带有头节点的循环链表。头节点的数据域为空,在查找某元素是否在链表中时,可用与存放该元素。头节点的next指针指向第一个元素。最后一个元素指向头节点。如图: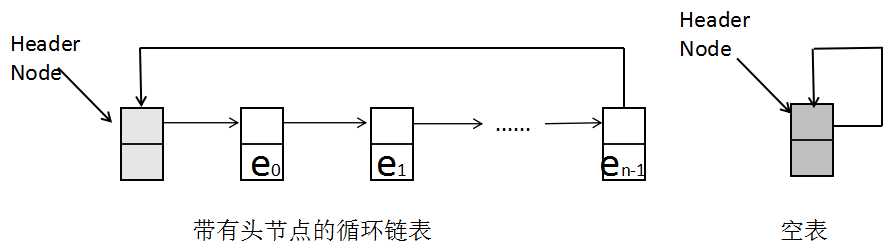
//CircularList.h文件 #pragma once template<class T> struct listNode{ T element; listNode<T>* next; listNode(){} listNode(const T&theElement){ this->element = theElement; } listNode(const T&theElement, listNode<T>*theNext){ this->element = theElement; this->next = theNext; } }; //有头节点的循环链表,头节点的指针域指向第一个元素 template<class T> class CircularList { public: CircularList(); CircularList(const CircularList<T>&); ~CircularList(); void insertFirstNode(const T& element); void insertLastNode(const T&element); void listInsert(int index, const T&element); void listDelete(int index); void print(); int listNodeFine(const T&); private: listNode<T>* ahead; int listSize; };
//CircularList.cpp文件 #include "CircularList.h" #include<iostream> using namespace std; #include "CircularList.h" #include<iostream> using namespace std; template<class T> //构造函数 CircularList<T>::CircularList() { ahead = new listNode<T>(); ahead->next = ahead; listSize = 0; } template<class T> //复制构造函数 CircularList<T>::CircularList(const CircularList<T>& List) { ahead = new listNode<T>; ahead->next = ahead; //首先形成一个空的循环链表 listNode<T>*current = ahead; listNode<T>*ListCurrent = List.ahead->next; if (List.ahead->next != List.ahead) //被拷贝的链表不为空 { while (ListCurrent->next != List.ahead) { listNode<T>*newNode = new listNode<T>(ListCurrent->element, current->next); current->next = newNode; current = current->next; ListCurrent = ListCurrent->next; listSize++; } if (ListCurrent->next == List.ahead) { listNode<T>*newNode = new listNode<T>(ListCurrent->element, current->next); current->next = newNode; listSize++; } } } template<class T> //析构函数 CircularList<T>::~CircularList() { while (ahead != NULL) { listNode<T>*current = ahead->next; delete ahead; ahead = current; } cout << "析构函数调用" << endl; } template<class T> //在头部插入元素 void CircularList<T>::insertFirstNode(const T& element) { listNode<T>*newNode = new listNode<T>(element,this->ahead->next); this->ahead->next = newNode; listSize++; } template<class T> //在尾部插入元素 void CircularList<T>::insertLastNode(const T&element) { listNode<T>*current = this->ahead; while (current->next != this->ahead) current = current->next; listNode<T>*newNode = new listNode<T>(element,current->next); current->next = newNode; listSize++; } template<class T> void CircularList<T>::listInsert(int index, const T&element) { listNode<T>*current = this->ahead->next; for (int i = 0; i < index-1; i++) current = current->next; listNode<T>*newNode = new listNode<T>(element, current->next); current->next = newNode; listSize++; } template<class T> void CircularList<T>::print() { listNode<T>*current = this->ahead->next; while (current != this->ahead) { cout << current->element << " "; current = current->next; } cout << endl; } template<class T> void CircularList<T>::listDelete(int index) { if (index<0 || index>this->listSize) { cout << "删除范围有错误,请重新输入!" << endl; return; } if (index == 0) { listNode<T>*current = this->ahead->next; ahead->next = current->next; delete current; } else { listNode<T>*current = this->ahead->next; for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) current = current->next; listNode<T>*temp = current->next; current->next = temp->next; delete temp; } listSize--; } template<class T> int CircularList<T>::listNodeFine(const T& A) { this->ahead->element = A; listNode<T>*current = this->ahead->next; int index = 0; while (current->element != A) { index++; current = current->next; } if (current == ahead) return -1; else return index; }
测试代码:

#include<iostream> #include<string> #include"CircularList.cpp" #include"CircularList.h" using namespace std; int main() { CircularList<int>y1; y1.insertFirstNode(1); y1.insertFirstNode(2); y1.insertLastNode(5); y1.insertLastNode(6); y1.listInsert(2, 10); y1.print(); CircularList<int>y3(y1); y3.print(); y1.listDelete(0); y1.print(); y1.listDelete(1); y1.print(); y1.listDelete(2); y1.print(); int index = y1.listNodeFine(2); cout << index; cout << "hello world" << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
