L2TP是常用的一种point-site的VPN。而目前在Azure上的VPN Gateway只支持IPsec和SSTP两种。如果客户需要L2TP服务器,需要自己在VM中搭建。本文将介绍如何在Azure上搭建基于CentOS65的L2TP服务器。
一、在Azure上创建VM
1. 创建CentOS6.5的VM
在Azure上创建虚拟机时选择CentOS6.5:
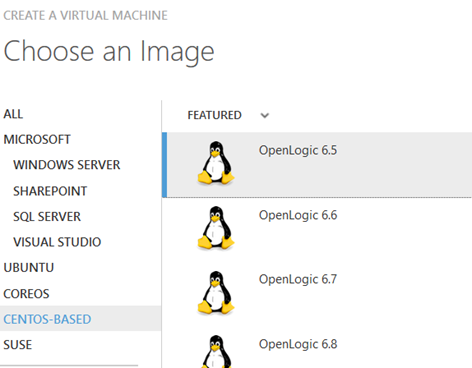
具体创建的过程就不再介绍了。
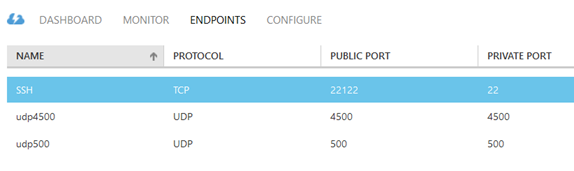
2. 给VM创建Endpoint
L2TP Over IPSec将使用UDP500和UDP4500两个端口,是标准的IPSEC的NAT-T端口。另外22端口也是需要的。具体的配置如下:
二、在VM上安装软件
通过SSH登陆VM。
1. 检查版本,配置YUM源
cat /etc/redhat-release CentOS release 6.5 (Final)
确认软件版本是CentOS6.5
vim /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo
[epel] name=epel baseurl=http://mirrors.sohu.com/fedora-epel/6/$basearch enabled=1 gpgcheck=0
2. 安装软件
a. 首先通过Yum安装:
yum install -y ppp iptables make gcc gmp-devel xmlto bison flex xmlto libpcap-devel lsof
b. 然后安装IPSEC:
下载最新的IPSEC:
wget https://download.openswan.org/openswan/openswan-2.6.49.tar.gz --no-check-certificate
解压:
tar vxf openswan-2.6.49.tar.gz
安装:
make programs install
c. 通过Yum安装epel里的xl2tpd:
yum install -y xl2tpd
三、配置各种服务
1. IPSEC的配置
vim /etc/ipsec.conf # /etc/ipsec.conf - Openswan IPsec configuration file # This file: /usr/local/share/doc/openswan/ipsec.conf-sample # # Manual: ipsec.conf.5 version 2.0 # conforms to second version of ipsec.conf specification # basic configuration config setup # Do not set debug options to debug configuration issues! # plutodebug / klipsdebug = "all", "none" or a combation from below: # "raw crypt parsing emitting control klips pfkey natt x509 dpd private" # eg: # plutodebug="control parsing" # Again: only enable plutodebug or klipsdebug when asked by a developer # # enable to get logs per-peer # plutoopts="--perpeerlog" # # Enable core dumps (might require system changes, like ulimit -C) # This is required for abrtd to work properly # Note: incorrect SElinux policies might prevent pluto writing the core dumpdir=/var/run/pluto/ # # NAT-TRAVERSAL support, see README.NAT-Traversal nat_traversal=yes # exclude networks used on server side by adding %v4:!a.b.c.0/24 # It seems that T-Mobile in the US and Rogers/Fido in Canada are # using 25/8 as "private" address space on their 3G network. # This range has not been announced via BGP (at least upto 2010-12-21) virtual_private=%v4:10.0.0.0/8,%v4:192.168.0.0/16,%v4:172.16.0.0/12,%v4:25.0.0.0/8,%v6:fd00::/8,%v6:fe80::/10 # OE is now off by default. Uncomment and change to on, to enable. oe=off # which IPsec stack to use. auto will try netkey, then klips then mast protostack=netkey #protostack=auto # Use this to log to a file, or disable logging on embedded systems (like openwrt) #plutostderrlog=/dev/null # Add connections here # sample VPN connection # for more examples, see /etc/ipsec.d/examples/ #conn sample # # Left security gateway, subnet behind it, nexthop toward right. # left=10.0.0.1 # leftsubnet=172.16.0.0/24 # leftnexthop=10.22.33.44 # # Right security gateway, subnet behind it, nexthop toward left. # right=10.12.12.1 # rightsubnet=192.168.0.0/24 # rightnexthop=10.101.102.103 # # To authorize this connection, but not actually start it, # # at startup, uncomment this. # #auto=add conn L2TP-PSK-NAT rightsubnet=vhost:%priv also=L2TP-PSK-noNAT conn L2TP-PSK-noNAT authby=secret pfs=no auto=add keyingtries=3 rekey=no ikelifetime=8h keylife=1h type=transport left=10.215.92.31 #AWS EC2 Internal IP leftprotoport=17/1701 right=%any rightprotoport=17/%any dpddelay=30 dpdtimeout=120 dpdaction=clear
2. 配置IPSEC的Security
vim /etc/ipsec.secrets # This file holds shared secrets or RSA private keys for inter-Pluto # authentication. See ipsec_pluto(8) manpage, and HTML documentation. # RSA private key for this host, authenticating it to any other host # which knows the public part. Suitable public keys, for ipsec.conf, DNS, # or configuration of other implementations, can be extracted conveniently # with "ipsec showhostkey". # this file is managed with debconf and will contain the automatically created RSA keys #include /var/lib/openswan/ipsec.secrets.inc %any %any: PSK "azure"
3. 配置sysctl.conf文件
vim /etc/sysctl.conf net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1 net.ipv4.conf.default.rp_filter = 0 net.ipv4.conf.all.send_redirects = 0 net.ipv4.conf.default.send_redirects = 0 net.ipv4.conf.all.log_martians = 0 net.ipv4.conf.default.log_martians = 0 net.ipv4.conf.default.accept_source_route = 0 net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects = 0 net.ipv4.conf.default.accept_redirects = 0 net.ipv4.icmp_ignore_bogus_error_responses = 1
通过下面的命令,是配置生效:
sysctl -p
service ipsec start
ipsec verify
4. 配置xl2tpd
vim /etc/xl2tpd/xl2tpd.conf ; ; This is a minimal sample xl2tpd configuration file for use ; with L2TP over IPsec. ; ; The idea is to provide an L2TP daemon to which remote Windows L2TP/IPsec ; clients connect. In this example, the internal (protected) network ; is 192.168.1.0/24. A special IP range within this network is reserved ; for the remote clients: 192.168.1.128/25 ; (i.e. 192.168.1.128 ... 192.168.1.254) ; ; The listen-addr parameter can be used if you want to bind the L2TP daemon ; to a specific IP address instead of to all interfaces. For instance, ; you could bind it to the interface of the internal LAN (e.g. 192.168.1.98 ; in the example below). Yet another IP address (local ip, e.g. 192.168.1.99) ; will be used by xl2tpd as its address on pppX interfaces. [global] ; listen-addr = 192.168.1.98 ; ; requires openswan-2.5.18 or higher - Also does not yet work in combination ; with kernel mode l2tp as present in linux 2.6.23+ ; ipsec saref = yes ; Use refinfo of 22 if using an SAref kernel patch based on openswan 2.6.35 or ; when using any of the SAref kernel patches for kernels up to 2.6.35. ; saref refinfo = 30 ; ; force userspace = yes ; ; debug tunnel = yes ipsec saref = no [lns default] ip range = 192.168.1.128-192.168.1.254 local ip = 192.168.1.99 require chap = yes refuse pap = yes require authentication = yes name = LinuxVPNserver ppp debug = yes pppoptfile = /etc/ppp/options.xl2tpd length bit = yes
5. 配置ppp的用户名密码
vim /etc/ppp/chap-secrets # Secrets for authentication using CHAP # client server secret IP addresses user * azure *
6. 配置iptables
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.1.0/24 -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE iptables -I FORWARD -s 192.168.1.0/24 -j ACCEPT iptables -I FORWARD -d 192.168.1.0/24 -j ACCEPT service iptables save
四、设置服务
service ipsec restart
service xl2tpd restart
service iptables restart
chkconfig xl2tpd on
chkconfig iptables on
chkconfig ipsec on
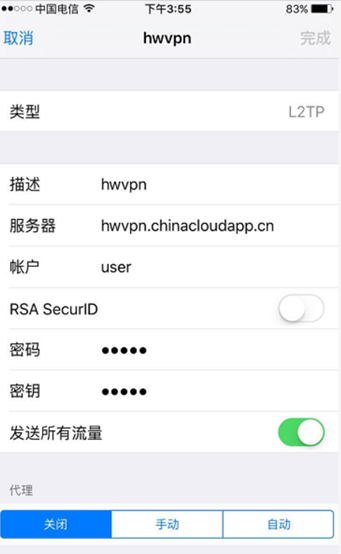
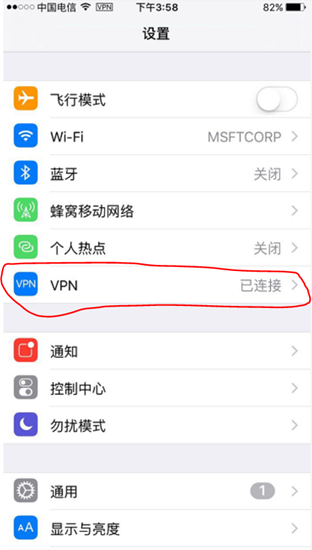
五、设置IPHONE