1.Swing组件类的层次
Swing组件分从显示效果上分为两种类型:JComponent类和Window类;
JComponent组件主要包括一些不能独立显示的组件(必须依附与其他组件才能显示)。
JPanel
JTable
JTree
JTextArea
JTextField
JButton
Window组件类主要包括可以独立显示的组件。
JFrame
JDialog
Swing组件从功能上分为三种类型:
顶级组件(顶级容器,可以独立显示)
JFrame、JApplet、JDialog、JWindow
中间组件
中间容器类(可以充当容器,但不能独立显示)
JPanel、JScrollPane、JSplitPane、JToolBar
特殊中间组件类(在GUI上起特殊作用的中间层,属于中间容器类,但是能起到美化和专业化的作用)
JInternalFrame、JLayeredPane、JRootPane等
基本组件(实现人机交互的组件,只能依附于中间组件才能显示)
JButton、JComboBox、JList、JMenu、JSlider、JTextField等
2.Window类
一切图形化的东西必须包括在顶级容器内。Swing中主要有三种可以使用的顶级容器:
JFrame(用于设计类似于Windows系统中的窗口程序)
内容面板(ContentPane)
基本组件
菜单条
JDialog(用于设计对话框)
3.JComponent类(所有轻量级组件的父类)
JComponent的九大特性:
Tooltips工具提示功能(鼠标停在组件上,显示提示),通过setToolTipText实现
绘画和边框(setBorder,BorderFactory)
可插入的观感器(定制自己的桌面,更换新的颜色方案,包括默认、Motif和Windows的L&F)
自定义属性
layout支持
无障碍
拖拽支持
双缓冲
键绑定
4.布局管理器
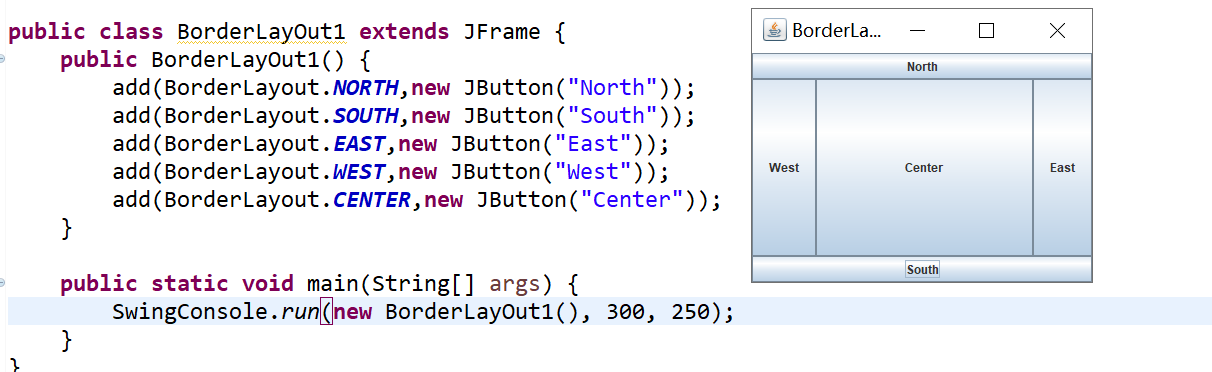
BorderLayout:东、南、西、北、中;(默认布局,默认被放置到中)
FlowLayout:按照加入的先后顺序排列,行满换行;从左到右,居中排列;

GridLayout:将空间划分为网状区域;

GriBagLayout:网状划分,功能较GridLayout复杂;
//太复杂了,给你个链接 https://www.cnblogs.com/aipan/p/6831872.html
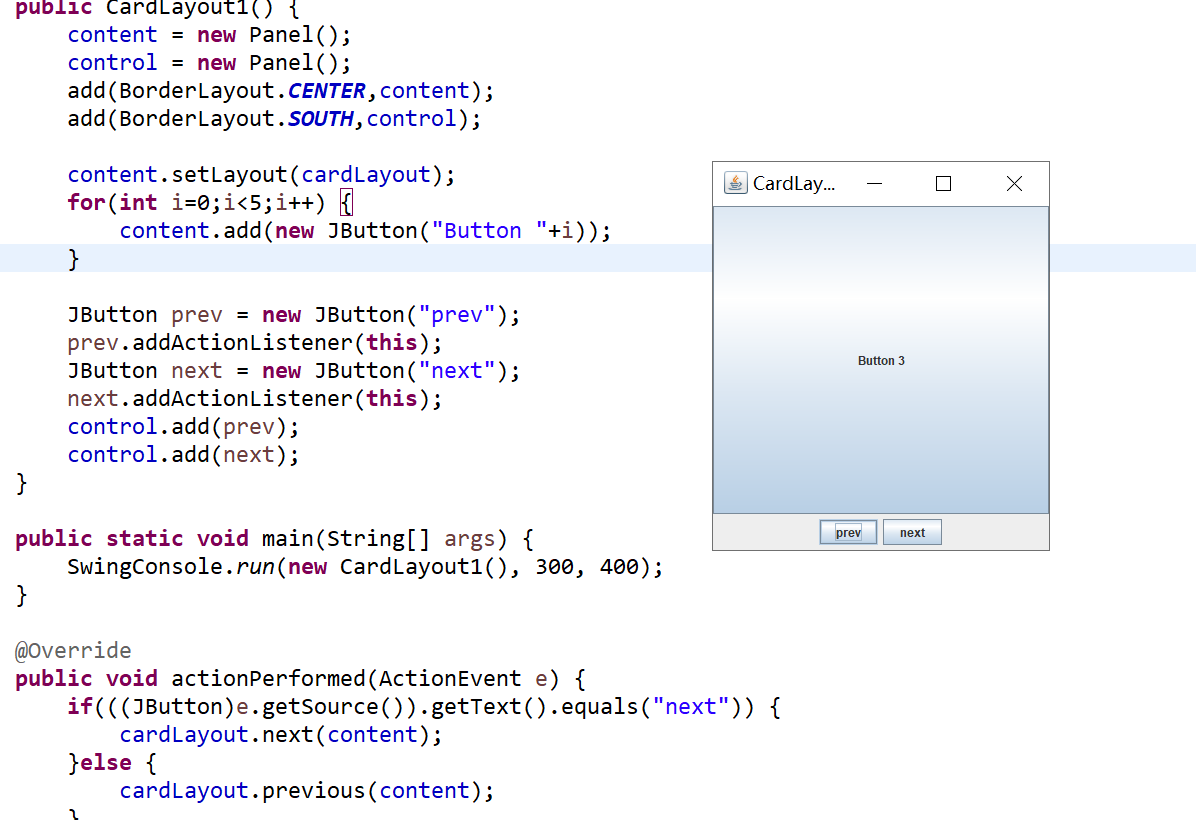
CardLayout:将组件当成卡片,每一只能显示一个。
BoxLayout:通过允许在容器中水平或垂直的方式安排多个组件;
SpringLayout:通过定义组件边沿的关系来实现布局;
GroupLayout:指定一个窗体上组件彼此之间的关系。
绝对定位,setLayout(null)把布局管理器设置为空,为每个组件调用setBounds()放啊发传递位置
5.常见组件
JPanel 普通面板组件
JScrollPane 带滚动的面板组件

JSplitPane 带分割的面板组件

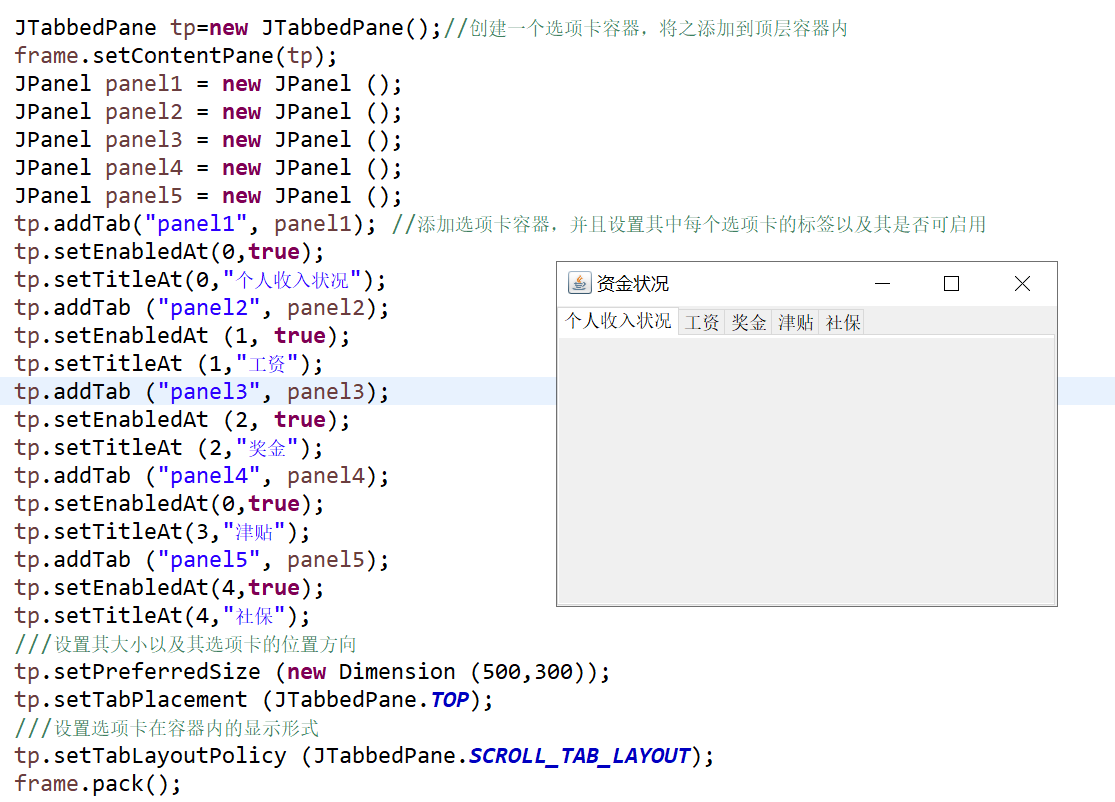
JTabbedPane 选项卡组件
JLabel 标签
JTextField 文本框
JTextArea 文本区域
JPasswordField 密码框
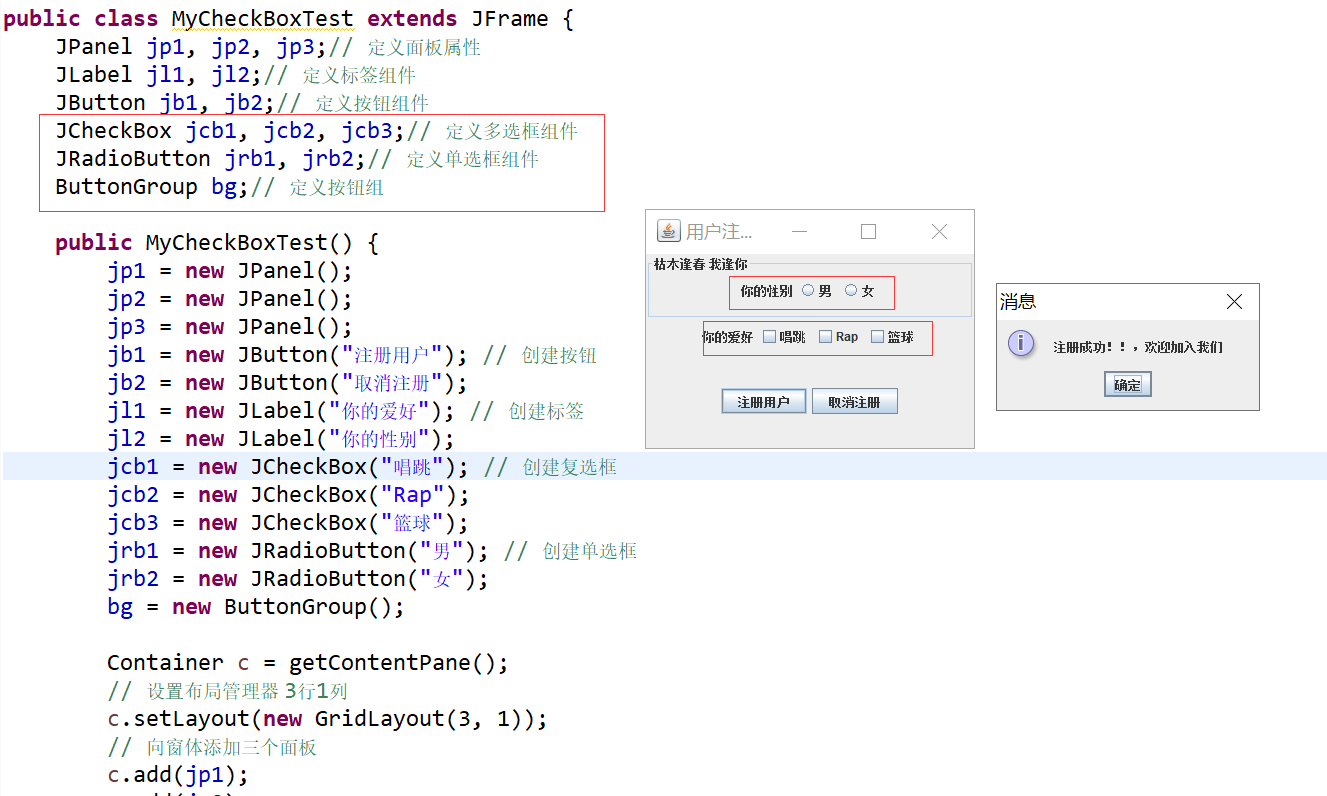
JRadioButton ButtonGroup 单选框
JCheckBox 复选框
JMenuBar

6. Swing与并发
当你使用swing编程时,就是在使用线程。在本章开头曾说过,所有的事物都应该通过SwingUtilities.invokeLater()提交swing事件分发线程。但是,不用显示的创建Thread对象这一事实意味着多线程问题可能会让你大吃一惊,你必须牢记存在着一个Swing事件分发线程,他始终在那里,通过从事件队列中拉出每个事件并依次执行它们,来处理所有的swing事件。牢记事件分发线程,将有助于确保你的应用免遭死锁和竞争条件影响。本节将讲述在使用Swing时所产生的多线程问题。
package com.example.demo.swing; import java.awt.Button; import java.awt.FlowLayout; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JFrame; public class LongRunningTask extends JFrame{ private JButton b1 = new JButton("Start long Running Task"); private JButton b2 = new JButton("End long Running Task"); public LongRunningTask() { b1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); } catch (InterruptedException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("Task completed"); } }); b2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } }); setLayout(new FlowLayout()); add(b1); add(b2); } public static void main(String[] args) { SwingConsole.run(new LongRunningTask(), 200, 150); } }
存在的问题,点击按钮之后无响应,点击第二个按钮并不会中断等待。
package com.example.demo.swing; import java.awt.FlowLayout; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JFrame; class Task implements Runnable{ private static int counter = 0; private final int id = counter++; @Override public void run() { System.out.println(this + " started"); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println(this + " interrupted"); return; } System.out.println(this + " comleted"); } public String toString() { return "Task " + id; } public long id() { return id; } } public class InterruptableLongRunningTask extends JFrame{ private JButton b1 = new JButton("Start long Running Task"); private JButton b2 = new JButton("End long Running Task"); ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); public InterruptableLongRunningTask() { b1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { Task task = new Task(); executorService.execute(task); System.out.println(task + " added to the queue"); } }); b2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { executorService.shutdownNow(); } }); setLayout(new FlowLayout()); add(b1); add(b2); } public static void main(String[] args) { SwingConsole.run(new InterruptableLongRunningTask(), 200, 150); } }
仍然存在问题shutdownNow()之后不能再执行任务了,所以需要Callable/Future.
public class TaskItem<R,C extends Callable<R>> { public final Future<R> future; public final C task; public TaskItem(Future<R> future,C task) { this.future = future; this.task = task; } } public class TaskManager<R,C extends Callable<R>> extends ArrayList<TaskItem<R,C>>{ private ExecutorService exec = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); public void add(C task) { add(new TaskItem<R, C>(exec.submit(task), task)); } public List<R> getResults(){ List<R> result = new ArrayList<>(); Iterator<TaskItem<R, C>> items = iterator(); while(items.hasNext()) { TaskItem<R, C> item = items.next(); if(item.future.isDone()) { try { result.add(item.future.get()); } catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } items.remove(); } } return result; } public List<String> purge(){ Iterator<TaskItem<R, C>> items = iterator(); List<String> results = new ArrayList<>(); while(items.hasNext()) { TaskItem<R, C> item = items.next(); if(!item.future.isDone()) { results.add("Cancelling "+item.task); item.future.cancel(true); items.remove(); } } return results; } } ============================================================================================================================ class Task implements Runnable{ private static int counter = 0; private final int id = counter++; @Override public void run() { System.out.println(this + " started"); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println(this + " interrupted"); return; } System.out.println(this + " comleted"); } public String toString() { return "Task " + id; } public long id() { return id; } } class CallableTask extends Task implements Callable<String>{ @Override public String call() throws Exception { run(); return "Return value of " + this; } } public class InterruptableLongRunningCallable extends JFrame{ private JButton b1 = new JButton("Start Long Running Task"); private JButton b2 = new JButton("End Long Running Task"); private JButton b3 = new JButton("Get results"); private TaskManager<String, CallableTask> manager = new TaskManager<>(); public InterruptableLongRunningCallable() { b1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { CallableTask task = new CallableTask(); manager.add(task); System.out.println(task + " added to the queue"); } }); b2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { for(String result:manager.purge()) { System.out.println(result); } } }); b3.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { for(TaskItem<String, CallableTask> tt:manager) { tt.task.id(); } for(String result:manager.getResults()) { System.out.println(result); } } }); setLayout(new FlowLayout()); add(b1); add(b2); add(b3); } public static void main(String[] args) { SwingConsole.run(new InterruptableLongRunningCallable(), 200, 150); } }
通常你还需要一个带进度条的友好提示界面
package com.example.demo.swing; import java.awt.FlowLayout; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.ProgressMonitor; import javax.swing.SwingUtilities; class MonitoredCallable implements Callable<String>{ private static int counter = 0; private final int id = counter++; private final ProgressMonitor monitor; private static final int MAX = 8; public MonitoredCallable(ProgressMonitor monitor) { this.monitor = monitor; monitor.setNote(toString()); monitor.setMaximum(MAX-1); monitor.setMillisToPopup(500); } @Override public String call() throws Exception { System.out.println(this + " stared"); try { for(int i=0;i<MAX;i++) { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500); if(monitor.isCanceled()) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } final int progess = i; SwingUtilities.invokeLater(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { monitor.setProgress(progess); } }); } }catch (Exception e) { monitor.close(); System.out.println(this + " interrupted"); return "Result: " + this + " interrupted"; } System.out.println(this + " completed"); return "Result: " + this + " completed"; } @Override public String toString() { return "Task " + id; } } public class MonitoredLongRunningCallable extends JFrame{ private JButton b1 = new JButton("Start Long Running Task"); private JButton b2 = new JButton("End Long Running Task"); private JButton b3 = new JButton("Get results"); private TaskManager<String, MonitoredCallable> manager = new TaskManager<>(); public MonitoredLongRunningCallable() { b1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { MonitoredCallable task = new MonitoredCallable(new ProgressMonitor(MonitoredLongRunningCallable.this, "Long-Running Task", "", 0, 0)); manager.add(task); System.out.println(task + " added to the queue"); } }); b2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { for(String resutl:manager.purge()) { System.out.println(resutl); } } }); b3.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { for(String result:manager.getResults()) { System.out.println(result); } } }); setLayout(new FlowLayout()); add(b1); add(b2); add(b3); } public static void main(String[] args) { SwingConsole.run(new MonitoredLongRunningCallable(), 200, 500); } }
22.10.2 可视化线程机制
package com.example.demo.swing; import java.awt.Color; import java.awt.Dimension; import java.awt.Graphics; import java.awt.GridLayout; import java.sql.Time; import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JPanel; class CBox extends JPanel implements Runnable{ private int pause; private static Random rand = new Random(); private Color color = new Color(0); public CBox(int pause) { this.pause = pause; } @Override protected void paintComponent(Graphics g) { g.setColor(color); Dimension s = getSize(); g.fillRect(0, 0, s.width, s.height); } @Override public void run() { while(!Thread.interrupted()) { color = new Color(rand.nextInt(0xFFFFFF)); repaint(); try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(pause); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } public class ColorBoxes extends JFrame{ private int grid = 12; private int pause = 50; private static ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); public void setUp() { setLayout(new GridLayout(grid,grid)); for(int i=0;i<grid*grid;i++) { CBox cBox = new CBox(pause); add(cBox); exec.execute(cBox); } } public static void main(String[] args) { ColorBoxes boxes = new ColorBoxes(); if(args.length>0) { boxes.grid = new Integer(args[0]); } if(args.length>1) { boxes.pause = new Integer(args[1]); } boxes.setUp(); SwingConsole.run(boxes, 500, 400); } }
22.11 可视化编程与JavaBean
Introspector(内省器)
package com.example.demo.swing; import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.Event; import java.awt.FlowLayout; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import java.beans.BeanInfo; import java.beans.EventSetDescriptor; import java.beans.IntrospectionException; import java.beans.Introspector; import java.beans.MethodDescriptor; import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.WildcardType; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JPanel; import javax.swing.JScrollPane; import javax.swing.JTextArea; import javax.swing.JTextField; public class BeanDumper extends JFrame{ private JTextField query = new JTextField(20); private JTextArea results = new JTextArea(); public void print(String s) { results.append(s+" "); } public void dump(Class<?> bean) { results.setText(""); BeanInfo bInfo = null; try { bInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(bean,Object.class); } catch (IntrospectionException e) { System.out.println("couldn't introspect " + bean.getName()); e.printStackTrace(); return; } for(PropertyDescriptor d:bInfo.getPropertyDescriptors()) { Class<?> p = d.getPropertyType(); if(p==null) continue; System.out.println("property type: " + p.getName() + "property name: "+d.getName()); Method readMethod = d.getReadMethod(); if(readMethod!=null) { System.out.println("read method: "+readMethod); } Method writeMethod = d.getWriteMethod(); if(writeMethod!=null) { System.out.println("write metho: "+writeMethod); } System.out.println("=============================="); } System.out.println("public methods:"); for(MethodDescriptor m:bInfo.getMethodDescriptors()) { System.out.println(m.getMethod().toString()); } System.out.println("=============================="); System.out.println("event support:"); for(EventSetDescriptor e:bInfo.getEventSetDescriptors()) { System.out.println("Listener type: "+e.getListenerType().getName()); for(Method lm:e.getListenerMethods()) { System.out.println("Listener method: "+lm.getName()); } for(MethodDescriptor lm:e.getListenerMethodDescriptors()) { System.out.println("method descriptor: "+ lm.getMethod()); } Method addListener = e.getAddListenerMethod(); System.out.println("Add listener Method "+ addListener); Method removeListener = e.getRemoveListenerMethod(); System.out.println("remove listener Method"+removeListener); System.out.println("=========================="); } } class Dumper implements ActionListener{ @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { String name = query.getText(); Class<?> c = null; try { c = Class.forName(name); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); results.setText("couldn't find "+name); return; } dump(c); } } public BeanDumper() { JPanel panel = new JPanel(); panel.setLayout(new FlowLayout()); panel.add(new JLabel("Qualified bean name")); panel.add(query); add(BorderLayout.NORTH,panel); add(new JScrollPane(results)); Dumper dumper = new Dumper(); query.addActionListener(dumper); query.setText("com.example.demo.swing.Frog"); dumper.actionPerformed(new ActionEvent(dumper, 0, "")); } public static void main(String[] args) { SwingConsole.run(new BeanDumper(), 600, 500); } }