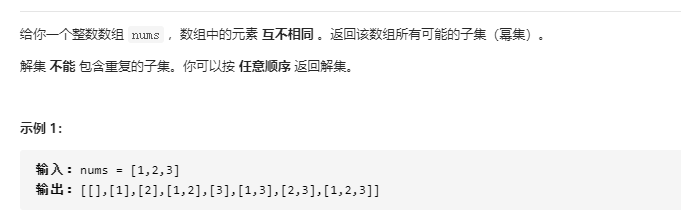
78
下面是我的写法 应该比较啰嗦
public static List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < nums.length-1; i++) { List<Integer> tp = Arrays.asList(nums[i]); List<List<Integer>> li = new ArrayList<>(); li.add(tp); for (int j = i+1; j < nums.length; j++) { List<List<Integer>> lis = new ArrayList<>(); for (List<Integer> integers : li) { List<Integer> tps = new ArrayList<>(integers); tps.add(nums[j]); lis.add(tps); } li.addAll(lis); } result.addAll(li); } result.add(Arrays.asList(nums[nums.length-1])); result.add(new ArrayList<>()); return result; }
下面是一个简洁一点的答案,原理应该是和我的一致

137 只出现一次的数

这个问题有点头痛,看了下官方题解。 解决这个问题要先理解 与操作是两个都为1则为1 ,否则为0;异或是相同为0,不同则为1;非运算时1变0,0变1。那也可以得到一些结论 0和任何数做异或操作结果是其本身。两个相同的数做异或操作结果为0。一个数做非操作也就是取反后的值再与数做与操作结果会为0; 然后观察题目可以看到 。只有一个数出现一次,其他都出现三次。这和之前的其他数只出现两次的问题不一样,如果直接用异或操作是不行的。那我相比于之前的两次出现的数的解决办法需要再加一个值来记录状态。
也就是说计算两次出现的数时我们 是 第一次出现时异或得到值本身,第二次出现时异或值变为0。计算本题中三次出现的数时我们要 第一次出现异或时得到值本身 将其记录在第一个值上,第二次出现时将其记录在第二个值上 第一个值变为0,第三次出现时第二个值变为0。此时只出现了一次的值就记录在第一个值上。
这儿贴一份官方的代码,注释写在里面了 传送门
class Solution { public int singleNumber(int[] nums) { int seenOnce = 0, seenTwice = 0; for (int num : nums) { // first appearence: // add num to seen_once // don't add to seen_twice because of presence in seen_once // second appearance: // remove num from seen_once // add num to seen_twice // third appearance: // don't add to seen_once because of presence in seen_twice // remove num from seen_twice seenOnce = ~seenTwice & (seenOnce ^ num); seenTwice = ~seenOnce & (seenTwice ^ num); } return seenOnce; } }
这儿可以以13为例(二进制 1101) 那么三次遍历的结果后 one和twice的值如下
- one 1101 ,twice 0000
- one 0000,twice 1101
- one 0000,twice 0000
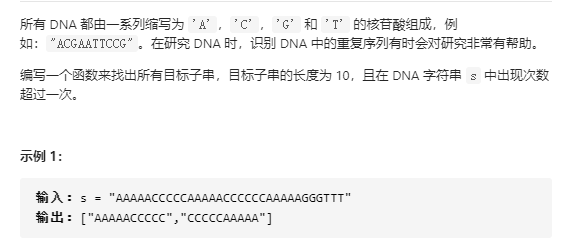
187 重复DNA序列
容易想到的解法是用一个hash表存下来,然后每次遍历的时候看下hash表里是否还有这个数据
public static List<String> findRepeatedDnaSequences(String s) { List<String> result = new ArrayList<>(); if (s.length()<=10){ return result; } Set<String> sets = new HashSet<>(); Set<String> rs = new HashSet<>(); sets.add(s.substring(0,10)); for (int i = 10; i < s.length(); i++) { String substring = s.substring(i - 9, i+1); if (sets.contains(substring)){ rs.add(substring); }else { sets.add(substring); } } result.addAll(rs); return result; }
还有一种官方题解自己难得也想到过, 就是只有四个字符,那么可以用00 10 01 11来表示,10个字符一共是 20位, 这样的话遍历的时候我们只需将最高的两位置为0,然后左移两位将当前字符补在最低的两位。这样就可以避免像上面的解法那样在用substring获取。不过自己嫌麻烦没写。。汗。。 具体代码可以看下官方解析。
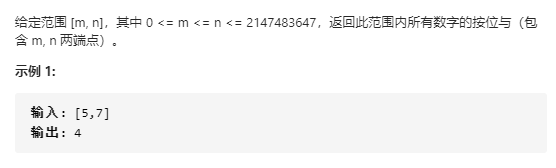
201 数字范围按位与或,这题感觉是找规律啊。二进制的最长公共前缀,具体解析看下官方,代码如下
class Solution { public int rangeBitwiseAnd(int m, int n) { int shift = 0; // 找到公共前缀 while (m < n) { m >>= 1; n >>= 1; ++shift; } return m << shift; } }
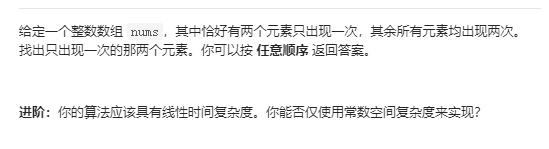
260 只出现一次数字
暴力解法可以如下
public int[] singleNumber(int[] nums) { Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap(); int[] result = new int[2]; int k = 0; for (Integer integer : nums) { map.put(integer,map.getOrDefault(integer,0)+1); } for (Integer integer : map.keySet()) { Integer tp = map.get(integer); if (tp == 1){ result[k++] = integer; } } return result; }
上面的方法明显不会是正确解,这儿可以根据分组异或的情况使用位运算来做,根据异或的性质,所有的数异或的结果就是这两个只出现了一次的数的异或的结果,所以我们要找到这两个数异或的结果中任意一个为1的位,因为根据异或的性质,相同为0,不同为1,所以位数为1代表着两个数在该位不同,那么根据这个位将数组分为两个,那两个只出现一次的数肯定被分到两个不同的数组,而由于两个一样的数在某个位肯定也是一样的,所以问题也就变成了求一个数组中只出现一次的某个数,其他均出现两次。代码也就是如下
class Solution { public int[] singleNumber(int[] nums) { int k = 0; for (int num : nums) { k^=num; } int s = 0; while (((k >>s)&1) == 0){ s++; } int index = 1<<s; int res1 = 0; int res2 = 0; for (int num : nums) { if ((num&index) == 0){ res1^=num; }else { res2^=num; } } return new int[]{res1,res2}; } }
338 比特位计数

实在妹想到, 这题的题解居然是动态规划,我看这是在为难我胖虎。递推式就是当前数的最后一个1变为0的数字+1。将当前数字的最后一个1变为0的快速计算表达式为n&(n-1) 所有就是 a[n] = a[n&(n-1)]+1,也就很容易得到结果了
class Solution { public int[] countBits(int num) { int[] ans = new int[num + 1]; for (int i = 1; i <= num; ++i) ans[i] = ans[i & (i - 1)] + 1; return ans; } }
393 这题本身应该是不难的,就是规则要仔细看
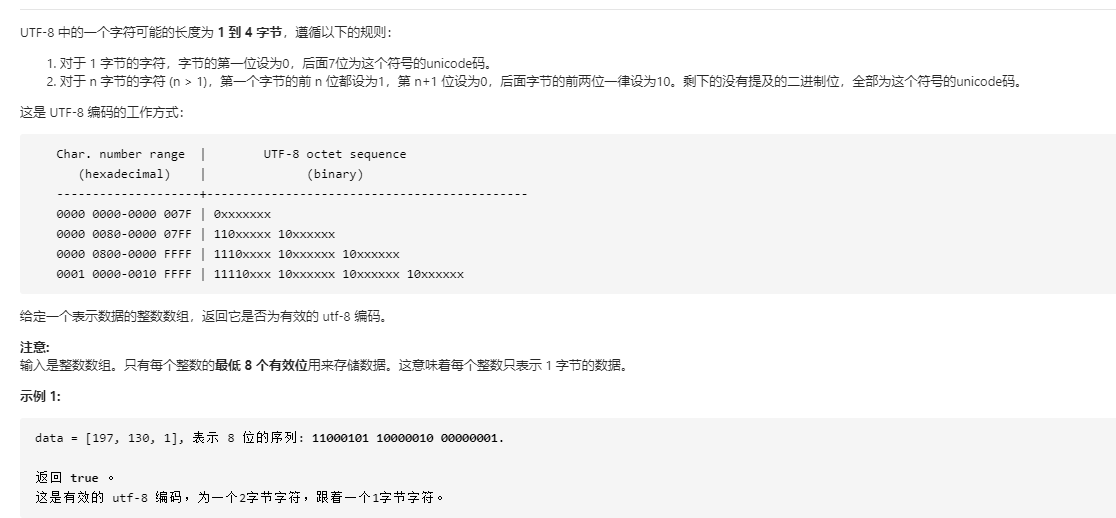
class Solution { public boolean validUtf8(int[] data) { if (data.length == 0){ return true; } for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) { int datum = data[i]; int s = 7; int c = 0; while (s >=0 &&((datum&(1<<s)) != 0)){ c++; s--; } if (c == 0){ continue; } if (c == 1){ return false; } if (c > 4){ return false; } for (int j = 1; j <= c-1; j++) { if (i+j>data.length-1){ return false; } if ((~data[i+j] & 0x80) != 0){ return false; } } i+=c-1; } return true; } }