1、AIDL和Binder
Android系统四大组件Activity, Content Provider, Broadcast和Service均可以进行跨进程数据传输。
Activity可以隐式调用其他进程的Activity; Content Provier可以跨进程访问其他应用中的数据;Broadcast通过广播的方式与其他应用进行通讯;Service则是通过Binder实现RPC
Binder的实现机制很复杂,在这里不展开叙述,只需要知道它是C/S模式实现RPC(Remote Procedure Call Protocol)——远程过程调用协议。例如应用程序A提供实现了加减乘除的操作,并对外提供的操作接口,其他应用程序就可以远程调用应 用程序A提供的接口实现运算,而不需要自己实现;
那么AIDL是什么呢,AIDL是AndroidInterface definition language的缩写,是android接口定义语言。把Binder比作一个管道,AIDL则定义了该管道中传输数据的格式。
下面我们以实例讲解如何使用AIDL实现远程服务的调用
2、服务端的实现
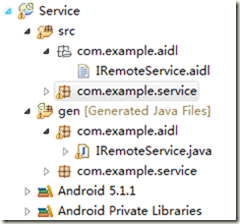
1、在Eclipse中新建Android工程,工程命名为Service。在Service工程的src目录上右键新建包,起名为com.example.aild;在新建的包中增加普通文件,命名为IRemoteService.aidl,标明该服务对外提供getPid()和basicTypes()两个接口;
package com.example.aidl; interface IRemoteService { /** Request the process ID of this service, to do evil things with it. */ int getPid(); /** Demonstrates some basic types that you can use as parameters * and return values in AIDL. */ int basicTypes(int anInt, long aLong, boolean aBoolean, float aFloat, double aDouble, String aString); }
aidl文件完成后,在gen目录下会自动生成com.example.aild包和IRemoteService.java文件,我们不需要进行任何修改,完成后,Service目录结构如下
2、在com.example.service下新建服务类AIDLService.java,代码如下
package com.example.service; import android.app.Service; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.IBinder; import android.os.Process; import android.util.Log; import com.example.aidl.IRemoteService; public class AIDLService extends Service { private String TAG = "REMOTESERVICE"; @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Log.d(TAG, "DDService onBind"); return mBinder; } @Override public void onCreate() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onCreate(); Log.d(TAG, "DDService onCreate........" + "Thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } /*与本地服务不同,此处新建Stub类型的Binder*/ private final IRemoteService.Stub mBinder = new IRemoteService.Stub() { public int getPid(){ Log.d(TAG, "Thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); /*返回给调用者当前的线程编号*/ return (int) Thread.currentThread().getId(); } public int basicTypes(int anInt, long aLong, boolean aBoolean, float aFloat, double aDouble, String aString) { Log.d(TAG, "Thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); Log.d(TAG, "basicTypes aDouble: " + aDouble +" anInt: " + anInt+" aBoolean " + aBoolean+" aString " + aString); /*返回给调用者当前的线程编号*/ return (int) Thread.currentThread().getId(); } }; }
可以看到,与本地服务不同的是,我们在onBind()中返回的是IRemoteService.Stub类型的变量,Stub类实际上是继承自Binder,并且定义了我们在AIDL中定义的接口;需要我们实现这些接口,即getPid()和basicTypes();
3、在AndroidMainfest.xml中声明该服务
<service android:name=".AIDLService" android:process=":xlzh" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="com.example.aidl" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /> </intent-filter> </service>
在Serivce的属性中增加了android:process,其中冒号后可自己随意填写。其含义请自行google。
OK,到此为止,服务端的工作已经全部结束了。接下来我们说下客户端如何使用服务端提供的接口
3、客户端的实现
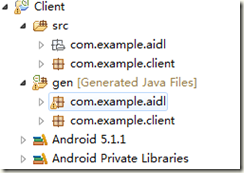
1、在Eclipse中新建工程,名称为Client;然后把Server工程中的com.example.aidl包整个拷贝到Client工程的src目录下;工程结构如下所示
2、定义布局文件,在布局文件中增加两个按钮,一个是bind服务,一个是unbind服务。activity_main.xml如下所示
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <Button android:id="@+id/binderButton" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="bind" /> <Button android:id="@+id/unbinderButton" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="unbind" /> </LinearLayout>
3、在Acitivity中使用远程服务,MainActivity.java内容如下
package com.example.client; import android.app.Activity; import android.content.ComponentName; import android.content.Context; import android.content.Intent; import android.content.ServiceConnection; import android.os.Bundle; import android.os.IBinder; import android.os.RemoteException; import android.util.Log; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; import com.example.aidl.IRemoteService; public class MainActivity extends Activity { private String TAG = "com.example.aidl"; private IRemoteService remoteService; private Button mBindButton; private Button mUnbindButton; @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); mBindButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.binderButton); mBindButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Log.d(TAG, "Bind Service"); //Intent intent = new Intent(IRemoteService.class.getName()); /*新建Intent,指定Service的AndroidMainfest.xml中声明的Action名称*/ Intent intent = new Intent("com.example.aidl"); /*在Android5.0以后,不允许隐式调用服务,故再次指定服务所在包名*/ intent.setPackage("com.example.service"); /*绑定服务*/ bindService(intent, conn, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE); } }); mUnbindButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.unbinderButton); mUnbindButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Log.d(TAG, "UnBind Service"); /*解绑服务*/ unbindService(conn); } }); } ServiceConnection conn = new ServiceConnection() { @Override public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) { Log.d(TAG, "UnBind Service success!"); } @Override public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) { Log.d(TAG, "Bind Service success!"); /*获取服务端handle*/ remoteService = IRemoteService.Stub.asInterface(service); try { int pid1 = remoteService.getPid(); int pid2 = remoteService.basicTypes(12, 1223, true, 12.2f, 12.3, "我们的爱,我明白"); /*打印带有getPid接口和basicTypes接口时服务端的线程号*/ Log.d(TAG, "remoteService.getPid(): " + pid1 + " remoteService.basicTypes(): " + pid2); } catch (RemoteException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }; @Override protected void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); /*正规做法是设置标记位,标志服务是否已经unbind,来决定是否调用unbindService * 此处,简便行事,默认此时服务已经unbind
*/ //unbindService(conn); } }
4、注意事项
1、Android5.0以后,不允许隐式调用服务,所以必须制定要调用的服务所在的包名(调了一下午才调通)
2、通过客户端的打印结果,可以知道当调用getpid和basicTypes的接口时,服务器端处理客户端调用的线程是不一样的。具体原因需要深入学习下Binder的机制
3、与本地服务的不同在于,服务器端返回的是继承自Binder的Stub类型的Binder,客户端获取服务器端的handle时使用了Stub的asInterface接口。另外服务器端需要在AndroidMainfest.xml中声明服务时指定android:process属性。
4、AIDL中支持以下的数据类型
Java 的原生类型
String 和CharSequence
List 和 Map ,List和Map 对象的元素必须是AIDL支持的数据类型; 以上三种类型都不需要导入(import)
AIDL 自动生成的接口 需要导入(import)
实现android.os.Parcelable 接口的类. 需要导入(import)。
5、总结
使用远程服务流程总结如下;
1、定义AIDL文件,声明该服务需要向外提供的接口
2、在服务器中实现AIDL中定义的接口
3、在AndroidMainfest.xml中声明远程服务
4、客户端中拷贝服务端的AIDL文件
5、客户端中指定服务器的服务名称和所在包,进行绑定
6、客户端使用Stub.asInterface接口获取服务器的hander,调用服务提供的接口