问题:
给定二叉树,
root坐标为(0,0),
对于任意节点 (x,y), 其左孩子(x+1, y-1), 右孩子(x+1, y+1)
按照列输出节点。(从左到右,对于每一列,从上到下)
若多个节点坐标相同,则按照值从小到大进行输出。
Example 1:
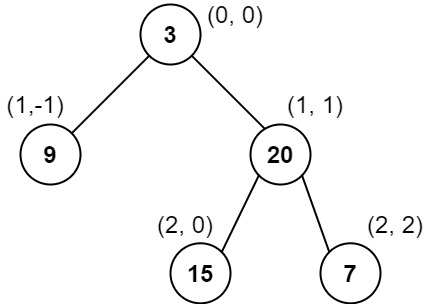
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]]
Explanation:
Column -1: Only node 9 is in this column.
Column 0: Nodes 3 and 15 are in this column in that order from top to bottom.
Column 1: Only node 20 is in this column.
Column 2: Only node 7 is in this column.
Example 2:
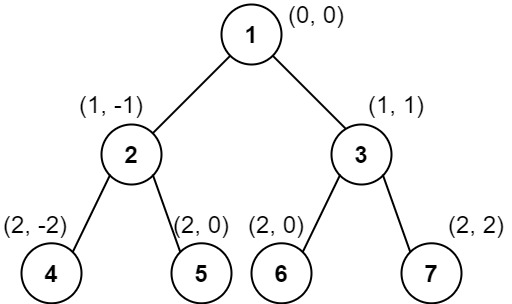
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]]
Explanation:
Column -2: Only node 4 is in this column.
Column -1: Only node 2 is in this column.
Column 0: Nodes 1, 5, and 6 are in this column.
1 is at the top, so it comes first.
5 and 6 are at the same position (2, 0), so we order them by their value, 5 before 6.
Column 1: Only node 3 is in this column.
Column 2: Only node 7 is in this column.
Example 3:
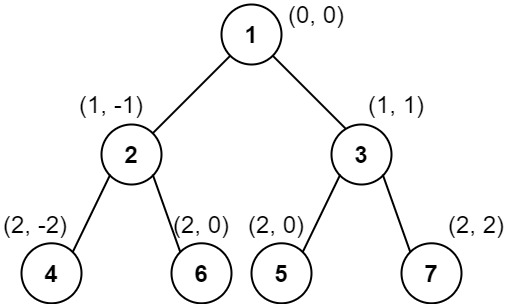
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,6,5,7]
Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]]
Explanation:
This case is the exact same as example 2, but with nodes 5 and 6 swapped.
Note that the solution remains the same since 5 and 6 are in the same location and should be ordered by their values.
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 1000].
0 <= Node.val <= 1000
example 1:
example 2:
example 3:
解法:BFS DFS
思路:对二叉树使用BFS或DFS进行遍历,
构造node结构体:node[y][x]={node1, node2, node3...}
最后,遍历node,对于每一列
node[y]
从第一行开始x=0...
node[y][0]={node1,node2...}
将该同一坐标的节点,按照value输出。加入结果中。
1 map<int, map<int, multiset<int>>> node;//{y,{x,{n1,n2,n3...}}} 2 dfs(node, root, 0, 0); 3 //bfs... 4 for(auto n:node) { 5 vector<int> col; 6 for(auto nc:n.second) { 7 col.insert(col.end(),nc.second.begin(),nc.second.end()); 8 } 9 res.push_back(col); 10 }
⚠️ 注意:node使用map:因为在遍历树之前,行数和列数都不确定,且需要按照从小到大存储。
对同一坐标,使用multiset:由于需要按照value大小输出,且,可能存在相同val的节点。
状态:
- TreeNode* root:当前节点
- (x, y):坐标
BFS
代码参考:
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 8 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 9 * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} 10 * }; 11 */ 12 class Solution { 13 public: 14 vector<vector<int>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode* root) { 15 vector<vector<int>> res; 16 map<int, map<int, multiset<int>>> node; 17 queue<pair<TreeNode*, pair<int,int>>> q; 18 q.push({root,{0,0}});//{node,{col,row}}//firstly sort by col 19 while(!q.empty()) { 20 int sz = q.size(); 21 for(int i=0; i<sz; i++) { 22 auto [cur, ord] = q.front(); 23 auto [y, x] = ord; 24 q.pop(); 25 node[y][x].insert(cur->val);//same(x,y) should sort by val 26 if(cur->left) { 27 q.push({cur->left,{y-1, x+1}}); 28 } 29 if(cur->right) { 30 q.push({cur->right,{y+1, x+1}}); 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 for(auto n:node) { 35 vector<int> col; 36 for(auto nc:n.second) { 37 col.insert(col.end(),nc.second.begin(),nc.second.end()); 38 } 39 res.push_back(col); 40 } 41 return res; 42 } 43 };
DFS
代码参考:
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 8 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 9 * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} 10 * }; 11 */ 12 class Solution { 13 public: 14 void dfs(map<int, map<int, multiset<int>>>& node, TreeNode* root, int x, int y) { 15 if(!root) return; 16 node[y][x].insert(root->val); 17 if(root->left) dfs(node, root->left, x+1, y-1); 18 if(root->right) dfs(node, root->right, x+1, y+1); 19 return; 20 } 21 vector<vector<int>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode* root) { 22 vector<vector<int>> res; 23 map<int, map<int, multiset<int>>> node;//{y,{x,{n1,n2,n3...}}} 24 dfs(node, root, 0, 0); 25 for(auto n:node) { 26 vector<int> col; 27 for(auto nc:n.second) { 28 col.insert(col.end(),nc.second.begin(),nc.second.end()); 29 } 30 res.push_back(col); 31 } 32 return res; 33 } 34 };