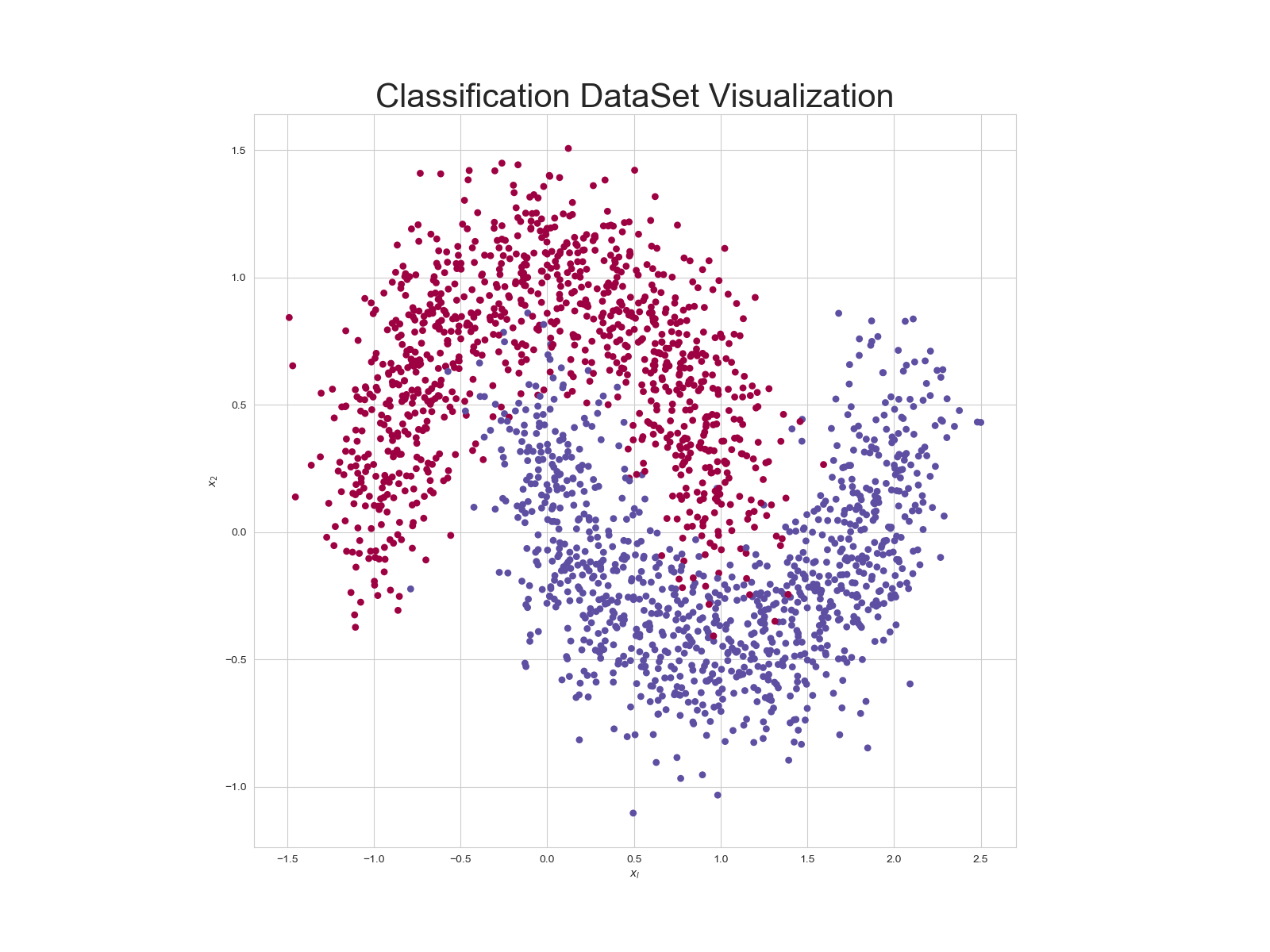
数据集为:
代码为:
1 # encoding: utf-8 2 3 import tensorflow as tf 4 import numpy as np 5 import seaborn as sns 6 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 7 from sklearn.datasets import make_moons 8 # from sklearn.datasets import make_circles 9 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 10 11 N_SAMPLES = 2000 # 采样点数 12 TEST_SIZE = 0.3 # 测试数量比率 13 14 # 产生一个简单的样本数据集,半环形图,类似的有make_circles,环形数据 15 X, y = make_moons(n_samples=N_SAMPLES, noise=0.2, random_state=100) # (2000, 2),(2000, 1) 16 # X, y = make_circles(n_samples = N_SAMPLES, noise=0.2, random_state=100) 17 # 将矩阵随机划分训练集和测试集 (1400,2),(600,2),(1400,1),(600,1) 18 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=TEST_SIZE, random_state=42) 19 print(X.shape, y.shape) 20 21 # 绘制数据集分布,X为2D坐标,y为数据点标签 22 23 24 def make_plot(X, y, plot_name=None, XX=None, YY=None, preds=None, dark=False): 25 if dark: 26 plt.style.use('dark_background') 27 else: 28 sns.set_style('whitegrid') 29 plt.figure(figsize=(16, 12)) 30 axes = plt.gca() 31 axes.set(xlabel="$x_l$", ylabel="$x_2$") 32 plt.title(plot_name, fontsize=30) 33 plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.20) # 调整边距和子图间距,子图的左侧 34 plt.subplots_adjust(right=0.80) 35 if XX is not None and YY is not None and preds is not None: 36 plt.contourf(XX, YY, preds.shape(XX.shape), 25, alpha=1, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral) 37 plt.contour(XX, YY, preds.reshape(XX.shape), levels=[1.5], cmap="Greys", vmin=0, vmax=.6) 38 # 根据标签区分颜色 39 plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y.ravel(), s=40, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral, edgecolors='none') 40 41 plt.savefig('data_set.png') 42 plt.close() 43 44 45 make_plot(X, y, "Classification DataSet Visualization") 46 plt.show() 47 48 49 class Layer: 50 # 全连接层网络 51 def __init__(self, n_input, n_neurons, activation=None, weights=None, bias=None): 52 """ 53 : int n_input: 输入节点数 54 :int n_neurons: 输出节点数 55 :str activation: 激活函数类型 56 : weights: 权值张量,内部生成 57 : bias: 偏置,内部生成 58 """ 59 # 通过正态分布生成初始化的参数 60 self.weights 61 = weights if weights is not None else 62 np.random.randn(n_input, n_neurons) * np.sqrt(1/n_neurons) 63 self.bias 64 = bias if bias is not None else 65 np.random.randn(n_neurons) * 0.1 66 self.activation = activation 67 self.last_activation = None 68 self.error = None 69 self.delta = None 70 71 # 网络的前向传播 72 def activate(self, x): 73 r = np.dot(x, self.weights) + self.bias # X@w + b 74 self.last_activation = self._apply_activation(r) # 激活函数 75 return self.last_activation 76 77 # 不同类型的激活函数 78 def _apply_activation(self, r): 79 if self.activation is None: 80 return r 81 elif self.activation == 'relu': 82 return np.maximum(r, 0) 83 elif self.activation == 'tanh': 84 return np.tanh(r) 85 elif self.activation == 'sigmoid': 86 return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-r)) 87 return r 88 89 # 不同类型激活函数的导数实现 90 def apply_activation_derivation(self, r): 91 if self.activation is None: 92 return np.ones_like(r) 93 elif self.activation == 'relu': 94 grad = np.array(r, copy=True) 95 grad[r > 0] = 1. 96 grad[r <= 0] = 0. 97 return grad 98 elif self.activation == 'tanh': 99 return 1 - r**2 100 elif self.activation == 'sigmoid': 101 return r * (1 - r) 102 return r 103 104 105 # 神经网络模型 106 class NeuralNetwork: 107 def __init__(self): # 需要实例化后对属性赋值 108 self._layers = [] # 网络层对象列表 109 110 def add_layer(self, layer): # 追加网络层 111 self._layers.append(layer) 112 113 # 前向传播只需要循环调用各网络层对象的前向计算函数 114 def feed_forward(self, X): 115 for layer in self._layers: 116 X = layer.activate(X) 117 return X 118 119 # 网络模型的反向传播 120 def backpropagation(self, X, y, learning_rate): 121 output = self.feed_forward(X) 122 # 反向循环 123 for i in reversed(range(len(self._layers))): 124 layer = self._layers[i] # 得到当前层对象 125 if layer == self._layers[-1]: #如果是输出层 126 layer.error = y - output 127 layer.delta = layer.error * layer.apply_activation_derivation(output) 128 else: # 计算隐藏层 129 next_layer = self._layers[i + 1] # 得到下一层对象 130 layer.error = np.dot(next_layer.weights, next_layer.delta) # 矩阵乘法 131 layer.delta = layer.error * 132 layer.apply_activation_derivation(layer.last_activation) 133 134 for i in range(len(self._layers)): 135 layer = self._layers[i] 136 # o_i为上一层网络输出 137 o_i = np.atleast_2d(X if i == 0 else self._layers[i - 1].last_activation) # 将数据视为2维数据 138 layer.weights += layer.delta * o_i.T * learning_rate # .T是转置 139 140 # 网络的训练 141 def train(self, X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test, learning_rate, max_epochs): 142 temp1 = y_train.shape[0] 143 y_onehot = np.zeros((temp1, 2)) 144 temp2 = np.arange(y_train.shape[0]) # 线性 0 - 1399 145 y_onehot[temp2, y_train] = 1 146 mses = [] 147 accuracy = [] 148 for i in range(max_epochs): 149 for j in range(len(X_train)): # 一次训练一个样本 150 self.backpropagation(X_train[j], y_onehot[j], learning_rate) 151 if i % 10 == 0: 152 mse = np.mean(np.square(y_onehot - self.feed_forward(X_train))) 153 mses.append(mse) 154 print('Epoch: #%s, MSE: %f' % (i, float(mse))) 155 acc = self.accuracy(self.predict(X_test), y_test.flatten()) 156 print('Accuracy: %.2f%%' % (acc * 100)) 157 accuracy.append(acc*100) 158 return mses, accuracy 159 160 def accuracy(self, y_output, y_test): 161 return np.mean((np.argmax(y_output, axis=1) == y_test)) 162 163 def predict(self, X_test): 164 return self.feed_forward(X_test) 165 166 167 # 4层全连接网络 实例化训练和预测 168 nn = NeuralNetwork() # 实列化网络 169 nn.add_layer(Layer(2, 25, 'sigmoid')) # 2 --> 25 170 nn.add_layer(Layer(25, 50, 'sigmoid')) # 25 --> 50 171 nn.add_layer(Layer(50, 25, 'sigmoid')) # 50 --> 25 172 nn.add_layer(Layer(25, 2, 'sigmoid')) # 25 --> 2 173 learning_rate = 0.01 174 max_epochs = 1000 175 mses, accuracy = nn.train(X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test, learning_rate, max_epochs) 176 177 plt.figure() 178 plt.plot(mses, 'b', label='MSE Loss') 179 plt.xlabel('Epoch') 180 plt.ylabel('MSE') 181 plt.legend() 182 plt.savefig('exam5.2 MSE Loss.png') 183 plt.show() 184 185 plt.figure() 186 plt.plot(accuracy, 'r', label='Accuracy rate') 187 plt.xlabel('Epoch') 188 plt.ylabel('Accuracy') 189 plt.legend() 190 plt.savefig('exam5.2 Accuracy.png') 191 plt.show()
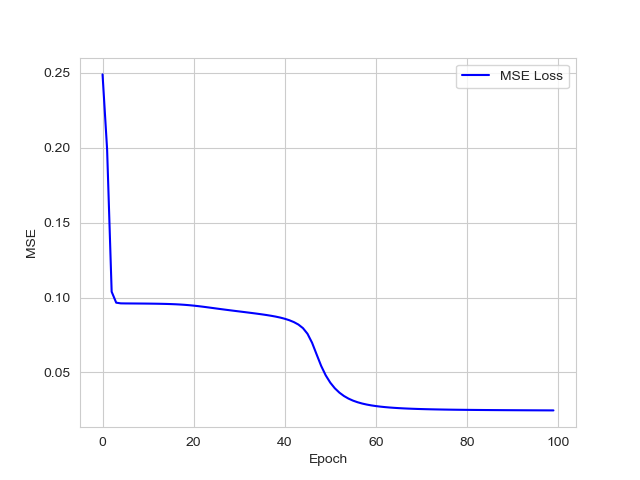
误差为:
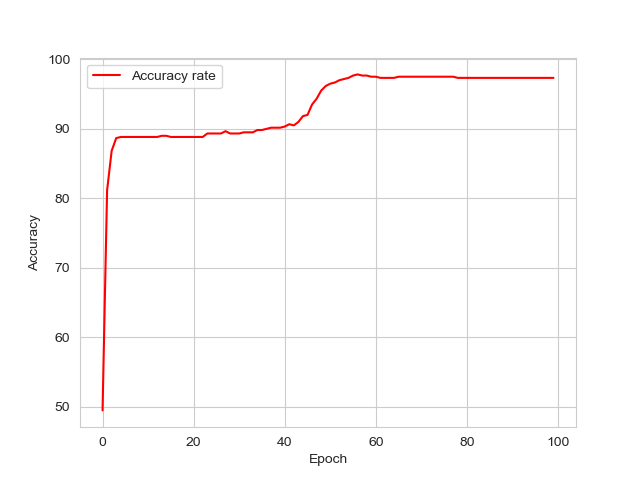
准确率为:
这个例子的目的是为让读者更进一步了解反向传播,包括数学上的理解和代码上的理解。
大体上还是能理解文中的含义,只是细节上要自己动手去算,故使用tensorflow封装好的函数,会简化很多代码,
会使学习者的成就感增加,否者的话,看到这么多数学公式以及代码的实现,早就放弃了!
下一次,我想更新关于tensorboard可视化的一些学习代码和感兴趣的东西。
但是下一次更新也不知道是好久,因为要做Geant4模拟,还有模拟内容相关的图像重建算法研究,
所以不知道什么时候可以继续学习tensorflow,但是也不能放弃,一定要把这本书过一遍!
最近solidorks的学习也遇到困难了,也不知道下一次更新是什么时候,可能2019年的更新就这些内容了!
不过对于我来说,也算开了个头!