好记性不如烂笔头,BOOST库的移植,我也记录一下。
1. BOOST库 版本1.66.0 下载地址, 附书籍C++ BOOST库开发指南:
https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_37372700/12960498
2.交叉编译:
当前环境:
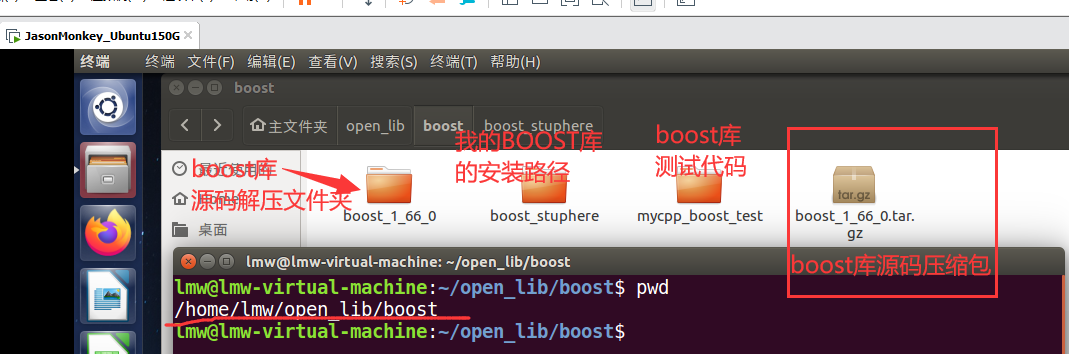
编译脚本:
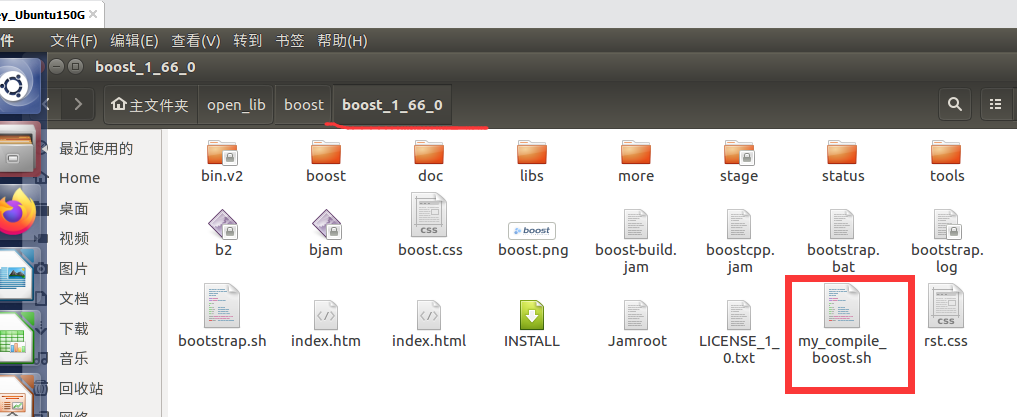
my_compile_boost.sh:
#xcompile_boost.sh
mfile=project-config.jam
if [ -e ${mfile} ];then
rm ${mfile}
echo "rm ${mfile}"
fi
#--with-libraries指定编译哪些boost库,all的话就是全部编译,
# 只想编译部分库的话就把库的名称写上,之间用 , 号分隔即可
#--with-libraries=system,filesystem,regex
./bootstrap.sh
--with-libraries=all
--prefix=/home/lmw/open_lib/boost/boost_stuphere
if [ -e ${mfile} ];then
mhost="mips-linux-gnu-g++ -fPIC"
sed -i "/using gcc/c using gcc : mips : ${mhost} ; " ${mfile}
fi
echo "After 5s start compile"
sleep 5s
./b2
echo "Afer 5s start install"
sleep 5s
./b2 install
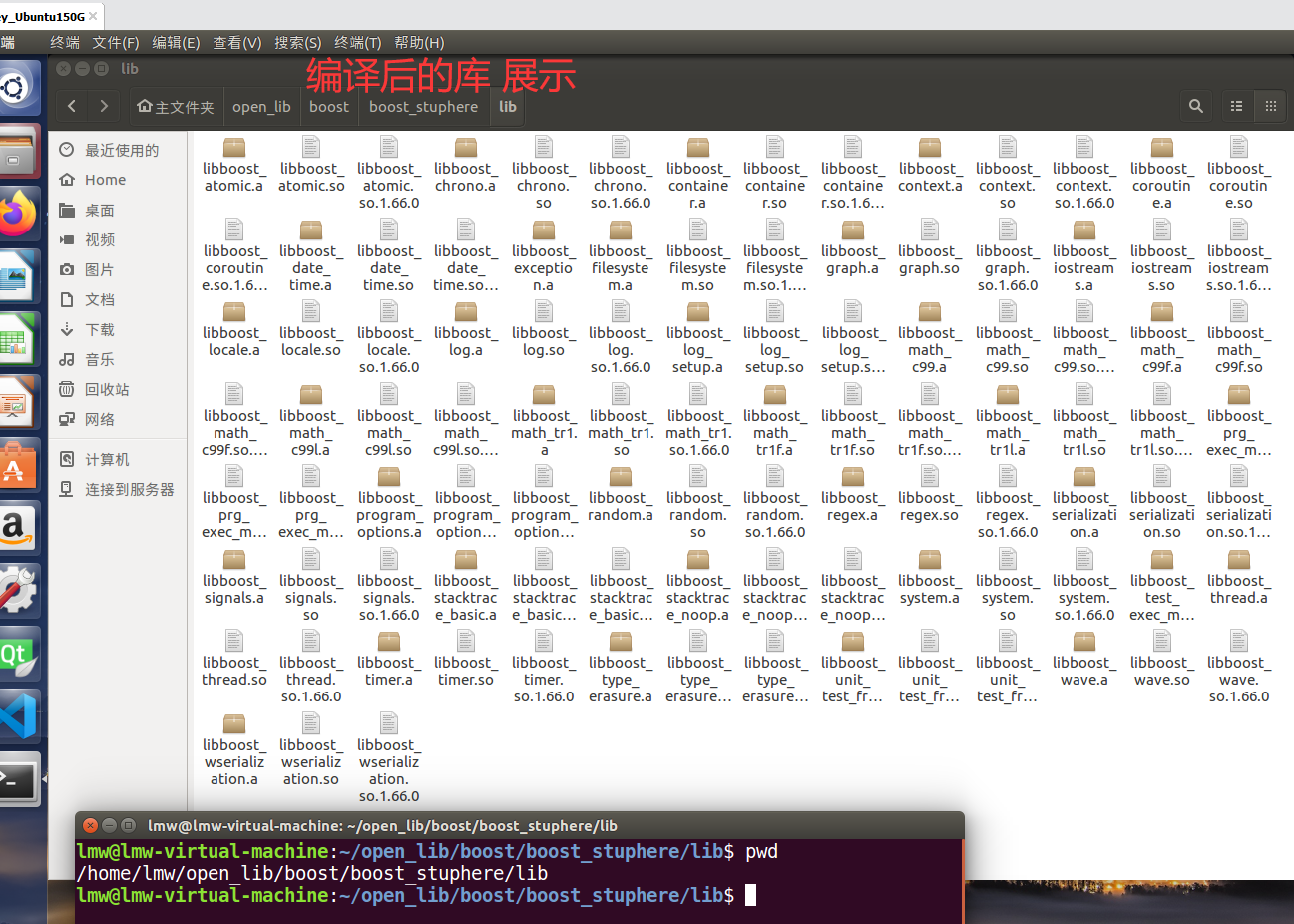
接着将所需的库文件挪到嵌入式系统内(根据自己调库的需要进行选择,同时考虑嵌入式的磁盘大小情况),
或者也可以直接把库文件放到ubuntu主机内的根文件系统内,重新制作下镜像,然后烧录系统到嵌入式设备上。
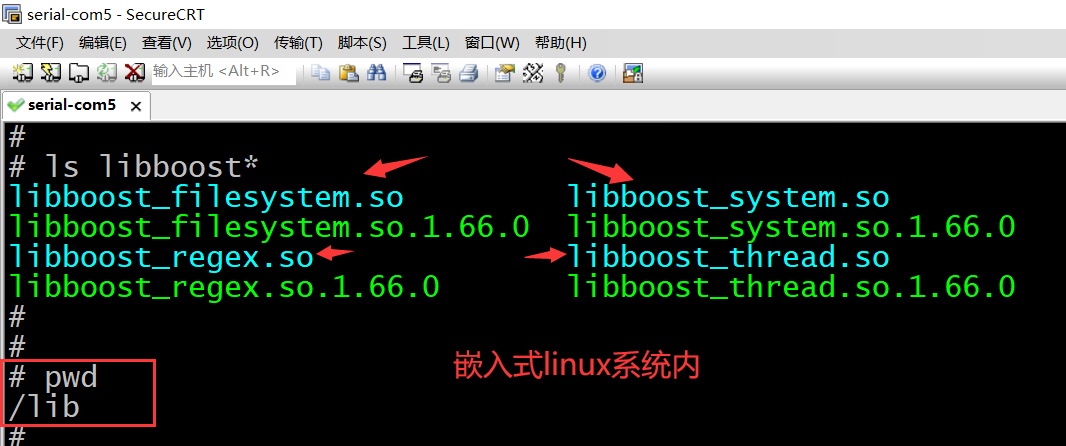
然后创建几个符号链接,如下图红色箭头所示。
3.测试代码
当前环境:

my_boost_test.cpp:
// test1 -- ( boost::this_thread::sleep() ) -- Success
#include <boost/thread/thread.hpp>
#include <iostream>
void wait(int seconds)
{
boost::this_thread::sleep(boost::posix_time::seconds(seconds));
}
void thread()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
wait(1);
std::cout << i << std::endl;
}
}
int main()
{
boost::thread t(thread);
t.join();
}
makefile:
.PHONY: DOIT
DOIT:
mips-linux-gnu-g++ -I. my_boost_test.cpp -L./lib -lboost_thread -lboost_system -o boost_app
.