======================Barycentric interpolation======================================
<1>2d/3d Check point in triangle test

float areas(vector p1;vector p2;vector p3) { return length(cross(p1-p2,p3-p2)) * 0.5f; } int ptInTri(vector inpt;vector p1;vector p2; vector p3) { float s = areas(p1,p2,p3); float s1 = areas(inpt,p2,p3) / s; float s2 = areas(inpt,p3,p1) / s; float s3 = areas(inpt,p1,p2) / s; if(s1<0.0f || s1>1.0f) { return false; } if(s2 < 0.0f || s2 >1) { return false; } if(s3 < 0.0f || s3 >1) { return false; } float all = s1 + s2 + s3; if (all-1.0f<0.000001f) return true; else return false; }
<2>2d check can use :
<test 3d in houdini found problem>

int ptInTri2(vector P;vector A;vector B; vector C) { vector u = B - A; vector v = C - A; vector w = P - A; vector vCrossW = cross(v, w); vector vCrossU = cross(v, u); if (dot(vCrossW, vCrossU) < 0) return false; vector uCrossW = cross(u, w); vector uCrossV = cross(u, v); // Test sign of t if (dot(uCrossW, uCrossV) < 0) return false; float denom = length(uCrossV); float r = length(vCrossW) / denom; float t = length(uCrossW) / denom; return (r + t <= 1); }
<3> Color Interpolation:
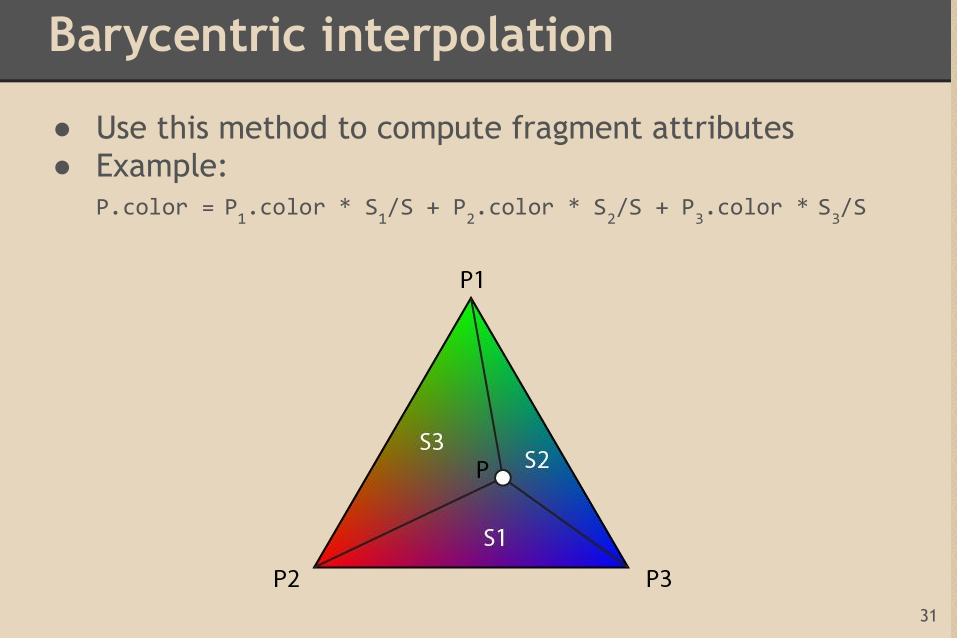

float areas(vector p1;vector p2;vector p3) { return length(cross(p1-p2,p3-p2)) * 0.5f; } vector P = getInputP(); float s = areas(p1,p2,p3); float s1 = areas(P,p2,p3) / s; float s2 = areas(P,p3,p1) / s; float s3 = areas(P,p1,p2) / s; vector PColor = p1.color * s1 + p2.color*s2 + p3.color*s3;
<4>we can use this method to getPointAt uv like maya function or houdini primuv();

float areas(vector p1;vector p2;vector p3) { return length(cross(p1-p2,p3-p2)) * 0.5f; } vector getPointAtUV(float u;float v) { clamp(u,0,1); clamp(v,0,1); // get current gdp's points vector gdpPtsPos[]; for(int i=0;i<3;i++) { vector curl = point(0,"P",i); //printf("%f ,%f , %f ",curl[0],curl[1],curl[2]); append(gdpPtsPos,curl); } vector p1 = gdpPtsPos[0]; vector p2 = gdpPtsPos[1]; vector p3 = gdpPtsPos[2]; // tri area float s = areas(p1,p2,p3); // reverse to get base on u value float uArea = u * 0.5 / s; // reverse to get base on v value float vArea = v * 0.5 / s ; // the w value float wArea =0; if(1 - uArea - vArea < 0) { wArea = 0; } else { wArea =( 1 - u - v )*0.5 / s; } //https://www.scratchapixel.com/lessons/3d-basic-rendering/ray-tracing-rendering-a-triangle/barycentric-coordinates //P=uA+vB+wC. vector retP = p1 * uArea + p2*vArea + p3*wArea; return retP; } #define maxscatter 100000 for(int i=0;i<maxscatter;i++) { float u = rand(i); float v = rand(i*100); vector retPos = getPointAtUV(u,v); addpoint(geoself(),retPos); }
<4>Color Define:
(1)ARGB:uint32_t,也就是单位为uint8_t ,共4个,a ,r ,g ,b 0xFF FF FF FF (255,255,255,255)
// uint32_t c; A:(uint8_t) ( (c & 0xFF 00 00 00) >>24) R:(uint8_t) ( (c & 0x00 FF 00 00) >>16) G:(uint8_t) ( (c & 0x00 FF 00 00) >>8) B:(uint8_t) ( (c & 0x00 00 00 FF) >>0)
(2)从uint8_t r,g,b,a转换到uint32_t,用位和求回去
((uint32_t)a<<24) | ((uint32_t)r<<16) | ((uint32_t)g<<8) | ((uint32_t)b<<0)
(2)float color:sixteen bytes:
struct color{float a, float r,float g,float b}
转换成ARGB(uint32_t)颜色也简单.
color fc = {1.0f,0.5f,0.0f,1.0f};
uint8_t r = (uint8_t) (floorf(fc.r*255.0f))
uint8_t g = (uint8_t) (floorf(fc.g*255.0f))
uint8_t b = (uint8_t) (floorf(fc.b*255.0f))
uint8_t a = (uint8_t) (floorf(fc.a*255.0f))
=========================Rasterization==================================================
<1>Line:
画斜线没用到斜率方程,直接用的线性差值。
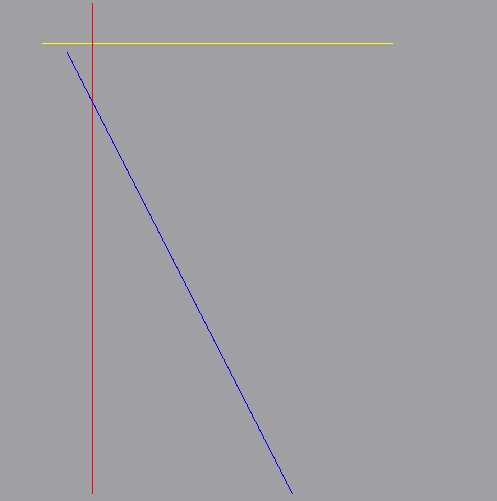
DrawApi.h

#ifndef DRAWAPI_H #define DRAWAPI_H #include <QImage> #include "LineSegment.h" #include <glm/glm.hpp> #include <iostream> #include "MathUtility.h" using namespace TopVertex; class DrawApi { public: template <typename T = glm::vec3> static void drawLine(QImage &image ,LineSegment<T> &line,const glm::vec3 &color) { auto &sp = line.startPoint(); auto &ep = line.endPoint(); float m = line.getSlope(); if(line.getType() == LineSegment<T>::HORIZON) { std::cout << "write horizon line "; auto y = sp[1]; for(int x=sp[0] ; x <= ep[0]; x++) { image.setPixel(x,y,qRgb(color[0],color[1],color[2])); } return; } if(line.getType() == LineSegment<T>::VERTICAL) { std::cout << "write verticle line "; auto x = sp[0]; auto y0 = sp[1]; auto y1 = ep[1]; if(y0 < y1) { for(int y=y0;y<=y1;y++) { image.setPixel(x,y,qRgb(color[0],color[1],color[2])); } } else { for(int y=y1;y<=y0;y++) { image.setPixel(x,y,qRgb(color[0],color[1],color[2])); } } return; } if(line.getType() == LineSegment<T>::NORMAL) { std::cout << "write normal line "; int startRow = 0; int endRow = 0; if(sp[1] < ep[1]) { startRow = sp[1]; endRow = ep[1]; } else { startRow = ep[1]; endRow = sp[1]; } for(int r = startRow;r<=endRow;r++) { auto bias = GLY_MATH::fit<float>(r,startRow,endRow,0.1f,1.0f); auto pos = GLY_MATH::linearInterpolation(sp,ep,bias); image.setPixel(pos[0],pos[1],qRgb(color[0],color[1],color[2])); } return; } } }; #endif // DRAWAPI_H
LineSegment.h

#ifndef LINESEGMENT_H #define LINESEGMENT_H #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #include <string> #include <iostream> #include <glm/glm.hpp> template <typename T> class LineSegment { public: typedef T value_type; enum TYPE{VERTICAL,HORIZON,NORMAL}; LineSegment(T startPoint,T endPoint): mStartPoint(startPoint),mEndPoint(endPoint) { // LINE PROPERTY evalLineProperty(); // LINE PROPERTY } LineSegment()=default; void setPoints(const T &startPoint , const T &endPoint) { mStartPoint = startPoint; mEndPoint = endPoint; evalLineProperty(); } inline T & operator[](int i) { if(i == 0) { return mStartPoint; } else if(i == 1) { return mEndPoint; } else { throw std::string("Can't get point over 2 ").c_str(); } } TYPE getType(); T &startPoint(); T &endPoint(); T startPoint()const; T endPoint()const; float getSlope()const; template <typename T2,typename T3> inline T2 intersect(const LineSegment<T3> &Line) { auto st_y = Line.startPoint()[1]; // get line y value auto it_x = (st_y - startPoint()[1] + startPoint()[0]*getSlope())/getSlope(); // y slope function get x pos return T2(it_x,st_y); } private: void evalLineProperty() { auto x0 = mStartPoint[0]; auto x1 = mEndPoint[0]; if(x0 > x1) { swap(mStartPoint,mEndPoint); } x0 = mStartPoint[0]; x1 = mEndPoint[0]; auto y0 = mStartPoint[1]; auto y1 = mEndPoint[1]; if(fabs(y1-y0) <= 0.0000001f) // horizon line slope = 0 { mSlope = 0.0f; mLineType = HORIZON; } else if(fabs(x1-x0) <= 0.000001f) // verticle line slope = 0 { mSlope = 0.0f; mLineType = VERTICAL; } else // slope !=0 { mSlope = (y1 - y0) / (x1-x0); mLineType = NORMAL; } } T mStartPoint; T mEndPoint; TYPE mLineType; float mSlope; }; template<typename T> typename LineSegment<T>::TYPE LineSegment<T>::getType() { return mLineType; } template<typename T> float LineSegment<T>::getSlope() const { return mSlope; } template<typename T> T &LineSegment<T>::startPoint() { return mStartPoint; } template<typename T> T &LineSegment<T>::endPoint() { return mEndPoint; } template<typename T> T LineSegment<T>::startPoint()const { return mStartPoint; } template<typename T> T LineSegment<T>::endPoint()const { return mEndPoint; } // ostream inline std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream &os,LineSegment<glm::vec3> line) { os << "Line start points:" << line.startPoint()[0] << " " <<line.startPoint()[1] << " "<<line.startPoint()[2] << " | " << "end:" << line.endPoint()[0]<< " "<< line.endPoint()[1] << " "<< line.endPoint()[2] ; return os; } inline std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream &os,LineSegment<glm::vec2> line) { os << "Line start points:" << line.startPoint()[0] << " " <<line.startPoint()[1] << "|" << "end:" << line.endPoint()[0]<< " "<< line.endPoint()[1] ; return os; } #endif // LINESEGMENT_H
MathUtility.h

#ifndef MATHUTILITY_H #define MATHUTILITY_H #include <string> #include <vector> #include <iostream> #include <sstream> using namespace std; namespace TopVertex { class GLY_MATH { public: template<typename T> static T linearInterpolation(T val1 , T val2,float bias) { return val1*(1-bias) + val2*bias; } template<typename T> static T min(T a, T b) { if (a > b) { return b; } else { return a; } } template<typename T> static T max(T a, T b) { if (a > b) { return a; } else { return b; } } template<typename T> static bool zero_compare(T a, double tol = 0.00001) { return a >= -tol && a <= tol; } // DO NOT USE THIS FIT TO FIT VECTOR VALUE template<typename T> static T fit(T var, T omin, T omax, T nmin, T nmax) { T d = omax - omin; if (zero_compare(d)) { return (nmin + nmax) * 0.5; } if (omin < omax) { if (var < omin) return nmin; if (var > omax) return nmax; } else { if (var < omax) return nmax; if (var > omin) return nmin; } return nmin + (nmax - nmin) * (var - omin) / d; } //return -1 to 1 template<typename T> static T fit_negate(T var, T omin, T omax) { return fit(var, omin, omax, -1.0, 1.0); } //string split static std::vector<std::string> split_string(std::string &inputString, char &split_char) { std::stringstream ss(inputString); std::string sub_str; std::vector<std::string> sp_strPath; sp_strPath.clear(); while (getline(ss, sub_str, split_char)) { sp_strPath.push_back(sub_str); } return sp_strPath; } //value to string template<typename T> // T must be a value int/float/double static std::string value_to_str(T &value) { std::ostringstream os; os << value; return os.str(); } static int wang_inthash(int key) { // From http://www.concentric.net/~Ttwang/tech/inthash.htm key += ~(key << 16); key ^= (key >> 5); key += (key << 3); key ^= (key >> 13); key += ~(key << 9); key ^= (key >> 17); return key; } static int fastRandomInt(int seed) { int nseed = seed * 1664525+0XFFFFFFF; return wang_inthash(nseed); } static float fastRandom01(int seed) { return float(fastRandomInt(seed) % 1000000) / 1000000.0f; } }; } #endif // MATHUTILITY_H
Renderer.h

#ifndef RENDERER_H #define RENDERER_H #include <QImage> #include <iostream> #include <glm/glm.hpp> using namespace std; class Renderer { public: Renderer(); void render(); }; #endif // RENDERER_H
Renderer.cpp

#include "Renderer.h" #include "DrawApi.h" Renderer::Renderer() { } void Renderer::render() { QImage image(512,512,QImage::Format_RGB32); image.fill(Qt::gray); glm::vec3 p0(150,20,0); glm::vec3 p1(50,100,0); glm::vec3 p2(250,150,0); // write horizon line glm::vec3 p3(400,50,0); glm::vec3 p4(50,50,0); auto hline1 = LineSegment<glm::vec3>(p3,p4); DrawApi::drawLine(image,hline1,glm::vec3(255,255,0)); // write verticle line glm::vec3 p5(100,10,0); glm::vec3 p6(100,500,0); auto hline2 = LineSegment<glm::vec3>(p5,p6); DrawApi::drawLine(image,hline2,glm::vec3(255,0,0)); // write normal line glm::vec3 p7(50,10,0); glm::vec3 p8(300,500,0); auto hline3 = LineSegment<glm::vec3>(p8,p7); DrawApi::drawLine(image,hline3,glm::vec3(0,0,255)); image.save("c:/Raster.jpg",0,100); return ; }
main.cpp

auto render = Renderer();
render.render();

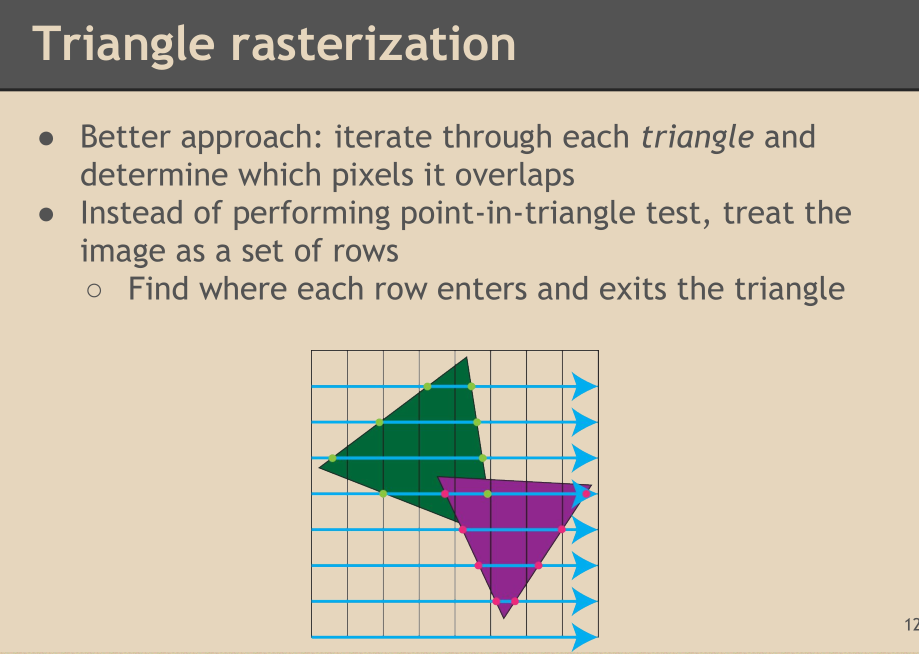
以上的方法不过还是垃圾,因为还是循环像素row。对于以上的方法如果不考虑计算成本,直接暴力法循环row,
然后判断pixelPos是不是在triangle里面。是就给他画出来。
最好的方法:
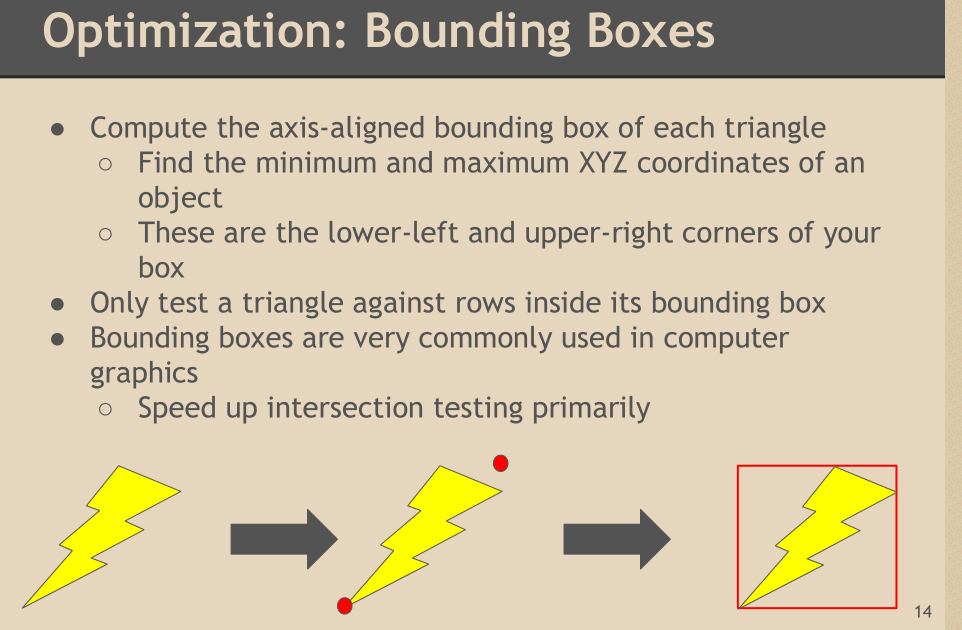
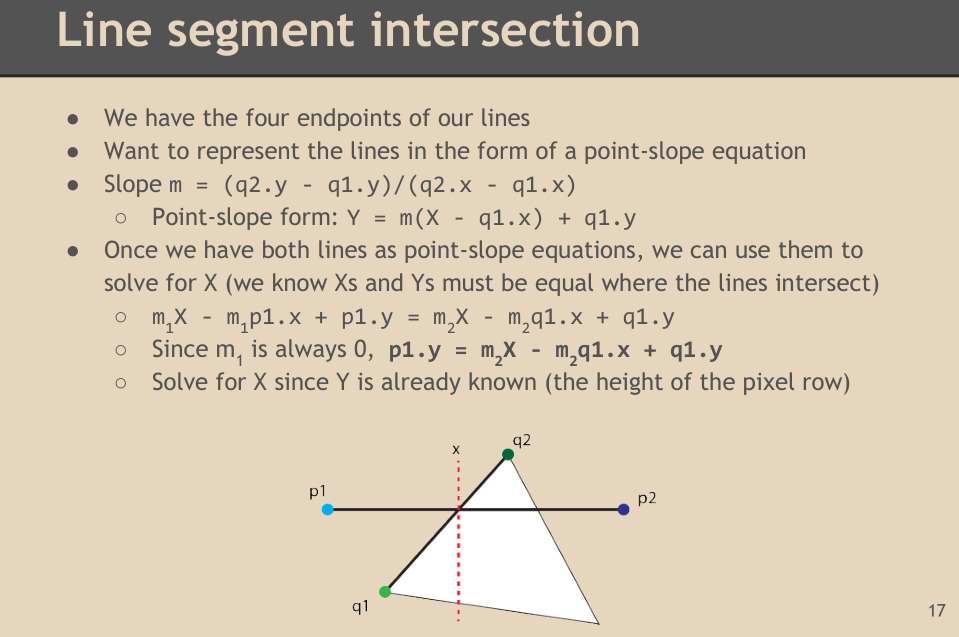
线求交:
2,矩阵大法:
计算 :
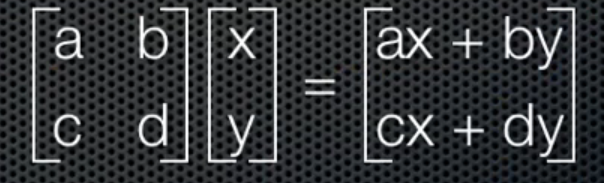
rotate:
![]()

Scale:
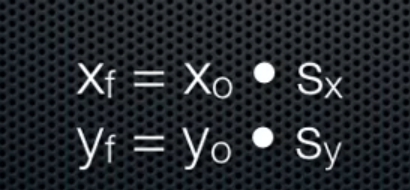
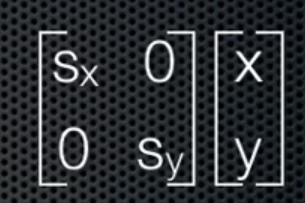
translate:
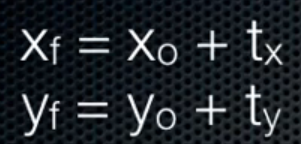

得到的XF = 1*x + 0*y + 1*tx = x + tx;
得到的YF = 0*x + 1*y + 1*ty = y + ty;
总体带x,y,w
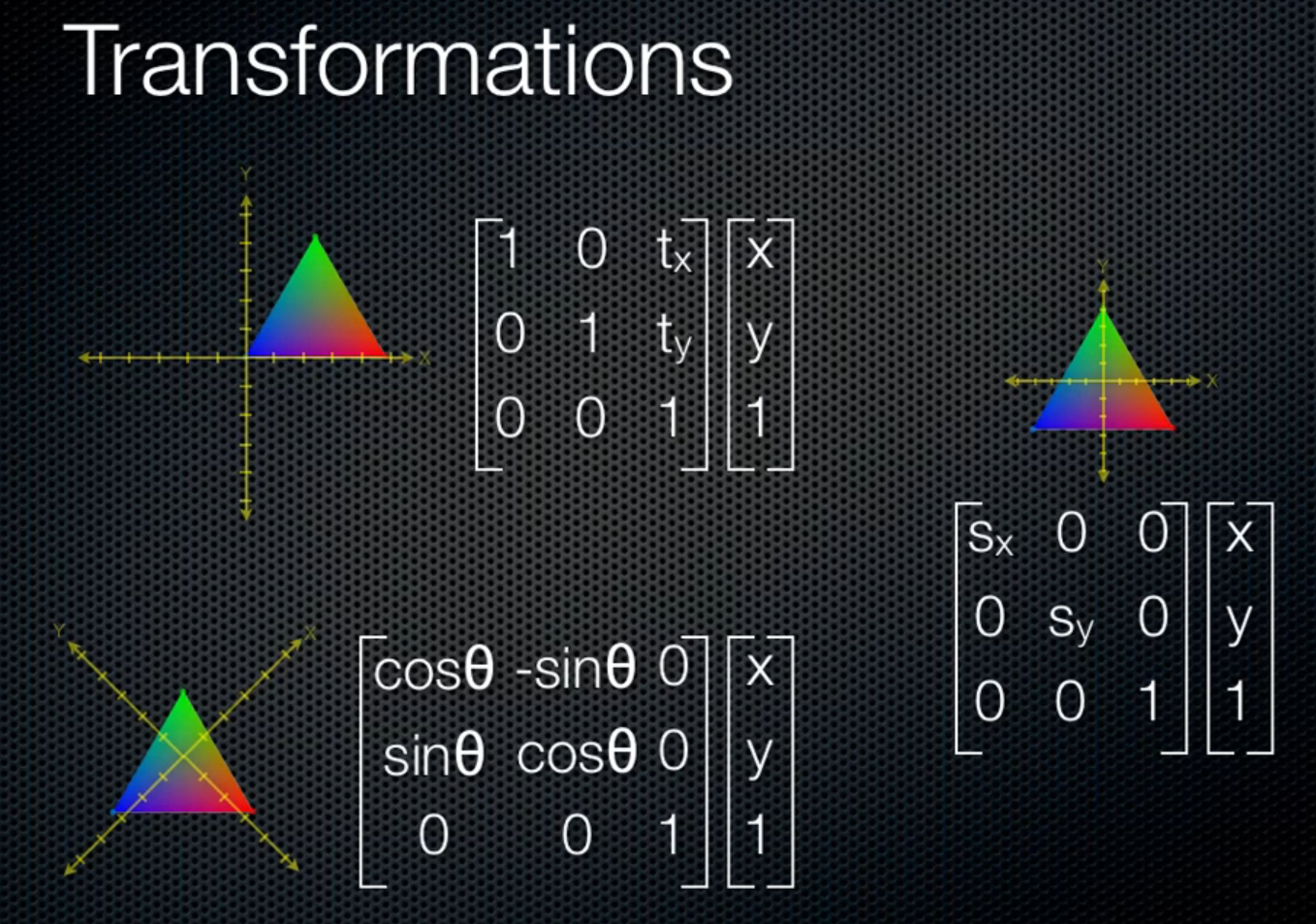
3d:

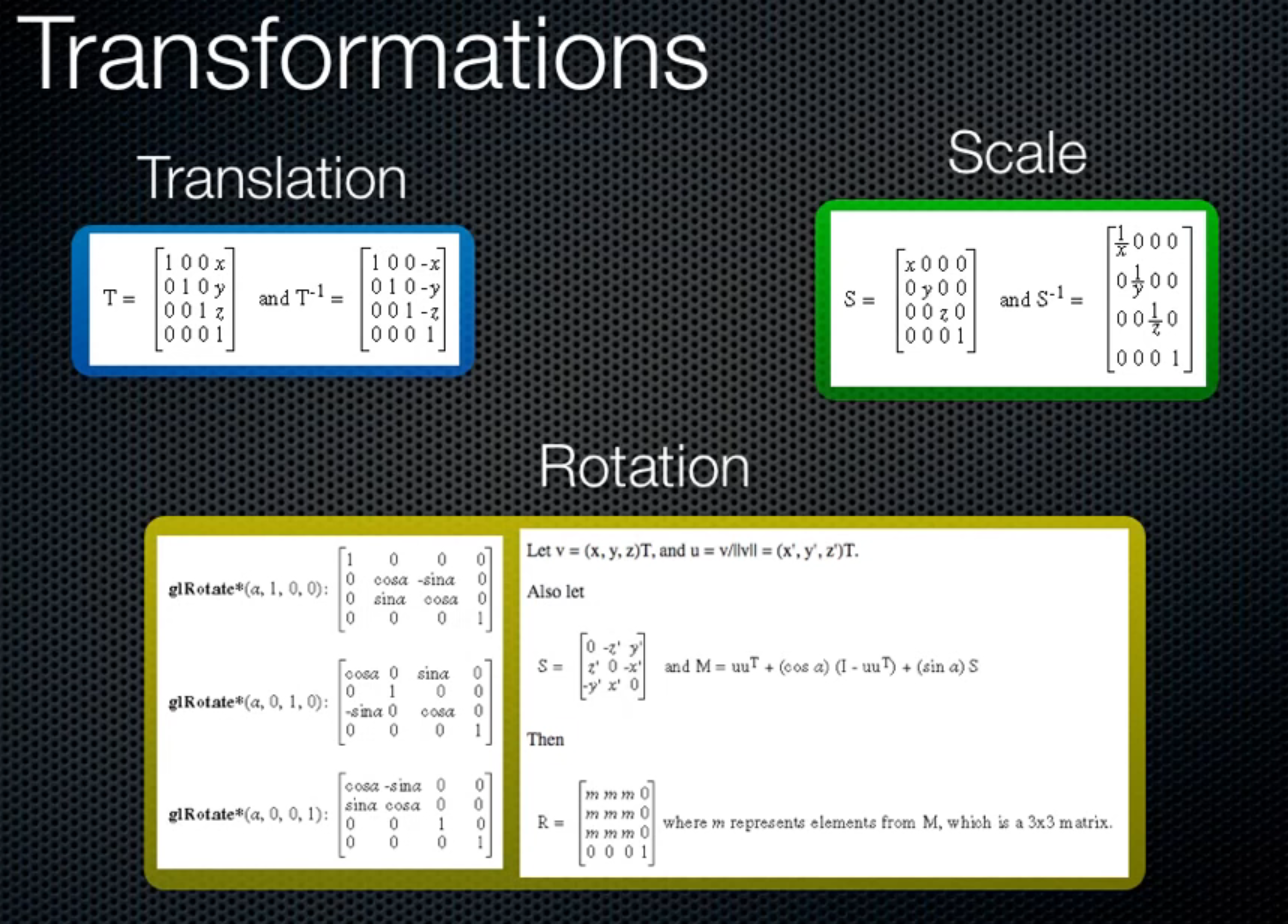
Orthographic Matrix:
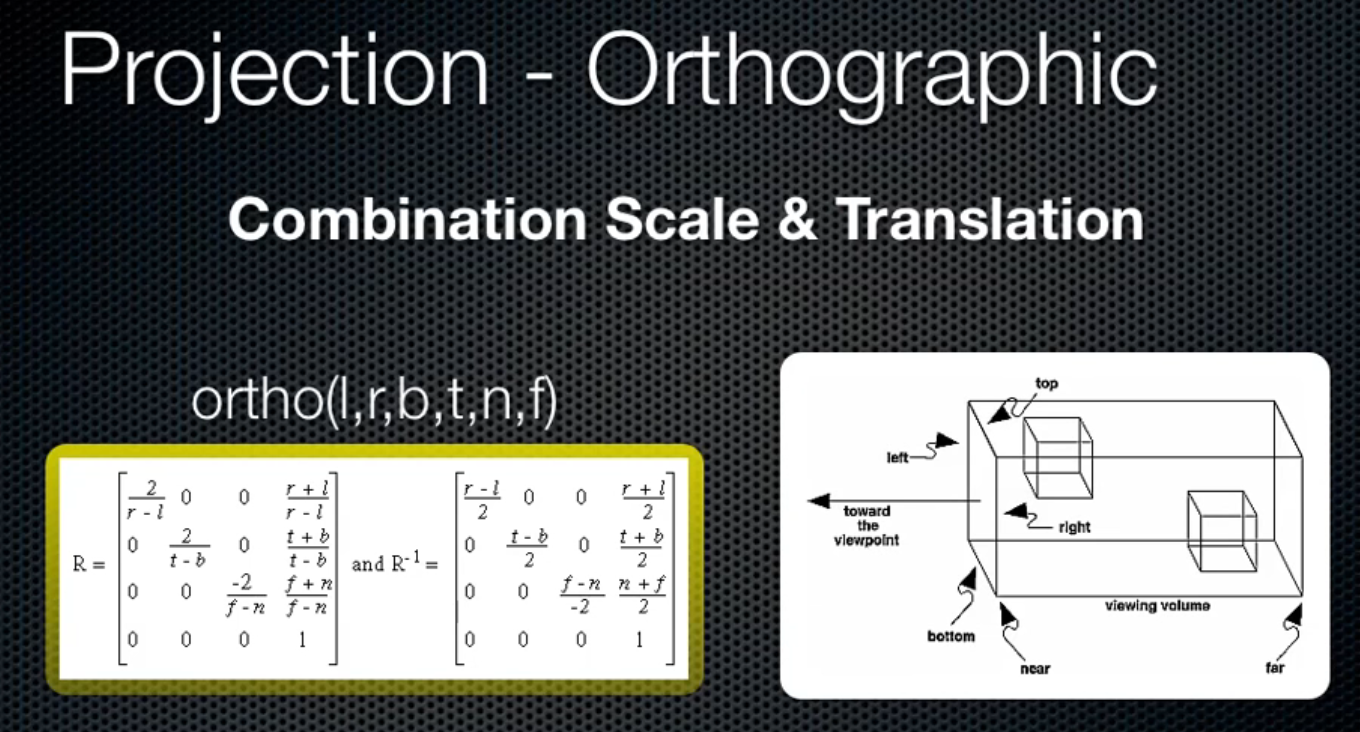
Perspective Matrix
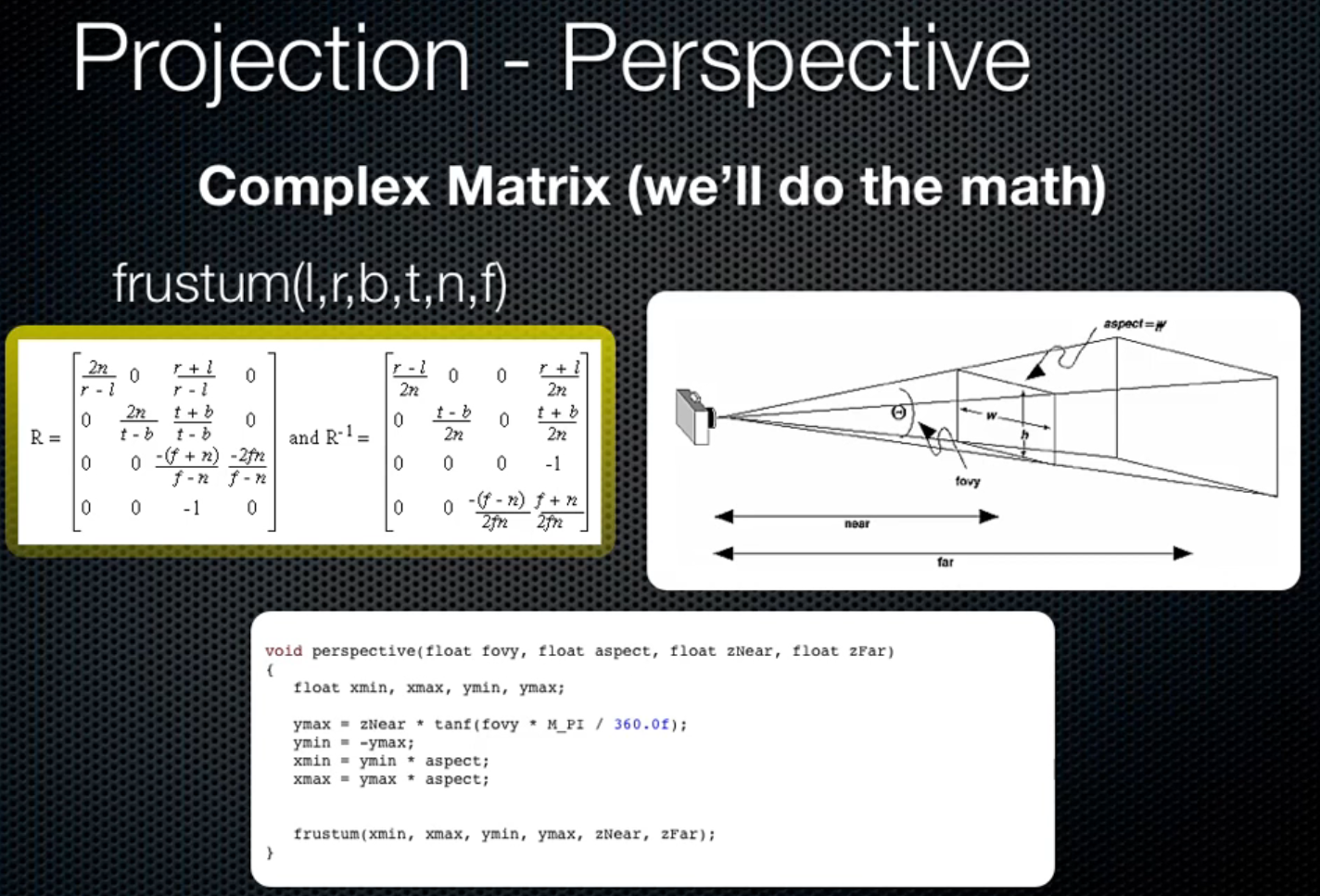
Viewport Transform:

Raster Pipeline:

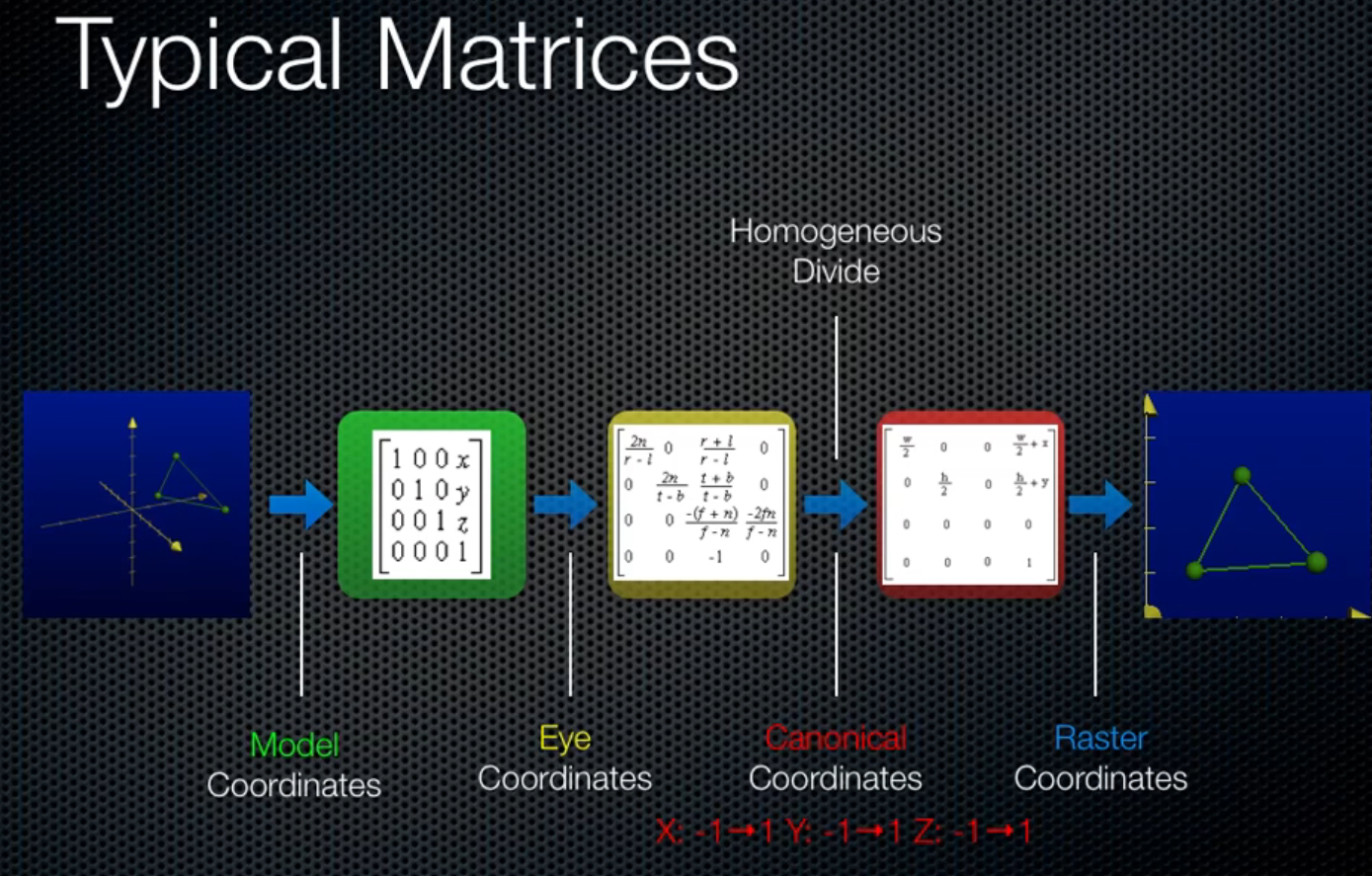
..
