C3:文件IO
1 引言
本章描述的函数被成为不带缓冲的IO,涉及5个函数:open、read、write、lseek、close。
文件控制:dup、sync、fsync、fdatasync、fcntl、ioctl。
2 文件描述符
文件描述符为非负整数,取值范围为0 ~ OPEN_MAX - 1,调用open、create返回参数路径的文件描述符,可以作为传递给read、write。
可使用shell命令查询系统对OPEN_MAX定义,grep -rn --col OPEN_MAX /usr/include
linux三个特殊的文件描述符:
0:标准读,STDIN_FILENO,该常亮在unistd.h中定义
1:标准写,STDOUT_FILENO
2:标准错误,STDERR_FILENO
3 函数open与openat
该方法可以打开或者创建一个文件,头文件 fctnl.h。成功返回文件描述符,失败返回-1。
1 /* Open FILE and return a new file descriptor for it, or -1 on error. 2 OFLAG determines the type of access used. If O_CREAT or O_TMPFILE is set 3 in OFLAG, the third argument is taken as a `mode_t', the mode of the 4 created file. 5 6 This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with 7 __THROW. */ 8 #ifndef __USE_FILE_OFFSET64 9 extern int open (const char *__file, int __oflag, ...) __nonnull ((1)); 10 #else 11 # ifdef __REDIRECT 12 extern int __REDIRECT (open, (const char *__file, int __oflag, ...), open64) 13 __nonnull ((1)); 14 # else 15 # define open open64 16 # endif 17 #endif 18 19 #ifdef __USE_ATFILE 20 /* Similar to `open' but a relative path name is interpreted relative to 21 the directory for which FD is a descriptor. 22 23 NOTE: some other `openat' implementation support additional functionality 24 through this interface, especially using the O_XATTR flag. This is not 25 yet supported here. 26 27 This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with 28 __THROW. */ 29 # ifndef __USE_FILE_OFFSET64 30 extern int openat (int __fd, const char *__file, int __oflag, ...) 31 __nonnull ((2)); 32 # else 33 # ifdef __REDIRECT 34 extern int __REDIRECT (openat, (int __fd, const char *__file, int __oflag, 35 ...), openat64) __nonnull ((2)); 36 # else 37 # define openat openat64 38 # endif 39 # endif 40 # ifdef __USE_LARGEFILE64 41 extern int openat64 (int __fd, const char *__file, int __oflag, ...) 42 __nonnull ((2)); 43 # endif 44 #endif
各参数释义如下:
path:打开或者创建文件的名字。
oflag:文件状态标志,如下:
| 常量 | 释义 |
| O_RDONLY | 只读打开 |
| O_WRONLY | 只写打开 |
| O_RDWR | 读写打开 |
| O_EXEC | 只执行打开 |
| O_SEARCH | 只搜索打开(仅应用于目录) |
| O_APPEND | 写文件时,追加到文件末尾 |
| O_CLOEXEC | 把FD_CLOEXEC设置为文件描述符标志 |
| O_CREATE | 创建文件,参数mode用于指定访问权限 |
| O_DIRECTORY | 如果path不是目录,则出错 |
| O_EXCL | 测试文件是否存在。不能与O_CREAT公用,否则会报错 |
| O_NOCTTY | 如果path是终端设备,则不降该设计分配为此进场的控制终端 |
| O_NOFOLLOW | 如果path是符号链接,则出错 |
| O_NONBLOCK | 如果path时FIFO、块特殊文件、字符特殊文件,则将本次打开操作及后续IO操作设置为非阻塞 |
| O_SYNC | 每次write等待IO操作完成 |
| O_TRUNK | 文件存在,且为写打开(包括只写、读写),则将文件长度截断为0。即写指针移位到0 |
| O_TTY_INIT | |
| O_DSYNC | write等待IO操作完成,如果写操作不影响读取刚写入的数据,则不需要等待文件属性被更新 |
| O_RSYNC | read操作等待,直至所有对文件同一部分挂起的写操作都完成 |
openat与open区别如下:
- 如果openat的path是绝对文件名,则fd参数被忽略,openat等同于open
- path参数是相对文件名,fd指定了相对路径名的文件描述符,fd参数通过打开相对路径名所在的目录获取文件。
- path指定相对路径名,fd参数具有特殊值AT_FDCWD,则路径名表示为当前目录获取,在操作上与open函数类似。
4 函数creat
创建一个新文件,头文件fcntl.h。成功返回文件描述符,失败返回-1
1 /* Create and open FILE, with mode MODE. This takes an `int' MODE 2 argument because that is what `mode_t' will be widened to. 3 4 This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with 5 __THROW. */ 6 #ifndef __USE_FILE_OFFSET64 7 extern int creat (const char *__file, mode_t __mode) __nonnull ((1)); 8 #else 9 # ifdef __REDIRECT 10 extern int __REDIRECT (creat, (const char *__file, mode_t __mode), 11 creat64) __nonnull ((1)); 12 # else 13 # define creat creat64 14 # endif 15 #endif 16 #ifdef __USE_LARGEFILE64 17 extern int creat64 (const char *__file, mode_t __mode) __nonnull ((1)); 18 #endif
等价于open(path, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNK, mode)
5 函数close
关闭一个打开的文件,头文件 unistd.h。成功返回0,失败返回-1
1 /* Close the file descriptor FD. 2 This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with 3 __THROW. */ 4 5 extern int close (int __fd);
关闭一个文件会释放该进程加在文件上的所以记录锁。
当一个进场终止时,内核会自动关闭它打开的所有文件,很多程序利用这一功能而不显示调用close关闭文件。
6 函数lseek
操作文件偏移量,头文件 unistd.h。成功返回文件偏移量,失败返回-1
1 /* Move FD's file position to OFFSET bytes from the 2 beginning of the file (if WHENCE is SEEK_SET), 3 the current position (if WHENCE is SEEK_CUR), 4 or the end of the file (if WHENCE is SEEK_END). 5 Return the new file position. */ 6 #ifndef __USE_FILE_OFFSET64 7 extern __off_t lseek (int __fd, __off_t __offset, int __whence) __THROW; 8 #else 9 # ifdef __REDIRECT_NTH 10 extern __off64_t __REDIRECT_NTH (lseek, 11 (int __fd, __off64_t __offset, int __whence), 12 lseek64); 13 # else 14 # define lseek lseek64 15 # endif 16 #endif
参数whence释义如下:
- 取值为SEEK_SET,则将文件偏移量设置为距离文件开始处offset个字节
- 取值为SEECK_CUR,则将文件偏移量设置为当前值加上offset,offset可正可负
- 取值为SEEK_END,则将文件偏移量设置为文件长度加上offset,offset可正可负
如果文件描述符是FIFO、pipe、socket,则返回-1,errno设置为ESPIPE。
注意
文件偏移量可能是负值,测试返回结果要测试 -1 == lseek( ... )
lseek不引发任何IO操作
文件偏移量可以大于文件当前长度,但是文件中没有写过的字节都会被设置为0。这部分文件数据被称为文件空洞
7 函数read
从打开的文件中读数据,头文件 unistd.h。返回读到的字节数,0表示文件末尾EOF,-1表示出错
1 /* Read NBYTES into BUF from FD. Return the 2 number read, -1 for errors or 0 for EOF. 3 4 This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with 5 __THROW. */ 6 extern ssize_t read (int __fd, void *__buf, size_t __nbytes) __wur;
8 函数write
向打开的文件中写数据,头文件 unistd.h。返回值应当于写入的数据长度相同,否则就表示出错。
1 /* Write N bytes of BUF to FD. Return the number written, or -1. 2 3 This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with 4 __THROW. */ 5 extern ssize_t write (int __fd, const void *__buf, size_t __n) __wur;
write出错的常见原因是磁盘满,或者超过一个给定进程的文件长度限制。
9 UNIX的IO数据结构
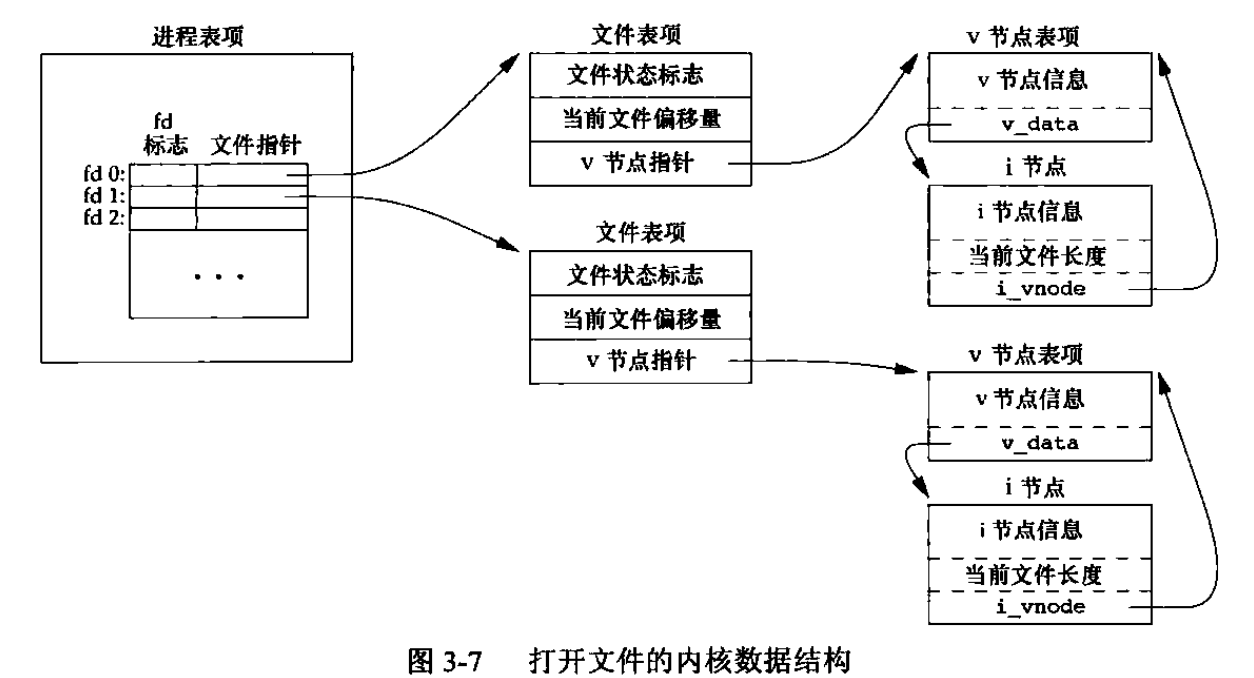 .
.
内核使用三种数据结构表示打开文件,它们之间的关系决定文件共享方面一个进程对另外一个进程可能产生的影响。
- 进程表项:列表,每项包含一个文件描述符标志,以及一个指向文件表项的指针
- 文件表:包含文件状态标志、当前文件偏移量、指向文件v节点的指针
- v节点:v节点包含文件类型、对此文件进行各种操作函数的指针。v节点还包含文件的i节点,i节点包含文件的所有者、文件长度、文件在磁盘上的指针等
understanding v-node(virtual node) : https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/en/ssw_aix_72/kernelextension/virtual_nodes.html
understanding i-noe : https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/en/ssw_aix_72/kernelextension/generic_inodes.html
图3-1表示进程打开了2个不同类型的文件,标准输入0,标准输出1。
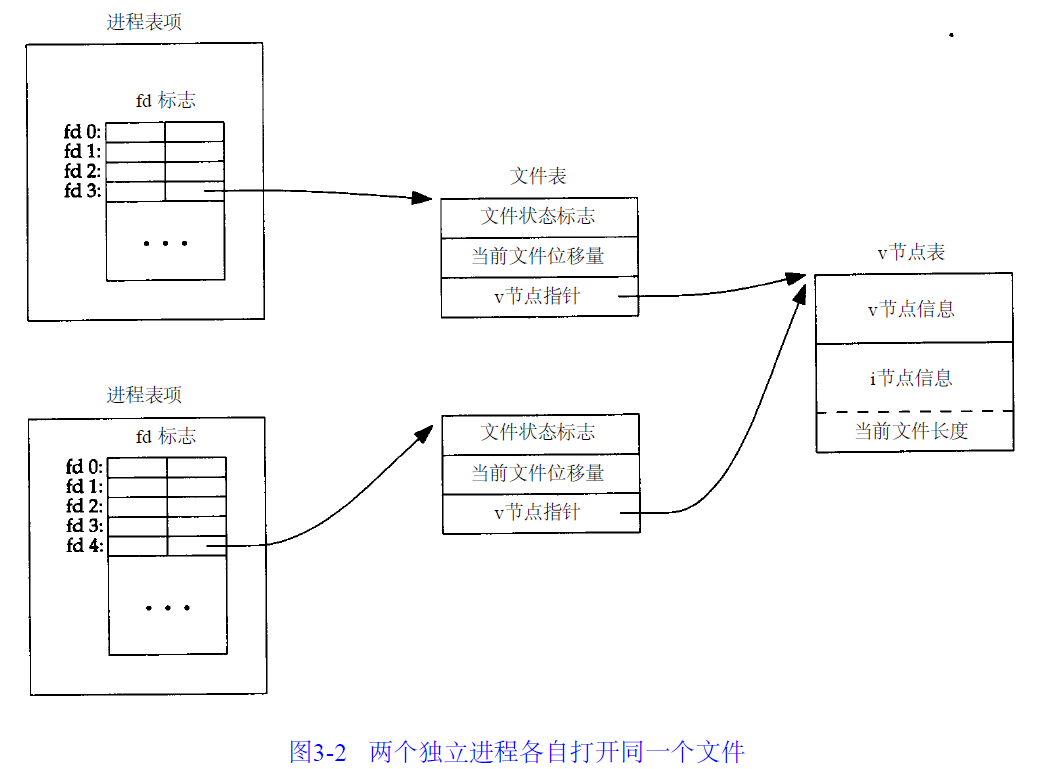
如果不同进程打开同一个文件,则有下图所示关系。
10 原子操作
10.1 写操作
以下两种操作并不等价
1 //1: lseek + write 2 lseek(fd, 0 ,SEEK_END); 3 write (fd, buf, bufsize); 4 5 //2: APPEND + write 6 open (path, O_WRONLY | O_APPEND); 7 write (fd, buf, bufsize);
第一种操作在每次write之前调用lseek将文件偏移量设置到文件末尾,再执行写操作。使用2个函数将无法保证操作的原子性。
第二种操作使用APPEND,内核在每次写操作之前将偏移量设置到该文件末尾,原子性由操作系统保证。
10.2 创建文件
open函数的O_CREAT(创建)和O_EXCL(检测文件是否存在)互斥,都是原子操作。
11 函数dup和dup2
用于复制一个现有的文件描述符,头文件 unistd.h。成功返回新的文件描述符,失败返回-1
1 /* Duplicate FD, returning a new file descriptor on the same file. */ 2 extern int dup (int __fd) __THROW __wur; 3 4 /* Duplicate FD to FD2, closing FD2 and making it open on the same file. */ 5 extern int dup2 (int __fd, int __fd2) __THROW;
由dup返回的新文件描述符一定是当前可用文件描述符的最小数值。对于dup2,如果fd2已经打开,则先将其关闭。如果fd等于fd2,则直接返回fd2。
12 函数sync、fsync、fdatasync
当linux向文件写入数据时,内核通常先将数据复制到缓冲区,再排入队列,晚些时候再写入磁盘,这种方式被称为延迟写。为保证磁盘上实际文件与缓冲区一致,UNIX提供了sync、fsync、fdatasync三个函数。
头文件 unistd.h。成功返回0,失败返回-1。
1 /* Make all changes done to all files actually appear on disk. */ 2 extern void sync (void) __THROW; 3 4 /* Make all changes done to FD actually appear on disk. 5 This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with __THROW. */ 6 extern int fsync (int __fd); 7 8 /* Synchronize at least the data part of a file with the underlying media. */ 9 extern int fdatasync (int __fildes);
区别:
- sync只是将所有修改的块缓冲区排入写队列,然后就返回,不等待写磁盘操作完成。通常,称为update的系统守护进程周期性的调用sync函数。
- fsync函数只对文件描述符指定的文件起作用,等待磁盘操作完成后返回。可用于数据库操作
- fdatasync只影响文件的数据部分
13 函数fcntl
可以改变打开的文件属性,头文件fcntl.h。成功,依赖cmd返回。失败,返回-1。
1 /* Do the file control operation described by CMD on FD. 2 The remaining arguments are interpreted depending on CMD. 3 4 This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with 5 __THROW. */ 6 extern int fcntl (int __fd, int __cmd, ...);
fcntl函数有以下5个功能:
- 复制一个文件描述符(cmd = F_DUPFD 或者 F_DUPFD_CLOEXEC)。函数dup包含close和fcntl,是原子操作。fcntl非原子操作。
- 获取、设置文件描述符标志 (cmd = F_GETFD 或 F_SETFD)。F_GETFD,当前只定义了一个文件描述符标志FD_CLOEXEC
- 获取、设置文件状态标志 (cmd = F_GETFL 或 F_SETFL)。文件状态标志为open函数的flag参数,见第三节
- 获取、设置异步IOS所有权 (cmd = F_GETOWN 或 F_SETOWN)
- 获取、设置记录锁 (cmd = F_GETLK、F_SETLK、F_SETLKW)
14 函数ioctl
控制IO操作的函数,第三章其余函数功能的补集。头文件unistd.h和sys/ioctl.h。
1 /* Perform the I/O control operation specified by REQUEST on FD. 2 One argument may follow; its presence and type depend on REQUEST. 3 Return value depends on REQUEST. Usually -1 indicates error. */ 4 extern int ioctl (int __fd, unsigned long int __request, ...) __THROW;
15 /dev/fd
打开文件 /dev/fd/n 等同于复制描述符 n。
例如:fd = open("/dev/fd/0“, mode)等价于 fd = dup(0)。
/dev/stdin == /dev/fd/0
/dev/stdout == /dev/fd/1
/dev/stderr == /dev/fd/2
如下图,利用cat显示,输入为/dev/stdin ,输出到/dev/stdout
