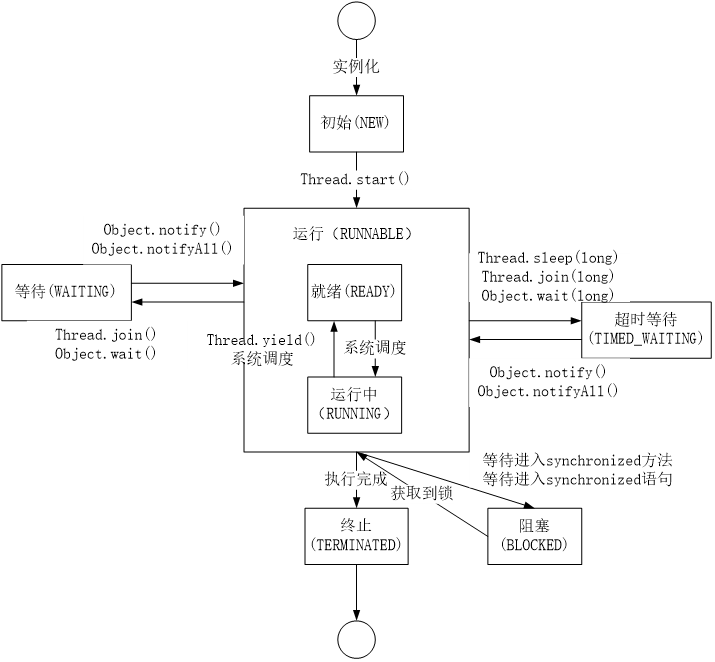
线程的几种状态
- 初始(NEW):新创建了一个线程对象,但还没有调用start()方法
- 运行(RUNNABLE):Java线程中将就绪(ready)和运行中(running)两种状态笼统的称为“运行”
- 阻塞(BLOCKED):表示线程阻塞于锁
- 等待(WAITING):进入该状态的线程需要等待其他线程做出一些特定动作(通知或中断)
- 超时等待(TIMED_WAITING):该状态不同于WAITING,它可以在指定的时间后自行返回
- 终止(TERMINATED):表示该线程已经执行完毕
线程状态的转换
线程的生命周期
- 新生(New):代表线程的对象已经被初始化,但尚未运行run方法。
- 可执行(Runnable):线程正在运行run方法,但这只说明线程目前处于的状态,如果系统没有能力拨出CPU执行时间给线程,线程就“不执行”,这里的“不执行”不代表“停滞”或“死亡”。
- 停滞(Blcked):线程是可以执行的,但由于某些因素的阻碍处于停滞状态,系统排程器略过了应给的CPU执行时间。
- 死亡(Dead):线程的正式结束方式,run方法执行完毕并返回。
生产者消费者模式
public class MainMethod {
/**
* 1、产品/食物
* 2、缓冲区/柜台的大小
* 3、生产者/厨师
* 4、消费者/顾客
*/
//主方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 实例化缓冲区/柜台
BlockingQueue<Product> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Product>(8);
// 实例化生产者/厨师
Producer producer = new Producer(blockingQueue);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(producer);
thread1.start();
// 实例化消费者/顾客
Consumer consumer = new Consumer(blockingQueue);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(consumer);
thread2.start();
}
}
//产品
public class Product {
public String name;
public Product(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
//生产者
public class Producer implements Runnable {
/**
* 缓冲区/柜台的大小
*/
public BlockingQueue<Product> blockingQueue;
public Producer(BlockingQueue<Product> blockingQueue) {
this.blockingQueue = blockingQueue;
}
/**
* 模拟生产者生产产品
*/
@Override
public void run() {
int i = 0;
while (true) {
Product product = new Product("产品名称" + i++);
try {
this.blockingQueue.put(product);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("生产者生产了产品" + product.getName());
}
}
}
//消费者
public class Consumer implements Runnable {
/**
* 缓冲区/柜台的大小
*/
public BlockingQueue<Product> blockingQueue;
public Consumer(BlockingQueue<Product> blockingQueue) {
this.blockingQueue = blockingQueue;
}
/**
* 模拟消费者消费产品
*/
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
Product product = null;
try {
product = this.blockingQueue.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("消费者消费了产品" + product.getName());
}
}
}
龟兔赛跑
public class Race implements Runnable{
//胜利者
private static String winner;
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
//模拟兔子睡觉
if (Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("兔子")&&i%10==0){
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//判断比赛是否结束
boolean flag=gameover(i);
if (flag){
break;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"跑了"+i+"步");
}
}
//判断比赛是否结束
private boolean gameover(int steps){
while (true){
//已经存在了胜利者
if (winner!=null){
return true;
}else{
if (steps==100){
winner = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("胜利者是"+winner);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Race race = new Race();
new Thread(race,"乌龟").start();
new Thread(race,"兔子").start();
}
}
第一个线程用来计算2~100000之间的素数的个数,第二个线程用来计算100000~200000之间的素数的个数
package Demo02;
public class ThreadTest extends Thread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread1 t1 = new Thread1();
t1.start();
Thread2 t2 = new Thread2();
t2.start();
}
}
class Thread1 extends Thread {
public void run() {
System.out.println("2 到 100000之间的素数有 " + getSum(2, 100000)+" 个");
}
//获取素数个数的方法
public int getSum(int inputMin, int inputMax) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = inputMin; i <= inputMax; i++) {
if (isPrime(i)) {
sum++;
}
}
return sum;
}
//判断是否为素数
public static boolean isPrime(int input) {
for (int i = 2; i < input; i++) {
if (input % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
//让第二个线程继承第一个线程重写run方法即可
class Thread2 extends Thread1 {
public void run() {
System.out.println("100000 到 200000 之间的素数有 " + getSum(100000, 200000)+" 个");
}
}
模拟多个人通过一个山洞的场景.这个山洞每次只能通过一个人,每个人通过山洞的时间为5秒,有10个人同时准备过此山洞,显示每次通过山洞的人的姓名和顺序.
public class ThreadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cave cave = new Cave();
int num=0;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Thread thread = new Thread(cave, "狠人" +((int)(Math.random()*100)));//使用数学类随机生成一些整数编号来记录通过山洞人的姓名
thread.start();
}
}
}
//山洞
class Cave implements Runnable {
//定义两个常量来记录通过几人和已经通过几人
int num=1;
int count=0;
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized ("") {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "
是第"+(num++)+"个通过");
System.out.println("已经通过了" + (++count) + "个人");
}
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);//延迟5s
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
