Given an integer array, sort it in ascending order. Use quick sort, merge sort, heap sort or any O(nlogn) algorithm.
Example
Given [3, 2, 1, 4, 5], return [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].
快速排序是排序算法中比较重要一种,也是经常容易考的一种排序算法,务必要掌握好。快排的优点是其平均时间复杂度为O(nlgn),这样在给大数据集排序的时候,其效率明显比一些O(n2)的算法要高很多。快排主要有三步:
1. 选定中枢点pivot value,中枢点可以选择中间那个点,也可以选末尾点,一般来说我们直接选取末尾点,如果选末尾点的话注意循环结束后要调换中枢点和第一个大于中枢点的数的位置。理论上来说中枢点可以为任意值,即使这个值不在数组上存在也无妨。
2. 分割Partition,重新安排数字的位置,让所有比中枢点小的数到左半边,所有大于中枢点的书到右半边,等于中枢点的数可以在任意一边,这样数组就被分为了两段,注意两段的长度可以不相等。
3. 分别给每段排序,调用递归算法给每一段排序。
下面这个图是用来说明步骤二,分割的过程,这是快排的核心,只要这一步搞清楚了,基本了快排就能掌握了。
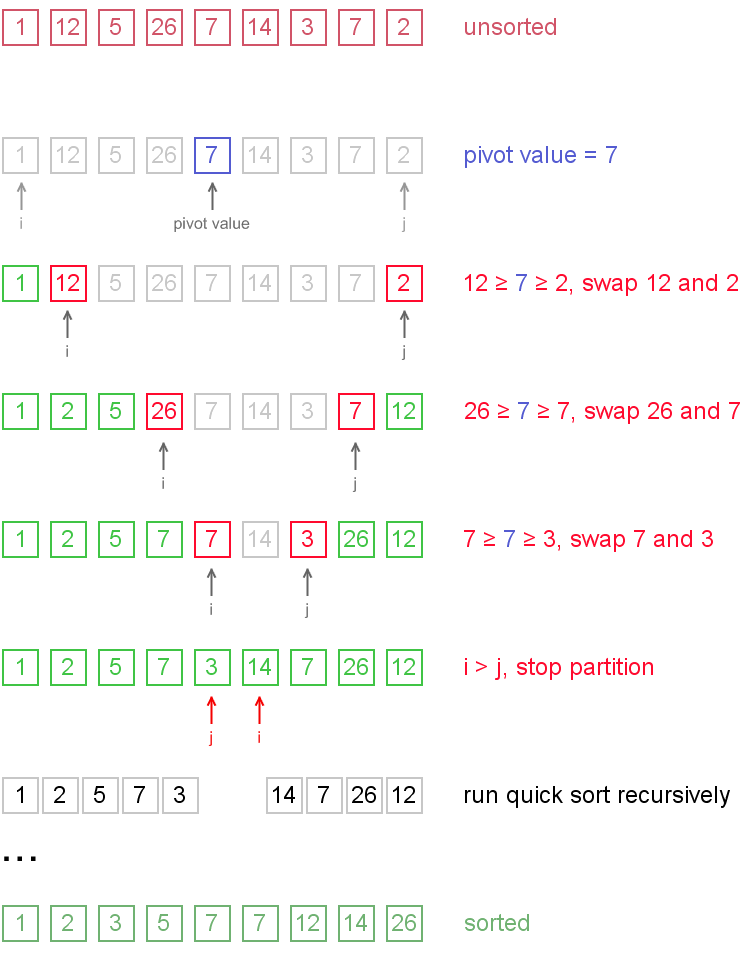
(from http://www.algolist.net/Algorithms/Sorting/Quicksort)
解法一:
// Quick sort class Solution { public: /** * @param A an integer array * @return void */ void sortIntegers2(vector<int>& A) { quick_sort(A, 0, A.size() - 1); } void quick_sort(vector<int> &A, int start, int end) { if (start >= end) return; int pos = partition(A, start, end); quick_sort(A, start, pos - 1); quick_sort(A, pos, end); } int partition(vector<int>& A, int start, int end) { int i = start, j = end, pivot = A[end]; while (i <= j) { while (A[i] < pivot) ++i; while (A[j] > pivot) --j; if (i <= j) { swap(A[i], A[j]); ++i; --j; } } swap(A[i], A[end]); return i; } };
下面这种方法的快排跟上面的一点不同在于partition函数,上面使用的是while循环下面这种使用的是for循环,看个人爱好了,两种都行:
解法二:
// Quick sort class Solution { public: /** * @param A an integer array * @return void */ void sortIntegers2(vector<int>& A) { quick_sort(A, 0, A.size() - 1); } void quick_sort(vector<int> &A, int start, int end) { if (start >= end) return; int pos = partition(A, start, end); quick_sort(A, start, pos - 1); quick_sort(A, pos, end); } int partition(vector<int>& A, int start, int end) { int i = start - 1, pivot = A[end]; for (int j = start; j < end; ++j) { if (A[j] <= pivot) { ++i; swap(A[i], A[j]); } } swap(A[i + 1], A[end]); return i + 1; } };
类似题目: