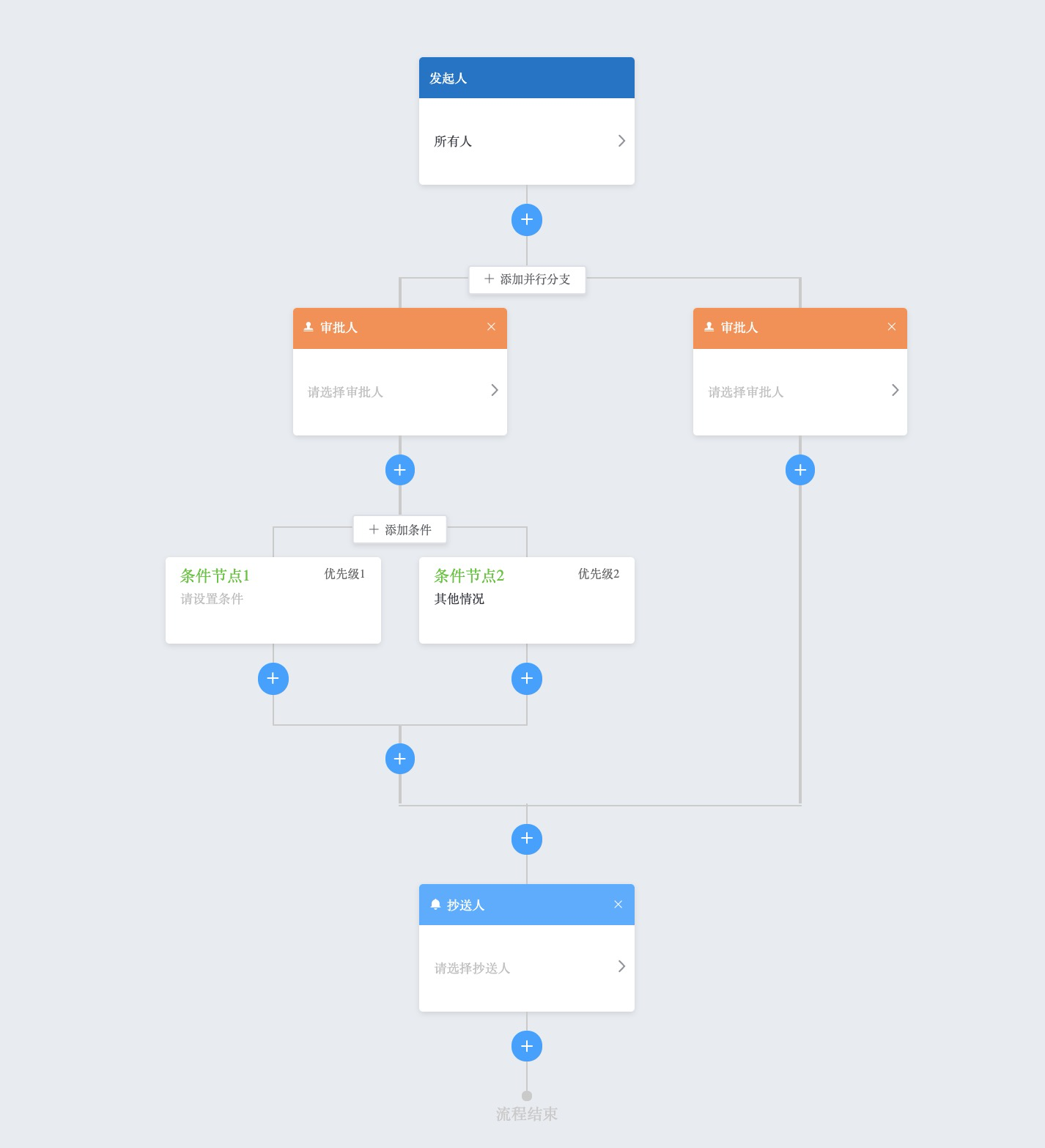
写于19年底,历时1个半月。程序主要用于绘制审批的各个节点流程。先看看效果(开源在社区的精简版):
为什么要写这个?S
公司内部为国内 TOP3 建筑集团分公司写内部一体化平台,其中许多业务涉及到需要定制审批流程。最终经过 PM 的一番调研,它们觉得钉钉后台的审批流程最简单好用,于是去看了看。用 React + antd 技术栈实现,而我们团队使用的是 Vue + element-ui 和基于 VueMfe 的微前端架构。
而这个审批系统,就是 wf, 即 work flow system。
它在整个平台应用中占了很大部分权重。除了所有服务都依赖的基础服务像 auth(权限)、mfe(微前端)之外,所有的重要业务几乎都要接入审批流程应用,用于上级批复。
所以办公场景中,审批,真的太多了吧。比如入职、请假、发工资、出差、报销、申请等等~~
多到泪目,审批起来不累吗?领导们,走流程好累。但是也必须得走,确实很累。
找了那些参考?T
这个说来惭愧,当时没找什么参考(害怕~~)。
看了钉钉后台的实现,觉得简单又方便。why?因为只用 div + css 绘制流程图,没有 canvas,也没有 贝塞尔曲线,不需要很复杂的背景知识。懂点数据结构和撸得出来初中级算法,就可以了。
有考虑过痛过 canvas 来实现,但是看了一些实现,觉得体验堪忧。可能是并没有找到很好的参考产品。记得当时产品找到的同类参考产品还有简道云的审批流,但是拖来拖去的并不如直接添加来得好用。
最终 TL 决定实现钉钉这种交互的审批流。
要怎么去做?A
根据产品和业务的需求,系统内部存在的几个节点。基本需求跟钉钉的基本一致,发起人、审批人、并行分支、条件分支、抄送人,不过节点的配置结合自身业务做了修改。
怎么处理数据?
最有意思的是这些节点的关系在UI上的直观体现是连线,节点与节点之间的连线。但是在代码中要用什么数据结构来表达这种关系?怎么渲染?用那种数据结构最方便?工作量最小?
如果没有分支节点,单纯的只有子节点,那么就是一个很简单的树形结构,递归渲染即可。但因为存在分支节点,而分支节点在同级中可以被不停的添加。且所有的节点,最终都会有指向一个结束节点。
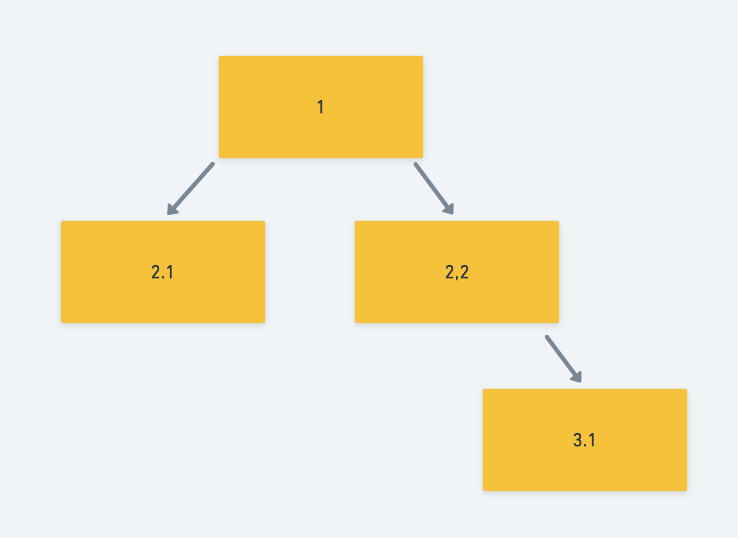
事情变得复杂了。得出的结论是用树形数据结构可以渲染,但不能绘制点与点之间的结束关系。举个例子:
const tree = {
key: 1,
children: [{
key: 2.1,
children: []
}, {
key: 2.2,
children: [{
key: 3.1,
children: []
}]
}]
}
根据上述数据,能画出如下结构:
但是审批流应用,最终都有一个兜底的流程结束节点(EndNode),像这样:

这个用什么实现呢?这不是 Tree 了,这明明是 Graph。下一个问题来了?Graph 要如何渲染呢?我懵了。
Tree 的数据结构很简单,TreeItem.Children: TreeItem[] 就是叶子节点。但是 Graph 很明显还不够,Graph 需要知道 prevItem 和 nextItem。而实现 graph 的方式有两种,邻接矩阵和邻接表。
在 wf 中使用邻接列表实现 graph,同时使用 LinkedList 关联以实现 graph 中的 edge(vertex1,vertex2) 关系。
怎么渲染 view?
节点类型
节点存在两种,普通节点和分支节点。在 wf 中,普通节点就是开始、发起人、审批人、抄送人、结束节点,而分支节点就是条件分支和并行分支节点。
普通节点
普通节点的渲染非常简单,FlowNode = Node(Title+Content)+PlusBtn+Line。
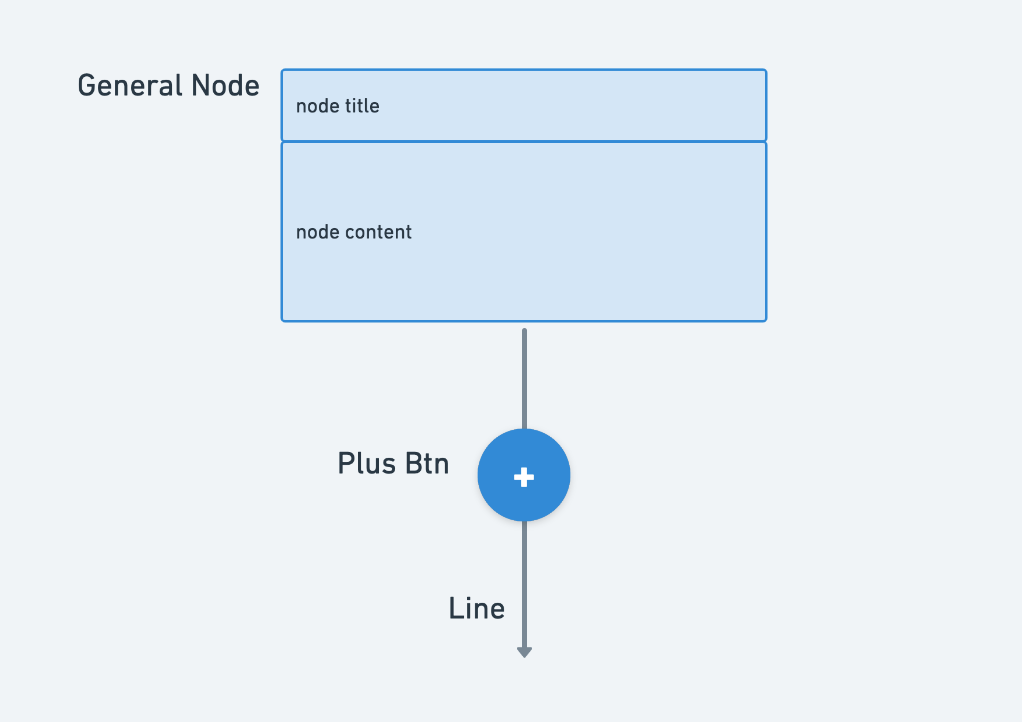
分支节点
分支节点的渲染则分为了 FlowBranchNode = BranchStartNode + (FlowBranchCol * N>FlowNode) + BranchEndNode。

渲染节点
首先实现了 Flow 的两个工厂方法,createNode 和 registerNode 用于新建节点和注册节点。而 createNode 返回新的 Node 实例。Node 实现了 add, remove, move, updateProps, updateModel 等方法。分别用于追加节点、删除节点、移动节点、更新节点属性和model。
现在回想起来,这里的 Node 节点应该使用继承来设计,提供 Node 作为基类并定义上述接口,不同的节点类型再定义自身方法的实现。从而遵从 S.O.L.I.D 设计原则。
BaseNode 基类,伪代码实现 :
export default class Node {
constructor(opts) {
Object.keys(opts).forEach((key) => (this[key] = opts) })
}
// 新增
create() {}
// 删除
remove() {}
// 更新
update(nodeOptions) {}
// 追加节点
append(nextNode) {}
// 移动节点
move() {}
// 上一个节点
prev() {}
// 下一个节点
next() {}
// 返回末尾节点(如果是分支节点返回分支结束节点,如果是普通节点返回自身)
end() {}
// 绘制节点
render() {}
}
StartNode 发起人节点的伪代码实现:
import BaseNode from './BaseNode'
import NodeManager from '../helpers/NodeManager'
import { geneNodeId, isBranchChildNode } from '../helpers/NodeUtils'
import { FLOW_NODE_TYPE } from '../constants/FLOW_NODE_TYPE'
import { FLOW_NODE_MODEL } from '../constants/FLOW_NODE_MODEL'
import StartNode from '../components/StartNode'
export default class StartNode extends BaseNode {
// 模拟单例
static _startNode = null
constructor(baseOpts = {}) {
if (StartNode._startNode) {
throw new Error(`The 'SponsorNode.created()' only could be called once.`)
} else {
super(baseOpts)
this.nodeId = geneNodeId()
this.type = FLOW_NODE_TYPE.START
StartNode._startNode = this
NodeManager.addNode(this)
}
}
remove() {
StartNode._startNode = null
NodeManager.removeNode(this)
return null
}
update(opts = {}) {
Object.keys(opts).forEach((key) => {
this[key] = opts[key]
})
return this
}
// 之前已存在节点
// Old LinkedList: S -> node -> E
// New LinkedList: S -> nextNode -> node -> E, S -> node -> nextNode -> E
append(nextNode) {
if (nextNode && nextNode instanceof BaseNode) {
// 分支节点的子节点是个数组
if (Array.isArray(nextNode)) {
this.childrenNodes = nextNode.map((node) =>
node.update({ prevId: this.nodeId })
)
} else {
if (isBranchChildNode(nextNode)) {
this.childrenNodes.push(nextNode)
} else {
if (this.childNode) {
let oldChildNode = this.childNode
this.childNode = nextNode
nextNode.childNode = oldChildNode
// this.childNode.append(oldChildNode)
} else {
this.childNode = nextNode
}
node.update({ prevId: this.nodeId })
}
}
return nextNode
}
}
prev() {
return null
}
next() {
return this.childNode
}
render() {
const viewModel = FLOW_NODE_MODEL[this.type]
return <StartNode {...viewModel} />
}
}
ApproverNode 审批人节点,
NotifierNode 抄送人节点,
EndNode 结束节点,
ConditionBranchStartNode 条件开始节点,
ConditionBranchNode 条件节点,
ConditionBranchEndNode 条件结束节点,
ParallelBranchStartNode 并行开始节点,
ParallelBranchEndNode 并行结束节点
NodeTypeEnum:
enum NodeTypeEnum = 'start' | 'approver' | 'cbs' | 'condition' | 'cbe' | 'pbs' | 'parallel' | 'pbe' | 'notifier' | 'end'
NodeOptions:
intereface NodeOptions = {
type: NodeTypeEnum,
childNode: Node | null,
childrenNodes: Node[] | null,
prevNodeId: Node | null,
}
普通节点
- 手动调用
const startNode = new StartNode({ type: 'start' })
const approverNode = new ApproverNode({ type: 'approver' })
const endNode = new EndNode({ type: 'end' })
startNode.append(approverNode).append(endNode)
- 工厂方法
const startNode = Flow.createNode(Node.TYPE.START)
const approverNode = Flow.createNode(Node.TYPE.APPROVAER)
const endNode = Flow.createNode(Node.TYPE.END)
startNode.append(approverNode).append(endNode)
分支节点
- 条件分支
/**
* createConditionNode
* @param {{type: string, prevId: string, formFieldList: []}} [opts]
*/
const createConditionNode = (opts) => {
return Flow.createNode({
type: Node.TYPE.CONDITION_NODE,
conditionType: GENERAL_CONDITION,
...opts,
})
}
/* ConditionNode = ConditionBranchStartNode -> [ConditionBranchNode, ConditionBranchNode] -> ConditionBranchEndNode */
const conditionBranchNode = Flow.createNode(Node.TYPE.CONDITION_BRANCH)
const conditionChildrenNodes = [
// 第一个条件为用户设置的条件
createConditionNode(opts),
// 默认第二个条件为"其他条件"
createConditionNode({
...opts,
conditionType: OTHER_CONDITION,
}),
]
const conditionBranchEndNode = Flow.createNode(Node.TYPE.CONDITION_BRANCH_END)
conditionBranchNode.append(conditionChildrenNodes)
conditionChildrenNodes.forEach(node => node.append(conditionBranchEndNode ))
// 分支条件提供 end() 方法直接定位到分支结束节点
/* StartNode -> ApprovaerNode -> ConditionNode -> EndNode */
startNode.append(approverNode).append(conditionBranchNode).end().append(endNode)
- 并行分支
/**
* createParallelNode
* @param {{type: string, prevId: string, formFieldList: []}} [opts]
*/
const createParallelNode = (opts) => {
return Flow.createNode({
// 并行分支节点是审批节点
type: Node.TYPE.APPROVER_NODE,
...opts,
})
}
/* ParallelBranch = ParallelBranchStartNode -> [Parallel1, Parallel2] -> ParallelBranchEndNode */
const parallelBranchNode = Flow.createNode(Node.TYPE.PARALLEL_BRANCH)
const parallelChildrenNodes = [
createParallelNode(opts),
createParallelNode(opts),
]
const parallelBranchEndNode = Flow.createNode(Node.TYPE.PARALLEL_BRANCH_END)
parallelBranchNode.append(parallelChildrenNodes)
parallelChildrenNodes.forEach(node => node.append(parallelBranchEndNode ))
startNode.append(parallelBranchNode).end().append(endNode)
最终数据
渲染数据
怎么转换数据?
当时对接的后端同事对数据的要求是,需要返回一个一维数组。数组 item 的数据结构是:
{
type: node.conditionType, // Node Type Enum
sourceTaskId: sourceNode.nodeId, // source node
targetTaskId: targetNode.nodeId, // target node
conditionList: [] // 如果是条件节点,则 conditionList 为用户设置的触发条件规则
}
谢谢阅读。