspendedState
else DefaultState
@tailrec def sendAllToDeadLetters(messages: EarliestFirstSystemMessageList): Unit =
if (messages.nonEmpty) {
val tail = messages.tail
val msg = messages.head
msg.unlink()
provider.deadLetters ! msg
sendAllToDeadLetters(tail)
}
def shouldStash(m: SystemMessage, state: Int): Boolean =
(state: @switch) match {
case DefaultState ⇒ false
case SuspendedState ⇒ m.isInstanceOf[StashWhenFailed]
case SuspendedWaitForChildrenState ⇒ m.isInstanceOf[StashWhenWaitingForChildren]
}
@tailrec
def invokeAll(messages: EarliestFirstSystemMessageList, currentState: Int): Unit = {
val rest = messages.tail
val message = messages.head
message.unlink()
try {
message match {
case message: SystemMessage if shouldStash(message, currentState) ⇒ stash(message)
case f: Failed ⇒ handleFailure(f)
case DeathWatchNotification(a, ec, at) ⇒ watchedActorTerminated(a, ec, at)
case Create(failure) ⇒ create(failure)
case Watch(watchee, watcher) ⇒ addWatcher(watchee, watcher)
case Unwatch(watchee, watcher) ⇒ remWatcher(watchee, watcher)
case Recreate(cause) ⇒ faultRecreate(cause)
case Suspend() ⇒ faultSuspend()
case Resume(inRespToFailure) ⇒ faultResume(inRespToFailure)
case Terminate() ⇒ terminate()
case Supervise(child, async) ⇒ supervise(child, async)
case NoMessage ⇒ // only here to suppress warning
}
} catch handleNonFatalOrInterruptedException { e ⇒
handleInvokeFailure(Nil, e)
}
val newState = calculateState
// As each state accepts a strict subset of another state, it is enough to unstash if we "walk up" the state
// chain
val todo = if (newState < currentState) unstashAll() reverse_::: rest else rest
if (isTerminated) sendAllToDeadLetters(todo)
else if (todo.nonEmpty) invokeAll(todo, newState)
}
invokeAll(new EarliestFirstSystemMessageList(message), calculateState)
}由于我们只是准备分析actor的创建过程,所以上面的代码,我们只关注对Create消息的处理:create(failure)。也就是说调用了create函数。
protected def create(failure: Option[ActorInitializationException]): Unit = {
def clearOutActorIfNonNull(): Unit = {
if (actor != null) {
clearActorFields(actor, recreate = false)
actor = null // ensure that we know that we failed during creation
}
}
failure.foreach { throw _ }
try {
val created = newActor()
actor = created
created.aroundPreStart()
checkReceiveTimeout
if (system.settings.DebugLifecycle) publish(Debug(self.path.toString, clazz(created), "started (" + created + ")"))
} catch {
case e: InterruptedException ⇒
clearOutActorIfNonNull()
Thread.currentThread().interrupt()
throw ActorInitializationException(self, "interruption during creation", e)
case NonFatal(e) ⇒
clearOutActorIfNonNull()
e match {
case i: InstantiationException ⇒ throw ActorInitializationException(
self,
"""exception during creation, this problem is likely to occur because the class of the Actor you tried to create is either,
a non-static inner class (in which case make it a static inner class or use Props(new ...) or Props( new Creator ... )
or is missing an appropriate, reachable no-args constructor.
""", i.getCause)
case x ⇒ throw ActorInitializationException(self, "exception during creation", x)
}
}
}我们来分析一下这个create函数。其中主要的逻辑都在try中,首先调用newActor函数,创建了Actor实例,然后赋值给actor字段。actor字段我们已经知道,这是ActorCell的最终actor实例。
/*
* ACTOR INSTANCE HANDLING
*/
//This method is in charge of setting up the contextStack and create a new instance of the Actor
protected def newActor(): Actor = {
contextStack.set(this :: contextStack.get)
try {
behaviorStack = emptyBehaviorStack
val instance = props.newActor()
if (instance eq null)
throw ActorInitializationException(self, "Actor instance passed to actorOf can't be 'null'")
// If no becomes were issued, the actors behavior is its receive method
behaviorStack = if (behaviorStack.isEmpty) instance.receive :: behaviorStack else behaviorStack
instance
} finally {
val stackAfter = contextStack.get
if (stackAfter.nonEmpty)
contextStack.set(if (stackAfter.head eq null) stackAfter.tail.tail else stackAfter.tail) // pop null marker plus our context
}
}newActor函数源码如上,抛去其他代码,该函数调用了props.newActor创建了最终的Actor实例,也就是我们自定义的Actor子类。通过源码注释我们知道behaviorStack是actor当前行为的一个栈。如果读者用过become的话,对这段代码应该比较好理解。我们在actor内部使用become方法改变当前actor实例的时候,其实是把新的receive函数压入栈顶,mailbox在调用receive时,其实是取出当前栈顶的receive函数进行处理的。当然这是akka以前版本的默认行为。为什么这样说呢?因为新版本默认行为就是简单的把最新的receive函数替换旧receive函数,如果想恢复旧receive函数,需要开发者在编码时,再次调用become用旧receive函数替换当前receive。为什么要这么做?当然是为了防止开发者恶意或者无意中胡乱调用become,造成栈溢出喽。
props.newActor我们不再深入分析,这应该就是通过反射创建Actor特质的子类,也就是我们自定义的actor。
至此,我们自定义的actor就真正完成了初始化。细心的读者一定会发现,就连actor最终的实例化,都是异步的。因为newActor是通过Create消息触发的,而Mailbox对所有消息的处理都是在单独的线程处理的。如果actor的创建过程中有一些线程不安全的代码,就需要注意喽。