一、背景
最近在自己搞一个项目时,遇到可需要开发自定义注解的需求,对于没有怎么关注这些java新特性的来说,比较尴尬,索性就拿出一些时间,来进行研究下自定义注解开发的步骤以及使用方式。今天在这里记下,方便以后学习复习以及分享给有需要的小伙伴们~
二、注解基本概念
什么是注解?
注解就是某种注解类型的一个实例,我们可以用它在某个类上进行标注,这样编译器在编译我们的文件时,会根据我们自己设定的方法来编译类。
注解的分类有哪些?

由上图可知:注解共分为:标记注解、标准元注解、一般注解三类。
注:Deprecated注解,除了多个删除线,并没有什么拦截功能。
标准元注解详解
标准元注解是自定义注解的注解,主要包含4个,都位于java.lang.annotation包中,我们创建自定义注解时会用到4个标准元注解。它们的名称以及含义如下:
1. @Documented:用于描述其它类型的annotation应该被作为被标注的程序成员的公共API,因此可以被例如javadoc此类的工具文档化。是一个标记注解,没有成员。
2. @Inherited:是一个标记注解阐述了某个被标注的类型是被继承的。使用了@Inherited修饰的注解类型被用于一个class时该class的子类也有了该注解。
3. @Retention:定义了该注解的生命周期:某些注解仅出现在源代码中,而被编译器丢弃;而另一些却被编译在class文件中;编译在class文件中的注解可能会被虚拟机忽略,而另一些在class被装载时将被读取(请注意并不影响class的执行,因为注解与class在使用上是被分离的)。使用这个元注解可以对自定义注解的“生命周期”进行限制。
生命周期策略枚举
RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME 注解会在class字节码文件中存在,在运行时可以通过反射获取到。
RetentionPolicy.CLASS 默认的保留策略,注解会在class字节码文件中存在,但运行时无法获得。
RetentionPolicy.SOURCE 注解仅存在于源码中,在class字节码文件中不包含。
4. @Target:说明了注解所修饰的对象范围:注解可被用于 packages、types(类、接口、枚举、Annotation类型)、类型成员(方法、构造方法、成员变量、枚举值)、方法参数和本地变量(如循环变量、catch参数)。
修饰范围枚举
ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR 作用于构造器
ElementType.FIELD 作用于域/属性
ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE 用于描述局部变量
ElementType.METHOD 作用于方法
ElementType.PACKAGE 用于描述包
ElementType.PARAMETER 用于描述参数
ElementType.TYPE 用于描述类、接口(包括注解类型) 或enum声明,最常用
三、开发自定义注解demo
1.开发自定义类注解
1 package com.hafiz.zhang.annotation; 2 3 import java.lang.annotation.Documented; 4 import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; 5 import java.lang.annotation.Retention; 6 import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; 7 import java.lang.annotation.Target; 8 9 /** 10 * @author hafiz.Zhang 11 * @Date 2016年5月18日 下午1:58:11 12 * @Description 自定义类注解 13 */ 14 @Documented //定义可以被文档工具文档化 15 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//声明周期为runtime,运行时可以通过反射拿到 16 @Target(ElementType.TYPE)//注解修饰范围为类、接口、枚举 17 public @interface ClassAnnotation { 18 public String name() default "defaultService"; 19 public String version() default "1.1.0"; 20 }
2.自定义方法注解
1 package com.hafiz.zhang.annotation; 2 3 import java.lang.annotation.Documented; 4 import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; 5 import java.lang.annotation.Retention; 6 import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; 7 import java.lang.annotation.Target; 8 9 import com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.en.MethodTypeEnum; 10 11 /** 12 * @author hafiz.Zhang 13 * @Date 2016年5月18日 下午1:58:26 14 * @Description 自定义方法注解 15 */ 16 @Documented 17 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 18 @Target(ElementType.METHOD) 19 public @interface MethodAnnotation { 20 public String name() default "defaultName"; 21 public MethodTypeEnum type() default MethodTypeEnum.TYPE1; 22 }
3.自定义域注解
1 package com.hafiz.zhang.annotation; 2 3 import java.lang.annotation.Documented; 4 import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; 5 import java.lang.annotation.Retention; 6 import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; 7 import java.lang.annotation.Target; 8 9 /** 10 * @author hafiz.Zhang 11 * @Date 2016年5月18日 下午1:58:37 12 * @Description 自定义域注解 13 */ 14 @Documented 15 @Target(ElementType.FIELD) 16 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 17 public @interface FieldAnnotation { 18 public String name() default "defaultName"; 19 public String value() default "defaultValue"; 20 21 }
4.方法类型枚举类
1 package com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.en; 2 3 /** 4 * @author hafiz.Zhang 5 * @Date 2016年5月18日 下午1:59:02 6 * @Description 方法类型枚举类 7 */ 8 public enum MethodTypeEnum { 9 TYPE1,TYPE2 10 }
5.测试注解Bean
1 package com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.bean; 2 3 import com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.ClassAnnotation; 4 import com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.FieldAnnotation; 5 import com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.MethodAnnotation; 6 import com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.en.MethodTypeEnum; 7 8 /** 9 * @author hafiz.Zhang 10 * @Date 2016年5月18日 上午11:59:37 11 * @Description 测试使用的bean 12 */ 13 @ClassAnnotation(name="personBean", version="1.2.1") 14 public class Person { 15 @FieldAnnotation(name="description", value="This is my personal annotation") 16 private String description; 17 18 public String getDescription() { 19 return description; 20 } 21 22 public void setDescription(String description) { 23 this.description = description; 24 } 25 @MethodAnnotation(name="sayHello", type = MethodTypeEnum.TYPE2) 26 public void sayHello() { 27 System.out.println("Hello Annotation!"); 28 } 29 }
6.自定义类注解测试类
1 package com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.test; 2 3 import com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.ClassAnnotation; 4 import com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.bean.Person; 5 6 /** 7 * @author hafiz.Zhang 8 * @Date 2016年5月18日 上午11:56:34 9 * @Description 测试类注解 10 */ 11 public class TestClassAnnotation { 12 13 private static Person person = new Person(); 14 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 Class<?> clazz = person.getClass(); 17 //因为注解是作用于类上面的,所以可以通过isAnnotationPresent来判断是否是一个具有指定注解的类 18 if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(ClassAnnotation.class)) { 19 System.out.println("This is a class with annotation ClassAnnotation!"); 20 //通过getAnnotation可以获取注解对象 21 ClassAnnotation annotation = clazz.getAnnotation(ClassAnnotation.class); 22 if(null != annotation) { 23 System.out.println("BeanName = " + annotation.name()); 24 System.out.println("BeanVersion = " + annotation.version()); 25 }else{ 26 System.out.println("the annotation that we get is null"); 27 } 28 }else{ 29 System.out.println("This is not the class that with ClassAnnotation"); 30 } 31 } 32 }
运行结果:

7.自定义方法注解测试类
1 package com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.test; 2 3 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 4 5 import com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.MethodAnnotation; 6 import com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.bean.Person; 7 8 /** 9 * @author hafiz.Zhang 10 * @Date 2016年5月18日 下午12:11:11 11 * @Description 测试方法注解 12 */ 13 public class TestMethodAnnotation { 14 15 private static Person person = new Person(); 16 17 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 18 Class<?> clazz = person.getClass(); 19 //因为是注解到method上的,所以首先要获取这个方法 20 Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("sayHello"); 21 if(method.isAnnotationPresent(MethodAnnotation.class)) { 22 System.out.println("===This is a method with a annotation:MethodAnnotation==="); 23 //通过getAnnotation可以获取注解对象 24 MethodAnnotation annotation = method.getAnnotation(MethodAnnotation.class); 25 if(null != annotation) { 26 System.out.println("MethodName = " + annotation.name()); 27 System.out.println("MethodType = " + annotation.type()); 28 }else{ 29 System.out.println("the annotation that we get is null"); 30 } 31 }else{ 32 System.out.println("This is not the class that with MethodAnnotation"); 33 } 34 } 35 }
运行结果:

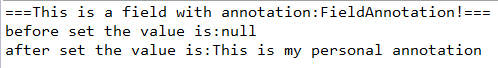
8.自定义域注解测试类
1 package com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.test; 2 3 import java.lang.reflect.Field; 4 5 import com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.FieldAnnotation; 6 import com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.bean.Person; 7 8 /** 9 * @author hafiz.Zhang 10 * @Date 2016年5月18日 下午12:17:49 11 * @Description 测试域注解 12 */ 13 public class TestFieldAnnotation { 14 15 private static Person person = new Person(); 16 17 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 18 Class<?> clazz = person.getClass(); 19 //因为是注解到Field上的,所以首先要获取这个字段 20 Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField("description"); 21 //判断这个Field上是否有这个注解 22 if(field.isAnnotationPresent(FieldAnnotation.class)) { 23 System.out.println("===This is a field with annotation:FieldAnnotation!==="); 24 //如果有这个注解,则获取注解类 25 FieldAnnotation annotation = field.getAnnotation(FieldAnnotation.class); 26 if(null != annotation){ 27 System.out.println("before set the value is:" + person.getDescription()); 28 //通过反射给私有变量赋值 29 field.setAccessible(true); 30 field.set(person, annotation.value()); 31 System.out.println("after set the value is:" + person.getDescription()); 32 }else{ 33 System.out.println("the annotation that we get is null"); 34 } 35 }else{ 36 System.out.println("This is not the class that with FieldAnnotation"); 37 } 38 } 39 }
运行结果:
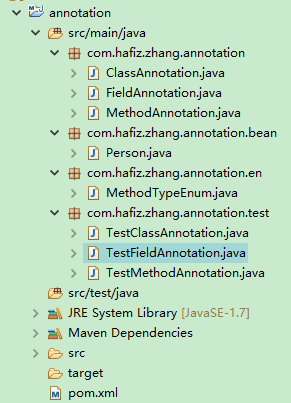
附:demo项目结构图
以上就是本人对自定义注解开发的理解以及开发测试了,如有错误希望大家能够批评指正!