线性回归问题
1 # encoding: utf-8 2 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 6 data = [] 7 for i in range(100): 8 x = np.random.uniform(-10., 10.) #均匀分布产生x 9 eps = np.random.normal(0., 0.01) #高斯分布产生一个误差值 10 y = 1.477*x + 0.089 +eps #计算得到y值 11 data.append([x, y]) #保存到data中 12 13 data = np.array(data) #转成数组的方式方便处理 14 plt.plot(data[:,0], data[:,1], 'b') #自己引入用于观察原始数据 15 #plt.show() 16 plt.savefig('original data.png') 17 18 19 def mse(b, w, points): #计算所有点的预测值和真实值之间的均方误差 20 totalError = 0 21 for i in range(0, len(points)): 22 x = points[i, 0] 23 y = points[i, 1] 24 totalError += (y -(w*x + b))**2 #真实值减预测值的平方 25 return totalError/float(len(points)) #返回平均误差值 26 27 28 def step_gradient(b_current, w_current, points, lr): #预测模型中梯度下降方式优化b和w 29 b_gradient = 0 30 w_gradient = 0 31 M = float(len(points)) 32 for i in range(0, len(points)): 33 x = points[i, 0] 34 y = points[i, 1] 35 b_gradient += (2/M) * ((w_current*x + b_current) - y) #求偏导数的公式可知 36 w_gradient += (2/M)*x*((w_current*x + b_current) - y) #求偏导数的公式可知 37 new_b = b_current - (lr*b_gradient) #更新参数,使用了梯度下降法 38 new_w = w_current - (lr*w_gradient) #更新参数,使用了梯度下降法 39 return [new_b, new_w] 40 41 42 def gradient_descent(points, starting_b, starting_w, lr, num_iterations): #循环更新w,b多次 43 b = starting_b 44 w = starting_w 45 loss_data = [] 46 for step in range(num_iterations): #计算并更新一次 47 b, w = step_gradient(b, w, np.array(points), lr) #更新了这一次的b,w 48 loss = mse(b, w, points) 49 loss_data.append([step+1, loss]) 50 if step % 50 == 0: #每50次输出一回 51 print(f"iteration:{step}, loss{loss}, w:{w}, b:{b}") 52 return [b, w, loss_data] 53 54 55 def main(): 56 lr = 0.01 #学习率,梯度下降算法中的参数 57 initial_b = 0 #初值 58 initial_w = 0 59 num_iterations = 1000 #学习100轮 60 [b, w, loss_data] = gradient_descent(data, initial_b, initial_w, lr, num_iterations) 61 loss = mse(b, w, data) 62 print(f'Final loss:{loss}, w:{w}, b:{b}') 63 64 plt.figure() #观察loss每一步情况 65 loss_data = np.array(loss_data) 66 plt.plot(loss_data[:,0], loss_data[:,1], 'g') 67 plt.savefig('loss.png') 68 #plt.show() 69 70 plt.figure() #观察最终的拟合效果 71 y_fin = w*data[:,0] + b + eps 72 plt.plot(data[:,0], y_fin, 'r') 73 #plt.show() 74 plt.savefig('final data.png') 75 76 77 if __name__ == '__main__': 78 main()
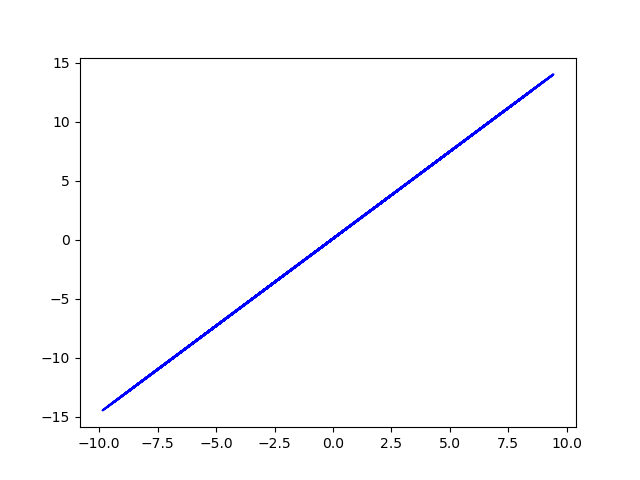
original data (y = w*x + b +eps)
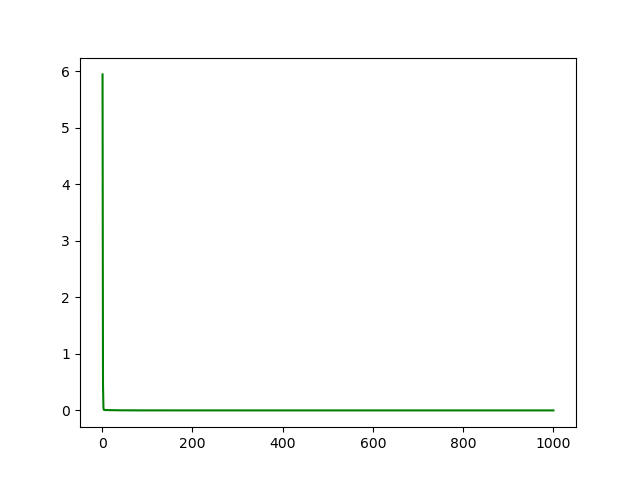
loss rate
final data (y' = w' *x + b' + eps )
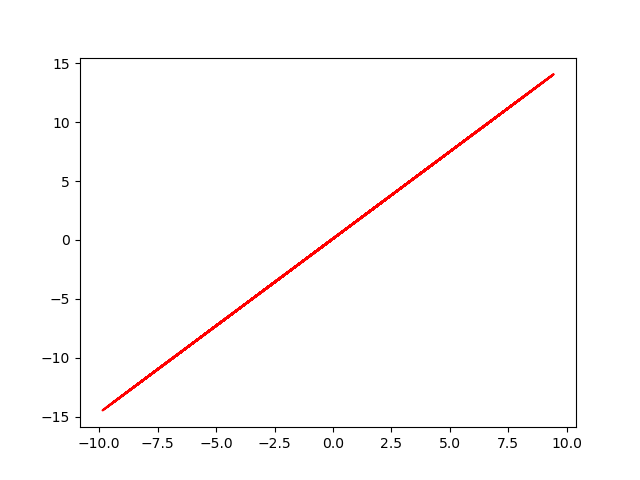
最终loss趋近9.17*10^-5, w趋近1.4768, b趋近0.0900
真实的w值1.477, b为0.089
对于线性回归问题,适用性挺好!
主要的数学代码能理解,唯有取梯度的反方向更新参数,不是很能理解!

这里还没有用到tensorflow,下一次更新基础知识!