多线程的实现方式:demo1、demo2
demo1:继承Thread类,重写run()方法
package thread_test; public class ThreadDemo1 extends Thread { ThreadDemo1(){ } ThreadDemo1(String szName){ super(szName); } //重载run函数 public void run() { for(int count = 1 , row = 1 ; row < 10 ; row ++ , count ++) { for(int i = 0 ; i < count ; i ++) { System.out.print("*"); } System.out.println(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { //线程赛跑 ThreadDemo1 td1 = new ThreadDemo1(); ThreadDemo1 td2 = new ThreadDemo1(); ThreadDemo1 td3 = new ThreadDemo1(); td1.start(); td2.start(); td3.start(); } }
demo2:实现runnable接口,实现run()方法
package thread_test; public class ThreadDemo2 implements Runnable{ public void run() { for(int count = 1 , row = 1 ; row < 10 ; row ++ , count ++) { for(int i = 0 ; i < count ; i ++) { System.out.print("*"); } System.out.println(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { //存在线程赛跑问题 Runnable rb1 = new ThreadDemo2(); Runnable rb2 = new ThreadDemo2(); Runnable rb3 = new ThreadDemo2(); Thread td1 = new Thread(rb1); Thread td2 = new Thread(rb2); Thread td3 = new Thread(rb3); td1.start(); td2.start(); td3.start(); } }
demo3:两种方法解决进程赛跑问题
package thread_test; //两种方法解决线程赛跑 class ThreadWait extends Thread{ public ThreadWait() { } public ThreadWait(String name) { super(name); } @Override public void run() { for(int count = 1 , row = 1 ; row < 10 ; row ++ , count ++) { for(int i = 0 ; i < count ; i ++) { System.out.print("*"); } System.out.println(); } } } public class ThreadDemo3{ public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadDemo3 td = new ThreadDemo3(); // td.Method1(); td.Method2(); } public void Method1() { ThreadWait tw1 = new ThreadWait(); ThreadWait tw2 = new ThreadWait(); tw1.start(); while(tw1.isAlive()) { try{ Thread.sleep(100); }catch(Exception e){ e.getMessage(); } } tw2.start(); } public void Method2() { ThreadWait tw1 = new ThreadWait(); ThreadWait tw2 = new ThreadWait(); tw1.start(); try { tw1.join(); // 等待该线程中止 }catch(Exception e){ e.toString(); } tw2.start(); } }
线程异步访问数据导致问题:
package thread_test; //线程异步访问数据导致问题 class ShareData{ public static String szData = ""; } class ThreadDemo extends Thread{ private static ShareData oShare; ThreadDemo(){ } ThreadDemo(String name, ShareData oShare){ super(name); this.oShare = oShare; } public void run() { for(int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i ++) { if(this.getName().equals("th1")) { oShare.szData = "这是第一个进程"; try { Thread.sleep(100); }catch(Exception e) { } System.out.println(this.getName() + oShare.szData); }else if(this.getName().equals("th2")) { oShare.szData = "这是第二个进程"; try { Thread.sleep(100); }catch(Exception e) { } System.out.println(this.getName() + oShare.szData); } } } } public class ThreadDemo5 { public static void main(String[] args) { ShareData oShare = new ShareData(); ThreadDemo th1 = new ThreadDemo("th1", oShare); ThreadDemo th2 = new ThreadDemo("th2", oShare); th1.start(); th2.start(); } }
得到的结果并不是我们想要的:

解决办法:
通过“锁”解决线程赛跑问题并实现多线程数据同步:
package thread_test;
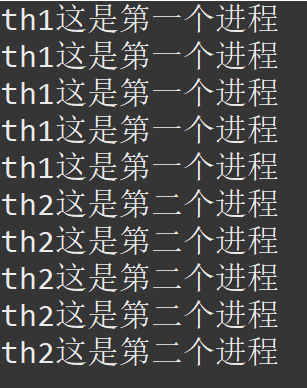
class ShareData0{ public static String szData = ""; } class ThreadDemo0 extends Thread{ private static ShareData0 oShare; ThreadDemo0(){ } ThreadDemo0(String name, ShareData0 oShare){ super(name); this.oShare = oShare; } public void run() { //同步快,并指出同步数据oShare synchronized(oShare){ for(int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i ++) { if(this.getName().equals("th1")) { oShare.szData = "这是第一个进程"; try { Thread.sleep(100); }catch(Exception e) { } System.out.println(this.getName() + oShare.szData); }else if(this.getName().equals("th2")) { oShare.szData = "这是第二个进程"; try { Thread.sleep(100); }catch(Exception e) { } System.out.println(this.getName() + oShare.szData); } } } } } public class ThreadDemo6 { public static void main(String[] args) { ShareData0 oShare = new ShareData0(); ThreadDemo0 th1 = new ThreadDemo0("th1", oShare); ThreadDemo0 th2 = new ThreadDemo0("th2", oShare); th1.start(); th2.start(); } }
得到结果:
死锁:由于两个线程都在等待对方释放各自拥有的锁的现象称为死锁,这种现象往往是由于相互潜逃的synchronized代码段而造成的,所以少用synchronized嵌套。
下面是一个死锁的例子:
package thread_test; public class LockedThread extends Thread{ private static Object A = new Object(); private static Object B = new Object(); private static boolean flag = true; public static void main(String[] args) { LockedThread th1 = new LockedThread(); LockedThread th2 = new LockedThread(); th1.start(); th2.start(); } public void AccessA() { flag = false; synchronized(A) { System.out.println("th1获得了A的锁"); try { Thread.sleep(1000); }catch(Exception e) { } System.out.println("th1还想要B的锁"); synchronized(B) { System.out.println("th1获得了B的锁"); } } } public void AccessB() { flag = true; synchronized(B) { System.out.println("th2获得了B的锁"); try { Thread.sleep(1000); }catch(Exception e) { } System.out.println("th2还想要A的锁"); synchronized(A) { System.out.println("th2获得了A的锁"); } } } public void run(){ if(flag) { AccessA(); }else { AccessB(); } } }
显示结果:

程序没有结束 而是停在了这里,这就是死锁。