第五周课堂测试补充
测试一:用数组实现栈
-
实验要求:
参考教材内容,实现ArrayStack,完成peek,isEmpty,size及toString方法,并用Junit进行单元测试(正常,异常,边界情况) -
实验过程:
1、peek方法:查看栈顶元素
代码如下:
@Override
public T peek() {
if (count == 0)
return null;
else
return stack[count];
}
}
2、isEmpty方法:判断栈中是否为空
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return (count == 0);
}
3、size方法:判定栈中元素的个数。
public int size()
{
return count;
}
4、toString方法:toString方法是将栈中的各个元素转换成String类型,然后便于打印出来。
public String toString() {
String result = "<top of stack>
";
for (int index = count-1; index>=0; index++)
result += stack[index]+ "
";
return result + "<bottom of stack>";
}
-
实验截图

-
代码链接
测试二:用链表实现栈
- 实验要求:
1 给出size,isEmpty及toString方法的定义,完成LinkedStack类并用Junit进行单元测试(正常,异常,边界情况)
2 提交测试代码运行截图,要全屏,包含自己的学号信息
3课下把代码推送到代码托管平台 - 实验过程(方法实现与数组实现栈大致相同):
1、isEmpty方法:判断栈中是否为空
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return (count == 0);
}
2、size方法:判定栈中元素的个数。
public int size()
{
return count;
}
3、toString方法:toString方法是将栈中的各个元素转换成String类型,利用while循环将栈中的元素遍历返回,赋给result,返回result。
public String toString()
{
String result = "<top of stack>
";
LinearNode current = top;
while (current != null)
{
result += current.getElement() + "
";
current = current.getNext();
}
return result + "<bottom of stack>";
}
-
实验截图:
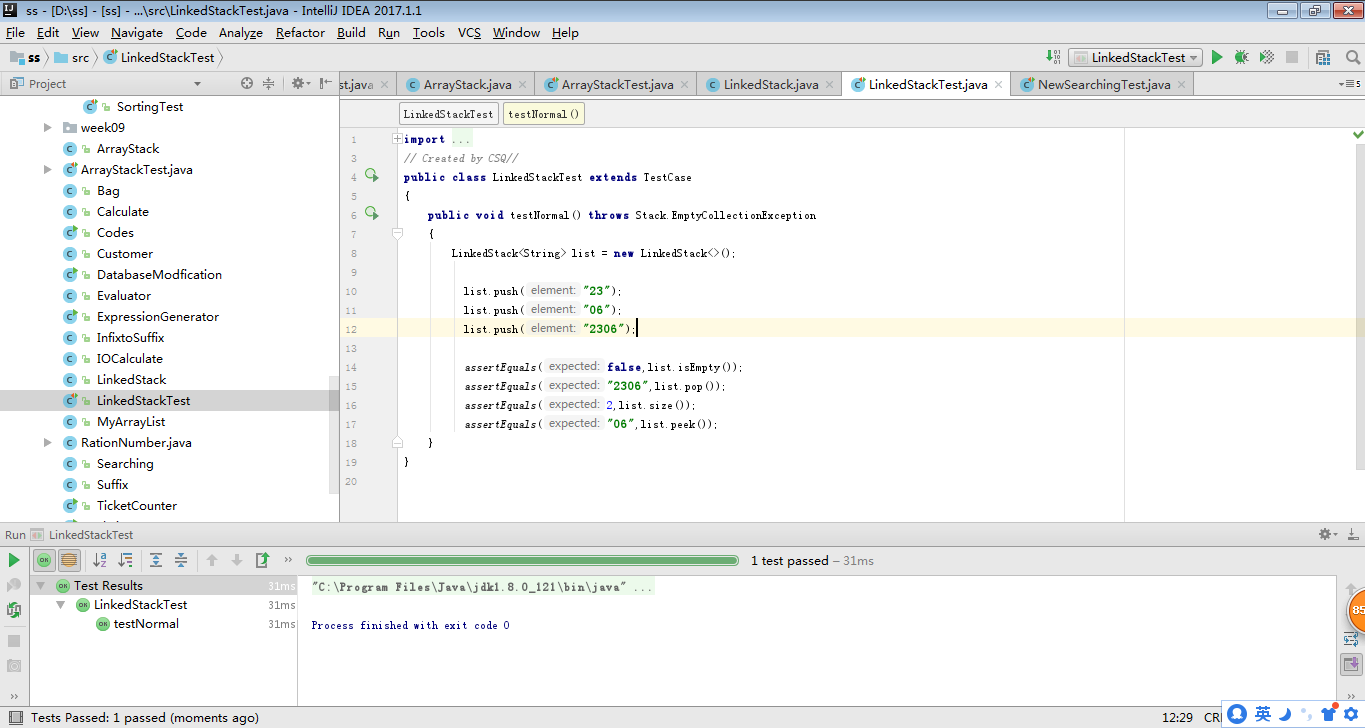
-
代码链接
测试三:查找课堂测试
-
实验要求:
1 用JDB或IDEA单步跟踪在下列数据中(3 8 12 34 54 84 91 110)查找45和54的过程,对比使用顺序查找和二分查找的执行过程
2提交测试找到或找不到那一步的截图,要全屏,包含自己的学号信息
3课下把代码推送到代码托管平台 -
实验过程:
分别调用Searching中的binarySearch和linearSearch方法,进行强制类型转换转为Integer类型后查找45和54,运用一个if-else循环来将找到和找不到的不同结果打印出来 -
实验截图:


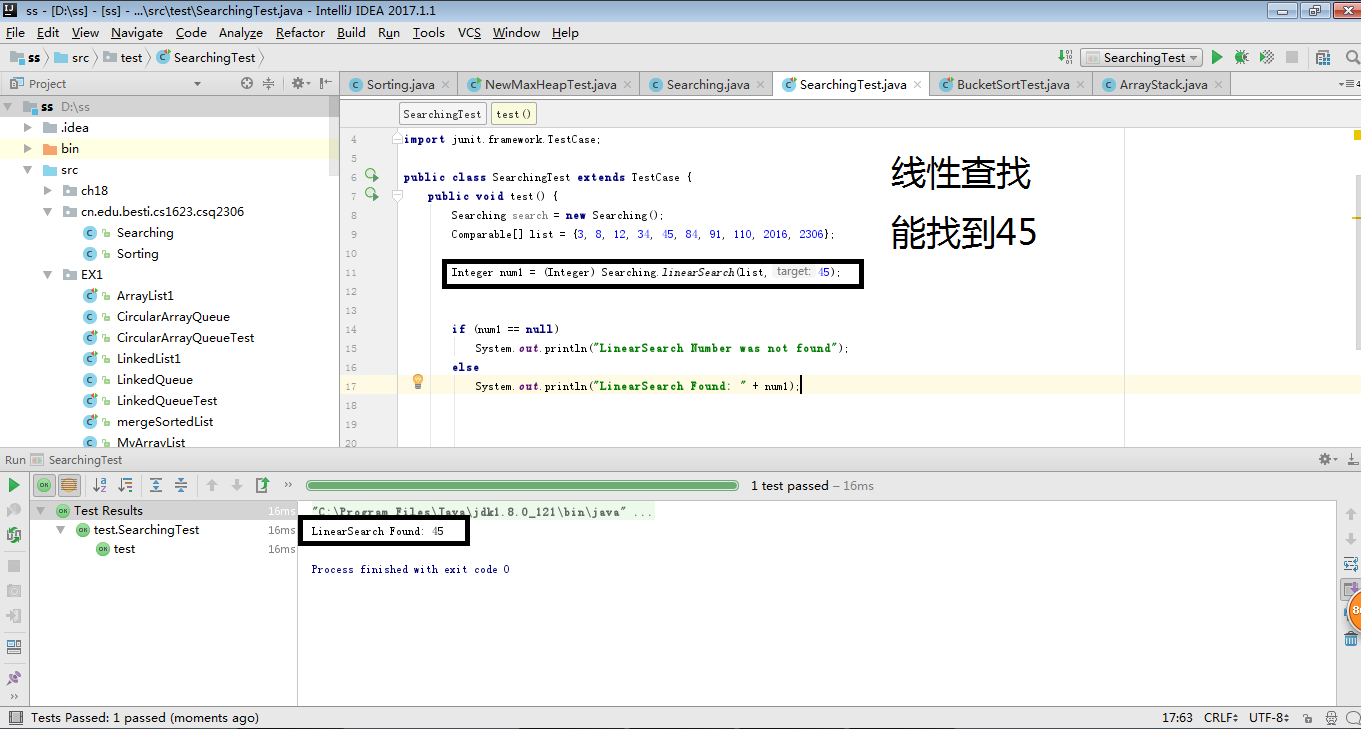
- 代码链接
测试四:排序课堂测试
-
实验要求:
1 用JDB或IDEA单步跟踪对3 8 12 34 54 84 91 110进行快速排序的过程
2 提交第一趟完成时数据情况的截图,要全屏,包含自己的学号信息
3 课下把代码推送到代码托管平台 -
实验过程:
调用Sorting中的quickSort的方法,用for循环将所有元素排序,按照从小到大的顺序打印。 -
实验截图:
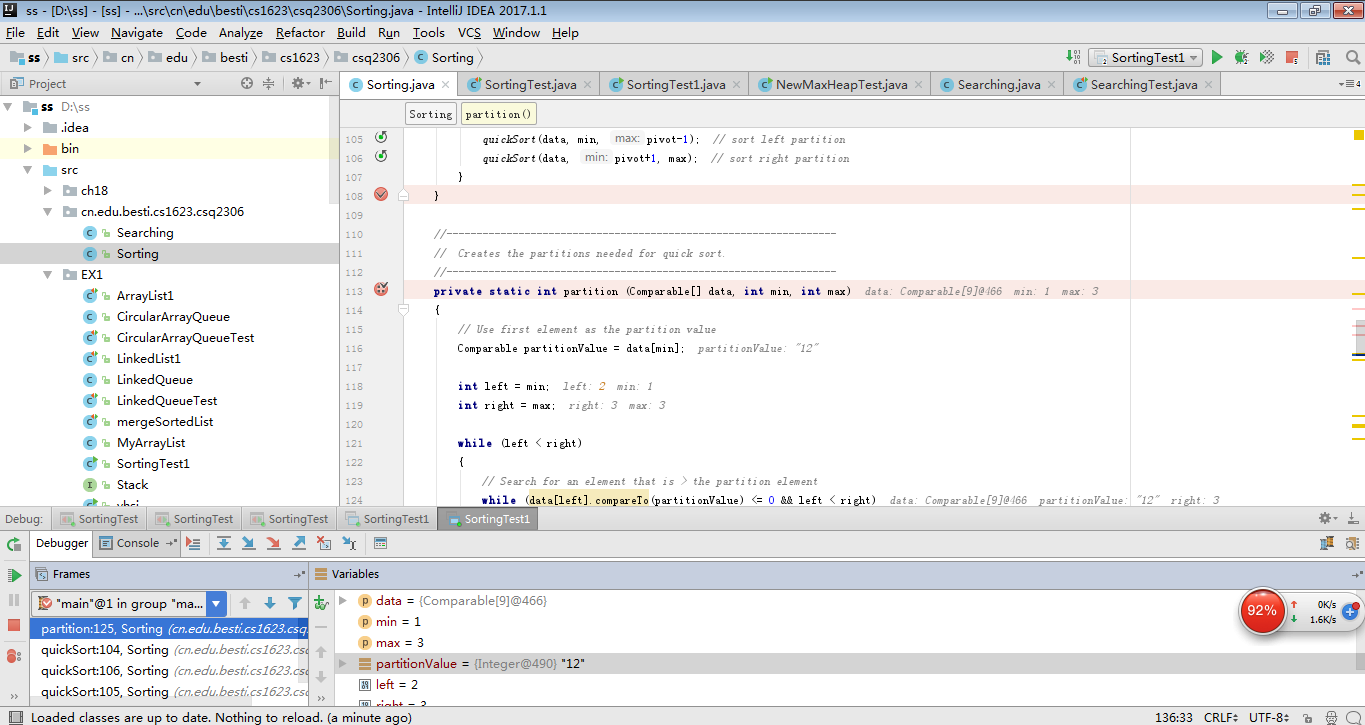
9.png)
- 测试代码
public class SortingTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Comparable []arr = {54, 110, 8, 34 ,84 ,91 ,3,12 ,2306};
System.out.println("未排序:");
for(Comparable num1:arr)
System.out.print(num1 +" ");
Sorting.quickSort(arr,0,8);
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("排序结果:");
for(Comparable num2:arr)
System.out.print(num2+ " ");
}
}
测试五:排序课下作业(上课没有完成实践内容的同学必做)
-
实验要求:
1 给定下列数据:90 8 7 56 123 235 9 1 653
用JDB或IDEA单步跟踪下列算法的执行过程:选择排序,插入排序,希尔排序,冒泡排序,快速排序,归并排序
2 提交每一趟的截图,要全屏,包含自己的学号信息
3 课下把代码推送到代码托管平台 -
实验过程:
分别调用Sorting中的排序方法,用for循环将所有元素排序,按照从小到大的顺序打印。 -
实验截图
-
1、总体测试
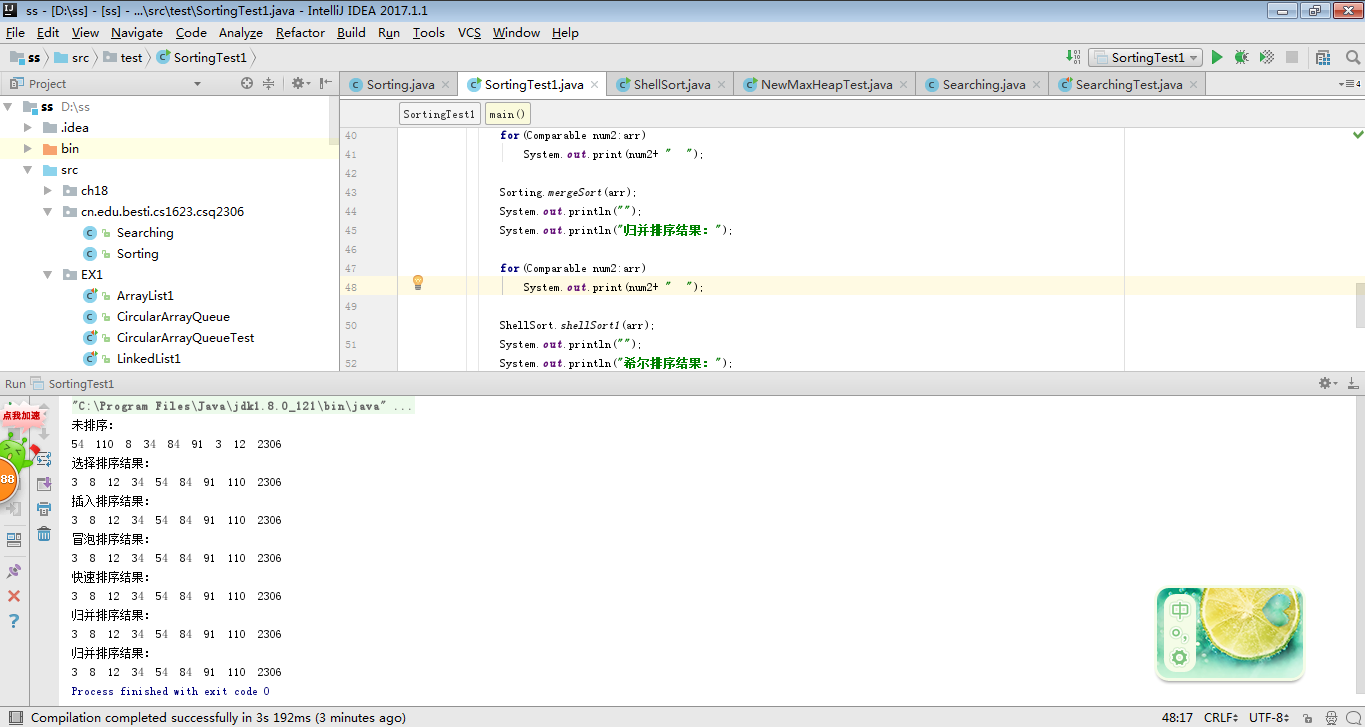
-
2、快速排序
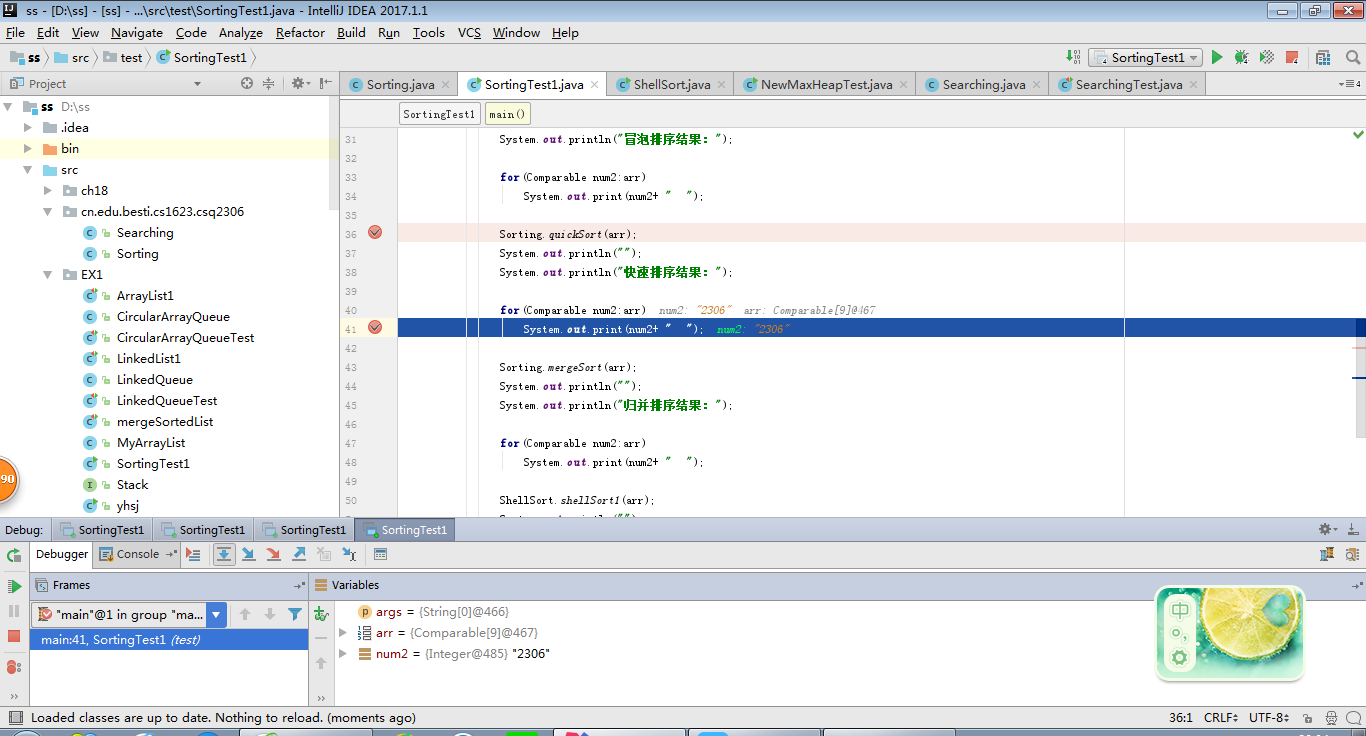
-
3、冒泡排序
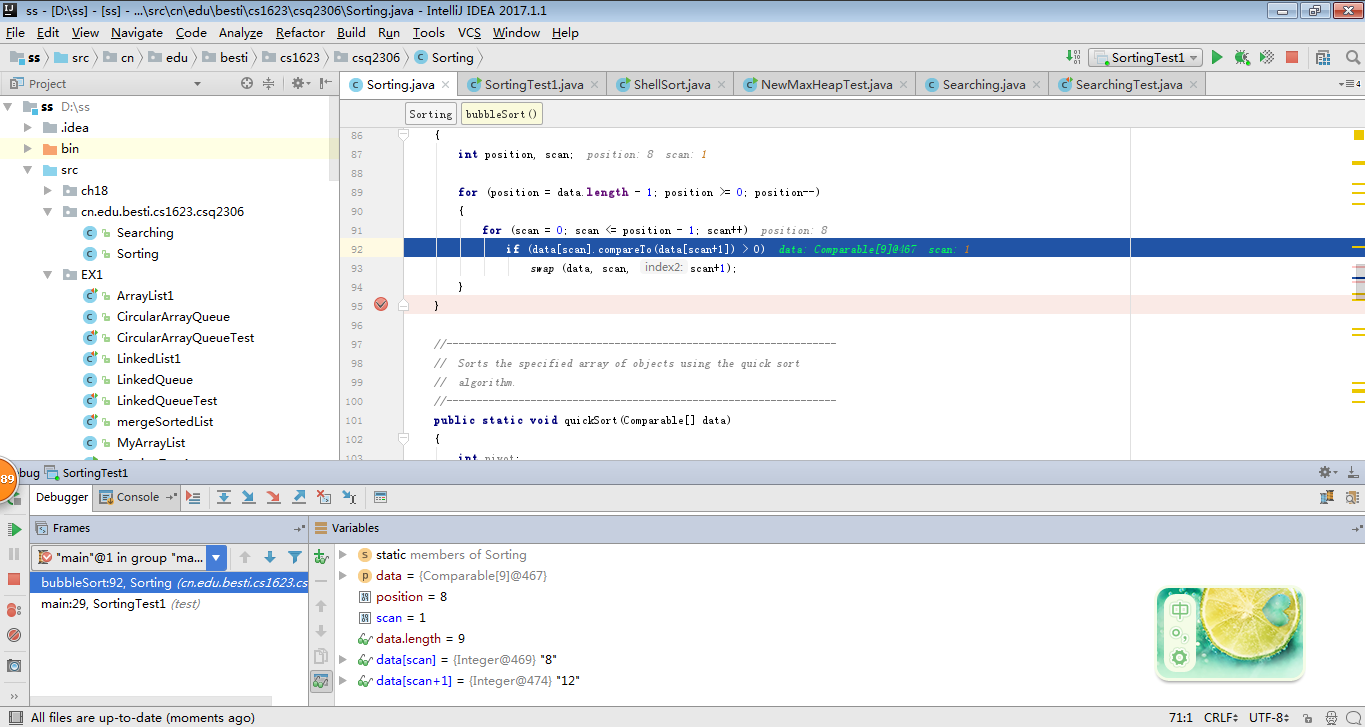
-
4、归并排序
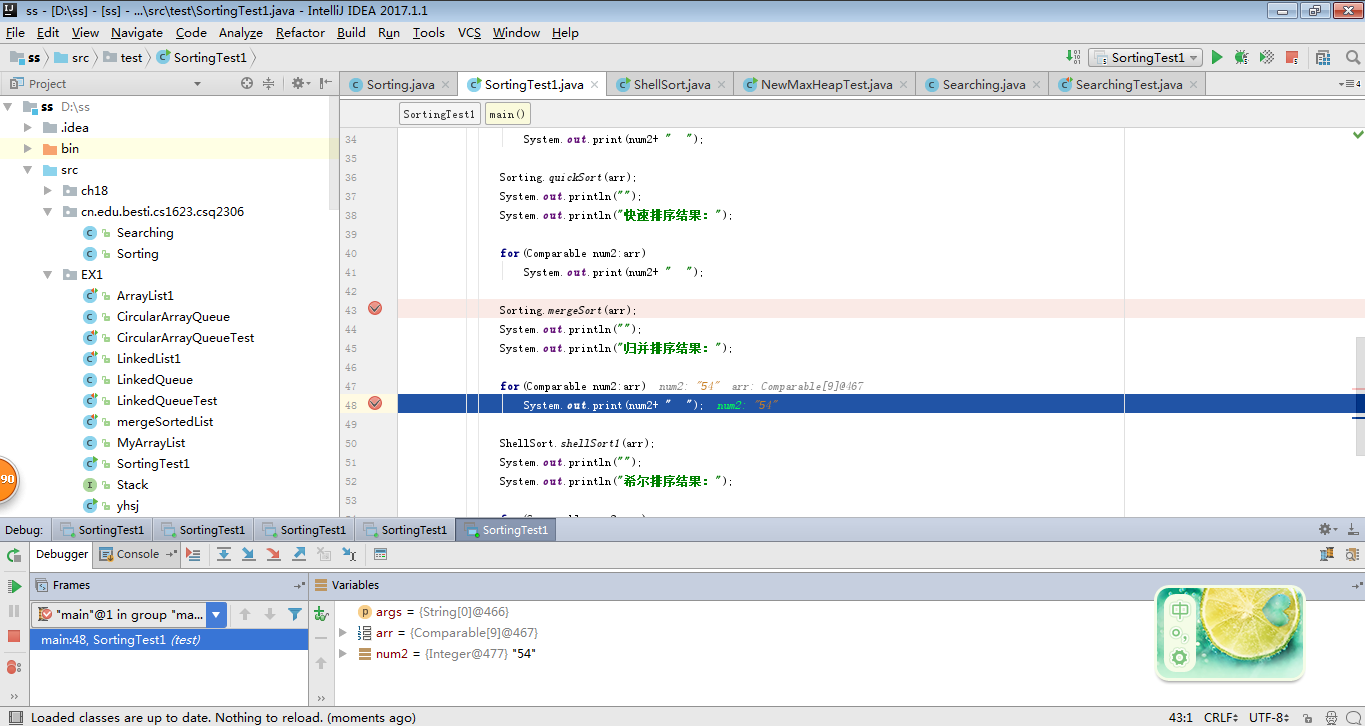
-
5、插入排序
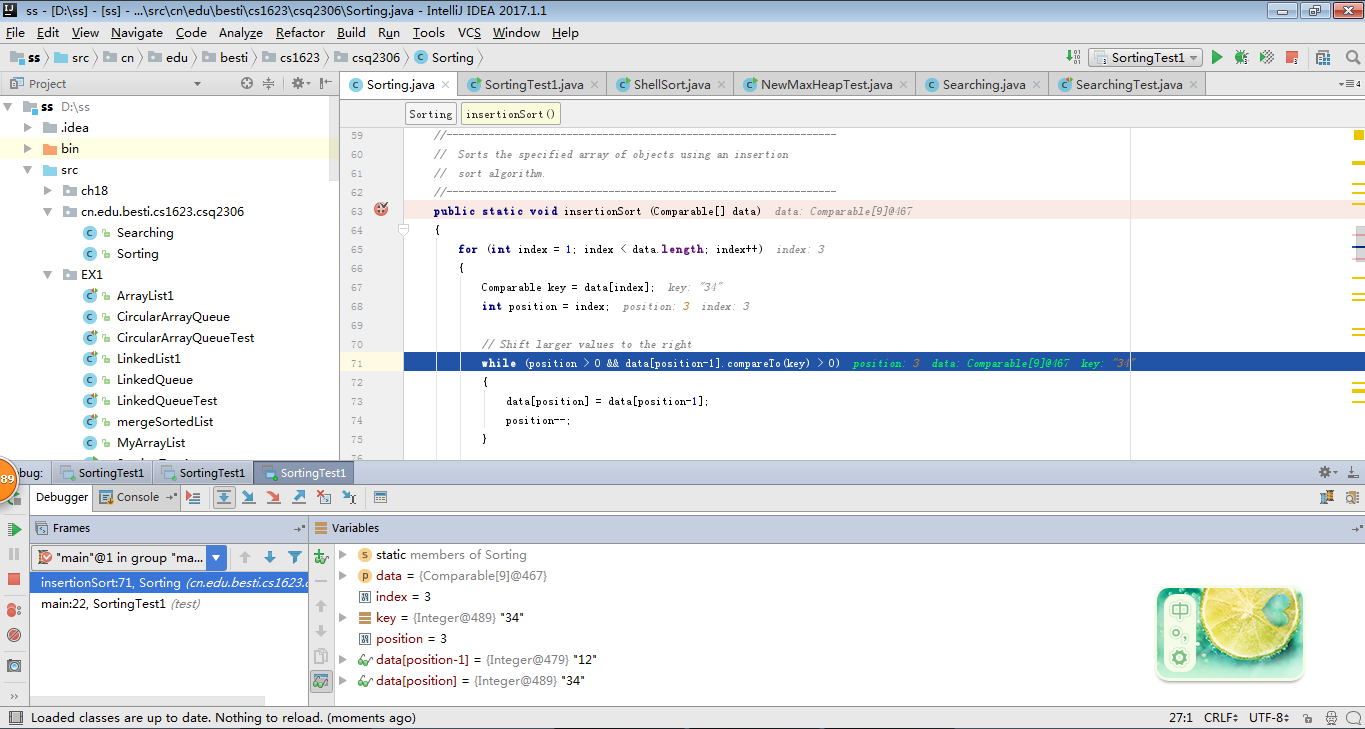
-
代码链接
第六周课堂测试补充
测试一:用链表实现队列
-
实验要求:
1 参考程序15.5给出方法deque,first,isEmpty,size,toString的定义,完成LinkedeQueue类并用Junit进行单元测试(正常,异常,边界情况)
2 提交测试代码运行截图,要全屏,包含自己的学号信息
3课下把代码推送到代码托管平台 -
实验过程:
1、dequeue方法:从队头删除元素,利用if-else循环判断队列是否为空,为空则返回The queue is empty;不为空则遍历队列中元素,删除队头元素
代码如下:
public T dequeue() throws EmptyCollectionException {
if (count == 0) {
System.out.println("The queue is empty");
return null;
}
else {
T result = front.getElement();
front = front.getNext();
count--;
return result;
}
}
2、isEmpty方法:判断队列中是否为空
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return (count == 0);
}
3、size方法:判定队列中元素的个数。
public int size()
{
return count;
}
4、toString方法:toString方法是将队列中的各个元素转换成String类型,然后便于打印出来。
public String toString(){
String result = "";
LinearNode<T> current = front;
while (current != null)
{
result = result + (current.getElement()).toString() + "
";
current = current.getNext();
}
return result;
}
}
5、first方法:检测队列中队头元素:判断队列是否为空,为空则返回The queue is empty;不为空则遍历队列中元素,返回队头元素
public T first() throws EmptyCollectionException {
if (count == 0) {
throw new EmptyCollectionException("The queue is empty.");
}
return front.getElement();
}
-
实验截图

-
测试代码
public class LinkedQueueTest extends TestCase{
public void test() {
LinkedQueue queue = new LinkedQueue();
queue.enqueue("2016");
queue.enqueue("2306");
queue.enqueue("20162306");
System.out.println(queue.first());
queue.dequeue();
System.out.println(queue.isEmpty());
System.out.println(queue.size());
String num1 = queue.toString();
System.out.println(num1);
assertEquals("2306", queue.dequeue());
System.out.println(queue.isEmpty());
System.out.println(queue.size());
String num2 = queue.toString();
System.out.println(num2);
}
}
- 代码链接
测试二:用数组实现循环队列
- 实验要求:
1 参考程序15.6给出方法deque,first,isEmpty,size,toString的定义,完成CireclularArrayQueue类并用Junit进行单元测试(正常,异常,边界情况)
2 提交测试代码运行截图,要全屏,包含自己的学号信息
3课下把代码推送到代码托管平台 - 实验过程:
1、dequeue方法:从队头删除元素,利用if-else循环判断队列是否为空,为空则返回The queue is empty;不为空则删除队头元素
代码如下:
public T dequeue() throws Stack.EmptyCollectionException {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new Stack.EmptyCollectionException("The queue is empty");
}
else {
T num = queue[front];
queue[front] = null;
front = (front + 1) % queue.length;
count--;
return num;
}
2、isEmpty方法:判断队列中是否为空
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return (count == 0);
}
3、size方法:判定队列中元素的个数。
public int size()
{
return count;
}
4、toString方法:toString方法是将队列中的各个元素转换成String类型,然后便于打印出来。
public String toString(){
String result = "";
LinearNode<T> current = front;
while (current != null)
{
result = result + (current.getElement()).toString() + "
";
current = current.getNext();
}
return result;
}
}
5、first方法:检测队列中队头元素:判断队列是否为空,为空则返回The queue is empty;不为空则遍历队列中元素,返回队头元素
public T first() throws EmptyCollectionException {
if (count == 0) {
throw new EmptyCollectionException("The queue is empty.");
}
return front.getElement();
}
- 测试代码
public class CircularArrayQueueTest extends TestCase {
public void test() throws Stack.EmptyCollectionException {
CircularArrayQueue Queue = new CircularArrayQueue();
Queue.enqueue("2016");
Queue.enqueue("2306");
Queue.enqueue("20162306");
assertEquals(3,Queue.size());
assertEquals(false,Queue.isEmpty());
assertEquals("2016",Queue.first());
assertEquals("2016",Queue.dequeue());
assertEquals(2,Queue.size());
}
}