相信使用过Spring的开发人员都用过@RequestBody、@ResponseBody注解,可以直接将输入解析成Json、将输出解析成Json,但HTTP 请求和响应是基于文本的,意味着浏览器和服务器通过交换原始文本进行通信,而这里其实就是HttpMessageConverter发挥着作用。
HttpMessageConverter
Http请求响应报文其实都是字符串,当请求报文到java程序会被封装为一个ServletInputStream流,开发人员再读取报文,响应报文则通过ServletOutputStream流,来输出响应报文。
从流中只能读取到原始的字符串报文,同样输出流也是。那么在报文到达SpringMVC / SpringBoot和从SpringMVC / SpringBoot出去,都存在一个字符串到java对象的转化问题。这一过程,在SpringMVC / SpringBoot中,是通过HttpMessageConverter来解决的。HttpMessageConverter接口源码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public interface HttpMessageConverter<T> { boolean canRead(Class<?> clazz, MediaType mediaType); boolean canWrite(Class<?> clazz, MediaType mediaType); List<MediaType> getSupportedMediaTypes(); T read(Class<? extends T> clazz, HttpInputMessage inputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotReadableException; void write(T t, MediaType contentType, HttpOutputMessage outputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotWritableException;} |
下面以一例子来说明,
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
@RequestMapping("/test")@ResponseBodypublic String test(@RequestBody String param) { return "param '" + param + "'";} |
在请求进入test方法前,会根据@RequestBody注解选择对应的HttpMessageConverter实现类来将请求参数解析到param变量中,因为这里的参数是String类型的,所以这里是使用了StringHttpMessageConverter类,它的canRead()方法返回true,然后read()方法会从请求中读出请求参数,绑定到test()方法的param变量中。
同理当执行test方法后,由于返回值标识了@ResponseBody,SpringMVC / SpringBoot将使用StringHttpMessageConverter的write()方法,将结果作为String值写入响应报文,当然,此时canWrite()方法返回true。
借用下图简单描述整个过程:

在Spring的处理过程中,一次请求报文和一次响应报文,分别被抽象为一个请求消息HttpInputMessage和一个响应消息HttpOutputMessage。
处理请求时,由合适的消息转换器将请求报文绑定为方法中的形参对象,在这里同一个对象就有可能出现多种不同的消息形式,如json、xml。同样响应请求也是同样道理。
在Spring中,针对不同的消息形式,有不同的HttpMessageConverter实现类来处理各种消息形式,至于各种消息解析实现的不同,则在不同的HttpMessageConverter实现类中。
替换@ResponseBody默认的HttpMessageConverter
这里使用SpringBoot演示例子,在SpringMVC / SpringBoot中@RequestBody这类注解默认使用的是jackson来解析json,看下面例子:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
@Controller@RequestMapping("/user")public class UserController { @RequestMapping("/testt") @ResponseBody public User testt() { User user = new User("name", 18); return user; }} |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
public class User { private String username; private Integer age; private Integer phone; private String email; public User(String username, Integer age) { super(); this.username = username; this.age = age; }} |
浏览器访问/user/testt返回如下:
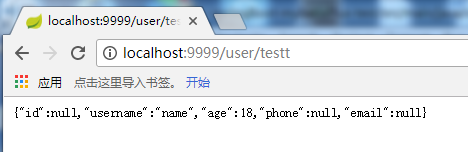
这就是使用jackson解析的结果,现在来改成使用fastjson解析对象,这里就是替换默认的HttpMessageConverter,就是将其改成使用FastJsonHttpMessageConverter来处理Java对象与HttpInputMessage/HttpOutputMessage间的转化。
首先新建一配置类来添加配置FastJsonHttpMessageConverter,Spring4.x开始推荐使用Java配置加注解的方式,也就是无xml文件,SpringBoot就更是了。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
|
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializerFeature;import com.alibaba.fastjson.support.config.FastJsonConfig;import com.alibaba.fastjson.support.spring.FastJsonHttpMessageConverter;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.HttpMessageConverters;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter;import java.nio.charset.Charset;@Configurationpublic class HttpMessageConverterConfig { //引入Fastjson解析json,不使用默认的jackson //必须在pom.xml引入fastjson的jar包,并且版必须大于1.2.10 @Bean public HttpMessageConverters fastJsonHttpMessageConverters() { //1、定义一个convert转换消息的对象 FastJsonHttpMessageConverter fastConverter = new FastJsonHttpMessageConverter(); //2、添加fastjson的配置信息 FastJsonConfig fastJsonConfig = new FastJsonConfig(); SerializerFeature[] serializerFeatures = new SerializerFeature[]{ // 输出key是包含双引号// SerializerFeature.QuoteFieldNames, // 是否输出为null的字段,若为null 则显示该字段// SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue, // 数值字段如果为null,则输出为0 SerializerFeature.WriteNullNumberAsZero, // List字段如果为null,输出为[],而非null SerializerFeature.WriteNullListAsEmpty, // 字符类型字段如果为null,输出为"",而非null SerializerFeature.WriteNullStringAsEmpty, // Boolean字段如果为null,输出为false,而非null SerializerFeature.WriteNullBooleanAsFalse, // Date的日期转换器 SerializerFeature.WriteDateUseDateFormat, // 循环引用 SerializerFeature.DisableCircularReferenceDetect, }; fastJsonConfig.setSerializerFeatures(serializerFeatures); fastJsonConfig.setCharset(Charset.forName("UTF-8")); //3、在convert中添加配置信息 fastConverter.setFastJsonConfig(fastJsonConfig); //4、将convert添加到converters中 HttpMessageConverter<?> converter = fastConverter; return new HttpMessageConverters(converter); }} |
这里将字符串类型的值如果是null就返回“”,数值类型的如果是null就返回0,重启应用,再次访问/user/testt接口,返回如下:
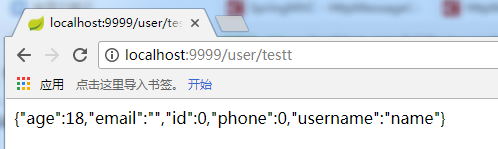
可以看到此时null都转化成“”或0了