一、概述
jdk的动态代理调用了Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,Class<?>[] interfaces,InvocationHandler h) 方法。
通过该方法生成字节码,动态的创建了一个代理类,interfaces参数是该动态类所继承的所有接口,而继承InvocationHandler 接口的类则是实现在调用代理接口方法前后的具体逻辑
二、Jdk代理的实现
首先要有一个接口:
public interface Person { void eat(String food); void sleep(String address); }
编写一个接口实现类:
@Getter @Setter public class Student implements Person { private String name; private Integer age; @Override public void eat(String food) { System.out.println("学生在吃" + food + "。。。"); } @Override public void sleep(String address) { System.out.println("学生在" + address + "睡觉。。。"); } }
再编写一个接口的代理类:用于对实现类的增强:
@Getter @Setter public class PersonProxy implements InvocationHandler { private Person person; public PersonProxy(Person person) { this.person = person; } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { System.out.println("proxy类: " + proxy.getClass() + " method: " + method + " args: " + Arrays.toString(args)); if (args != null) { for (Object arg : args) { System.out.println(arg + " "); } } // 在目标对象的方法执行之前简单的打印一下 System.out.println("------------------before------------------"); // 动态的调用目标方法 Object result = method.invoke(person, args); // 在目标对象的方法执行之后简单的打印一下 System.out.println("-------------------after------------------"); return result; } } ·
编写测试类进行测试
@Test public void testJdkInterfaceProxy() { // 创建一个是具体的接口实例 Person person = new Student(); /*Person studentProxy = (Person) Proxy.newProxyInstance(person.getClass().getClassLoader(), person.getClass().getInterfaces(), new PersonProxy(person));*/ // 通过反射包下的Proxy类调用静态方法生成一个代理对象 Person studentProxy = (Person) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Person.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Person.class}, new PersonProxy(person)); // 通过代理对象进行调用接口方法 studentProxy.eat("米饭"); studentProxy.sleep("教室"); }
测试结果:
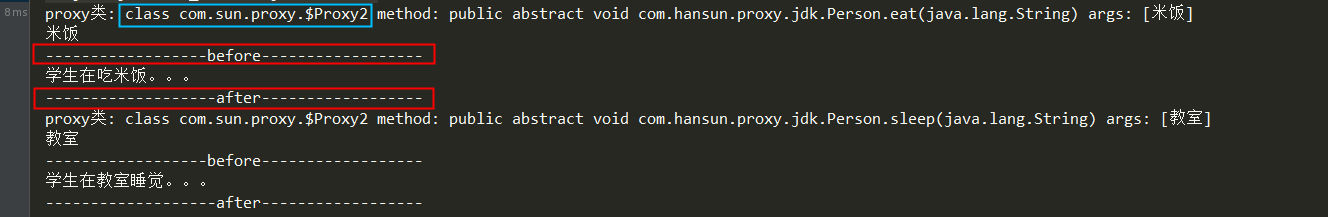
这说明代理类实现InvocationHandler接口后,通过Proxy生成了一个接口的代理对象来对实例进行增强操作。
三、如果没有接口是否还可以动态代理?
在上面的操作中有一个Person接口,然后Student类实现了Person接口, PersonProxy代理类对接口进行invoke()动态调用方法。
那么Proxy.newProxyInstance()方法可不可以对普通类生成代理对象呢?
测试代码:
@Test public void testJdkClassProxy() { Student student = new Student(); Student studentProxy = (Student) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Student.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Student.class}, new PersonProxy(student)); studentProxy.eat("米饭"); studentProxy.sleep("教室"); }
测试结果:
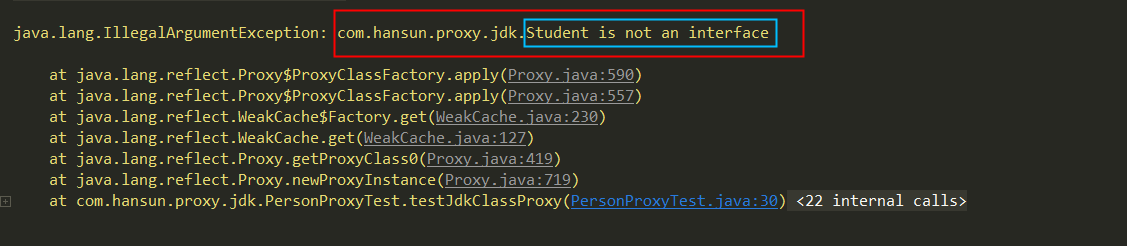
这说明Jdk的动态代理是不能对普通类生成代理对象的。
Student虽然是Person接口的实现类,但是如果直接去代理Student类是不可行的。
四、Jdk动态代理的原理实现
首先看看在Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces, InvocationHandler h)静态调用的时候发生了什么
java.lang.reflectProxy.Proxy类中部分源码:
1 public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, 2 Class<?>[] interfaces, 3 InvocationHandler h) 4 throws IllegalArgumentException 5 { 6 Objects.requireNonNull(h); 7 8 final Class<?>[] intfs = interfaces.clone(); 9 final SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager(); 10 if (sm != null) { 11 checkProxyAccess(Reflection.getCallerClass(), loader, intfs); 12 } 13 14 /* 15 * Look up or generate the designated proxy class. 16 */ 17 Class<?> cl = getProxyClass0(loader, intfs); 18 19 /* 20 * Invoke its constructor with the designated invocation handler. 21 */ 22 try { 23 if (sm != null) { 24 checkNewProxyPermission(Reflection.getCallerClass(), cl); 25 } 26 27 final Constructor<?> cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams); 28 final InvocationHandler ih = h; 29 if (!Modifier.isPublic(cl.getModifiers())) { 30 AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() { 31 public Void run() { 32 cons.setAccessible(true); 33 return null; 34 } 35 }); 36 } 37 return cons.newInstance(new Object[]{h}); 38 } catch (IllegalAccessException|InstantiationException e) { 39 throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e); 40 } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { 41 Throwable t = e.getCause(); 42 if (t instanceof RuntimeException) { 43 throw (RuntimeException) t; 44 } else { 45 throw new InternalError(t.toString(), t); 46 } 47 } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { 48 throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e); 49 } 50 }
在第17行:通过ClassLoader,所实现的接口列表来获取Class对象;
在第27行:通过反射机制获取到被代理类的构造器
在第37行:通过传入实现InvocationHandler子类的对象,利用反射机制得到一个代理对象
newProxyInstance方法执行了以下几种操作:
1.生成一个实现了参数interfaces里所有接口且继承了Proxy代理类的字节码,
然后用参数里的ClassLoader加载这个代理类。
2.使用代理类父类的构造函数 Proxy(InvocationHandler h)来创造一个代理类的实例,
将我们自定义的InvocationHandler的子类传入。
3.返回这个代理类实例。
在测试类中加入以下代码,会将生成的代理类对象Class文件写到磁盘中:
private void writeProxyClassFile() { byte[] bytes = ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass("PersonProxy", new Class[]{Person.class}); FileOutputStream out; try { out = new FileOutputStream("PersonProxy" + ".class"); out.write(bytes); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
利用反编译工具查看---生成的代理类 class字节码文件:
// // Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA // (powered by Fernflower decompiler) // import com.hansun.proxy.jdk.Person; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.lang.reflect.UndeclaredThrowableException; public final class PersonProxy extends Proxy implements Person { private static Method m1; private static Method m2; private static Method m4; private static Method m3; private static Method m0; public PersonProxy(InvocationHandler var1) throws { super(var1); } public final boolean equals(Object var1) throws { try { return (Boolean)super.h.invoke(this, m1, new Object[]{var1}); } catch (RuntimeException | Error var3) { throw var3; } catch (Throwable var4) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var4); } } public final String toString() throws { try { return (String)super.h.invoke(this, m2, (Object[])null); } catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) { throw var2; } catch (Throwable var3) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3); } } public final void eat(String var1) throws { try { super.h.invoke(this, m4, new Object[]{var1}); } catch (RuntimeException | Error var3) { throw var3; } catch (Throwable var4) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var4); } } public final void sleep(String var1) throws { try { super.h.invoke(this, m3, new Object[]{var1}); } catch (RuntimeException | Error var3) { throw var3; } catch (Throwable var4) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var4); } } public final int hashCode() throws { try { return (Integer)super.h.invoke(this, m0, (Object[])null); } catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) { throw var2; } catch (Throwable var3) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3); } } static { try { m1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("equals", Class.forName("java.lang.Object")); m2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("toString"); m4 = Class.forName("com.hansun.proxy.jdk.Person").getMethod("eat", Class.forName("java.lang.String")); m3 = Class.forName("com.hansun.proxy.jdk.Person").getMethod("sleep", Class.forName("java.lang.String")); m0 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("hashCode"); } catch (NoSuchMethodException var2) { throw new NoSuchMethodError(var2.getMessage()); } catch (ClassNotFoundException var3) { throw new NoClassDefFoundError(var3.getMessage()); } } }
这个生成的代理类对象是重写了接口的eat()和sleep()方法;
并且每一个方法体中都是类似这样的调用 super.h.invoke(this, m3, new Object[]{var1}) ;
这是调用动态代理类InvocationHandler具体实现类中的方法。
这表示当在测试类中 运行 studentProxy.eat("米饭"); 真正的逻辑操作是生成的Proxy代理对象去调用了,
InvocationHandler接口的具体实现类重写的invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)方法,
而invoke方法对方法的调用做了前置、后置处理;所以才会对接口的实现类进行增强操作。
// 在目标对象的方法执行之前简单的打印一下 System.out.println("------------------before------------------"); // 动态的调用目标方法,这才是真正调用接口实现类的方法 Object result = method.invoke(person, args); // 在目标对象的方法执行之后简单的打印一下 System.out.println("-------------------after------------------");
总结:
在通过JDK代理类工具Proxy获取代理newProxyInstance时,
其实获取的是Java类$proxy对象,并不是该对象的本事this。
五、为什么JDK动态代理必须针对接口
在生成的代理类对象的class字节码文件中:
// // Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA // (powered by Fernflower decompiler) // import com.hansun.proxy.jdk.Person; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.lang.reflect.UndeclaredThrowableException; public final class PersonProxy extends Proxy implements Person { private static Method m1; private static Method m2; private static Method m4; private static Method m3; private static Method m0; public PersonProxy(InvocationHandler var1) throws { super(var1); } 。。。。。。。 }
由于java的单继承,动态生成的代理类已经继承了Proxy类的,就不能再继承其他的类;
所以只能靠实现被代理类的接口的形式,故JDK的动态代理必须有接口。
六、代理对象调用方法为什么会自动进入InvocationHandler实现类 的 invoke()方法呢?
在上图的代理对象代码中它的构造器是有参构造器,参数为InvocationHandler接口实例对象。
// 当调用Proxy.newProxyInstance public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces, InvocationHandler h){ ....... return cons.newInstance(new Object[]{h}); }
而生成代理对象的每一个方法体都包含这样的调用:
// h 标识 InvocationHandler实例 super.h.invoke(this, m4, new Object[]{var1});
这就表示代理对象调用接口的方法时候,是调用InvocationHandler接口实现类中的invoke方法。
然后在我们的invoke() 方法中,再利用jdk反射的方式去调用真正的被代理类的业务方法(),Object result = method.invoke(被代理对象, args);而且还可以在方法的前后去加一些我们自定义的逻辑。比如切面编程AOP等。