keras构造神经网络,非常之方便!以后就它了。本文给出了三个例子,都是普通的神经网络
例一、离散输出,单标签、多分类
例二、图像识别,单标签、多分类。没有用到卷积神经网络(CNN)
例三、时序预测,单标签、多分类。(LSTM)
说明
keras对于神经网络给出的流程图,非常容易理解。
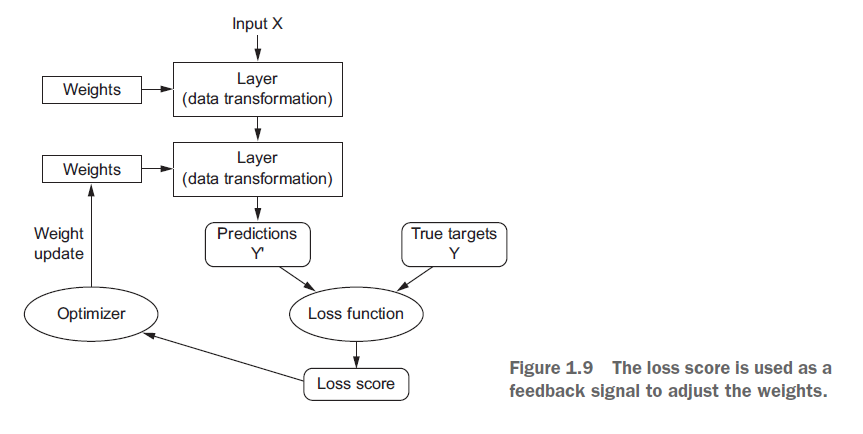
图片来源:https://www.jianshu.com/p/6c08f4ceab4c
【重点】训练神经网络围绕以下对象:
1. 层,用于合并成网络(或模型)
2. 输入数据和相应的目标
3. 损失函数, 定义了用于学习的反馈信号
4. 优化器, 这决定了学习如何进行
例一
离散输出,单标签、多分类
本例来源:https://www.jianshu.com/p/f1332c58ca86
数据来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41090915/article/details/79521161
数据是自己构造的,分有三类,如图
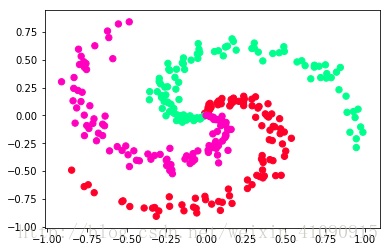 图片来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41090915/article/details/79521161
图片来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41090915/article/details/79521161
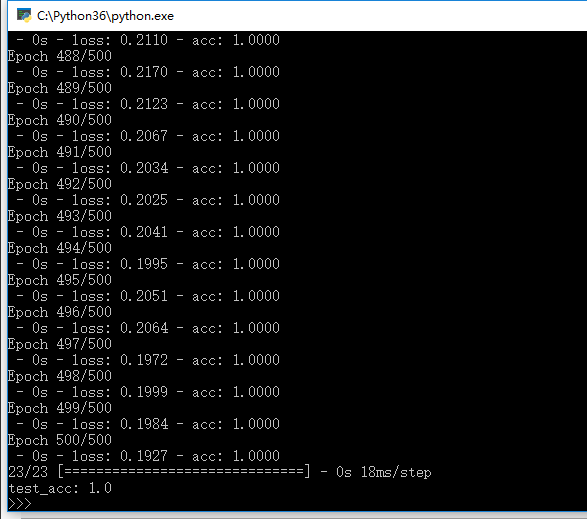
import numpy as np import pandas as pd # ===================================================== # 准备数据 N = 100 # number of points per class D = 2 # dimensionality K = 3 # number of classes X = np.zeros((N * K, D)) # data matrix (each row = single example) y = np.zeros(N * K, dtype='uint8') # class labels for j in range(K): ix = list(range(N*j, N*(j + 1))) r = np.linspace(0.0, 1, N) # radius t = np.linspace(j*4, (j+1)*4, N) + np.random.randn(N)*0.2 # theta X[ix] = np.c_[r*np.sin(t), r*np.cos(t)] y[ix] = j # 打标签 # 将y转化为one-hot编码 #y = (np.arange(K) == y[:,None]).astype(int) y = np.eye(K)[y] # ===================================================== from keras import models from keras import layers # 使用Sequential类定义两层模型 model = models.Sequential() model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation='relu', input_shape=(2,))) model.add(layers.Dense(3, activation='softmax')) # 编译。指定模型的优化器、损失函数、监控指标。 # 对于一个两类分类问题,您将使用二元交叉熵(binary crossentropy) # 对于一个多类分类问题使用分类交叉熵(categorical crossentropy) # 对于回归问题使用均方差(meansquared error) # 对于序列学习问题使用连接主义时间分类(connectionist temporal classification, CTC) from keras import optimizers model.compile(optimizer=optimizers.RMSprop(lr=0.001), loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) ''' from keras import optimizers from keras import losses from keras import metrics #from keras import optimizers, losses, metrics model.compile(optimizer=optimizers.RMSprop(lr=0.001), loss=losses.binary_crossentropy, metrics=[metrics.binary_accuracy]) ''' # 训练网络 model.fit(X, y, batch_size=50, epochs=1000) # ===================================================== # 重新生成数据 X = np.zeros((N * K, D)) # data matrix (each row = single example) y = np.zeros(N * K, dtype='uint8') # class labels for j in range(K): ix = list(range(N*j, N*(j + 1))) r = np.linspace(0.0, 1, N) # radius t = np.linspace(j*4, (j+1)*4, N) + np.random.randn(N)*0.2 # theta X[ix] = np.c_[r*np.sin(t), r*np.cos(t)] y[ix] = j # 打标签 # 将y转化为one-hot编码 #y = (np.arange(K) == y[:,None]).astype(int) y = np.eye(K)[y] # ===================================================== #检查模型在测试集上的表现是否良好 test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(X, y) print('test_acc:', test_acc)
注意:就本例而言,如果标签数据不进行one-hot编码,则损失函数要更改为:loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
效果图
例二
图像识别,没有用到卷积神经网络(CNN)
本例来源:https://www.jianshu.com/p/ba51e470b736
手写数字的识别,如图

''' 试图解决的问题是对灰度图像进行分类的手写数字(28×28个像素)到他们的10个分类(0到9)。 ''' # 导入数据 from keras.datasets import mnist (train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = mnist.load_data() # 了解数据情况 #test_images.shape # (10000, 28, 28) #test_labels # array([7, 2, 1, ..., 4, 5, 6], dtype=uint8) # 将输入数组形状由(60000,28,28)转换为(60000,28 * 28) train_images = train_images.reshape((60000, 28 * 28)) test_images = test_images.reshape((10000, 28 * 28)) # 将[0,255]区间的整数转换为[0,1]之间的浮点数 train_images = train_images.astype('float32') / 255 test_images = test_images.astype('float32') / 255 # 对分类标签y进行one-hot编码 from keras.utils import to_categorical train_labels = to_categorical(train_labels) test_labels = to_categorical(test_labels) from keras import models from keras import layers network = models.Sequential() #我们的网络由两个密集层(Dense layers)组成,它们紧密连接(也称为完全连接)神经层。 #第二个(也是最后一个)层是10路softmax层,这意味着它将返回一个包含10个概率分数的数组(总和为1), #每个分数都将是当前数字图像属于我们的10个分类之一的概率。 network.add(layers.Dense(512, activation='relu', input_shape=(28 * 28,))) network.add(layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')) #为了使网络为训练做好准备,我们需要再选择三样东西,作为编译步骤的一部分: #损失函数: 网络如何能够测量它在训练数据上的表现,如何能够引导自己走向正确的方向 #优化器:网络根据所接收的数据及其损失函数进行自我更新的机制 #监控指标:这里,我们在训练和测试期间只关心准确性(正确分类的图像的一部分) network.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) #训练这个网络 network.fit(train_images, train_labels, epochs=5, batch_size=128) #检查模型在测试集上的表现是否良好 test_loss, test_acc = network.evaluate(test_images, test_labels) print('test_acc:', test_acc)
效果图
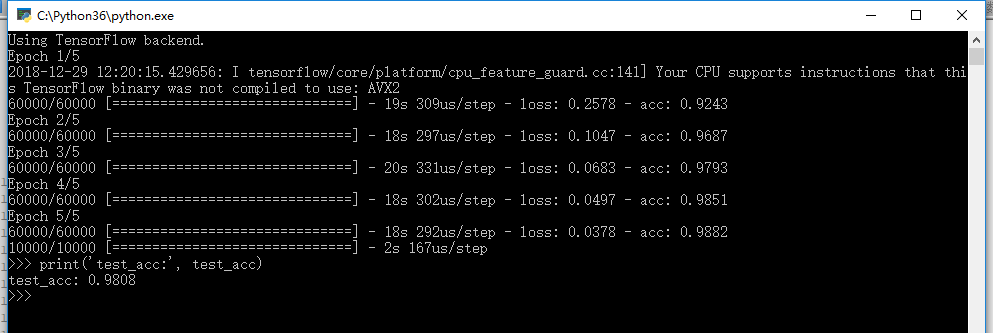
例三
时间序列预测(LSTM)
本例来源:https://blog.csdn.net/zwqjoy/article/details/80493341
字母表的一个简单的序列预测问题。
也就是说,根据字母表的字母,预测字母表的下一个字母。
['A', 'B', 'C'] -> D
['B', 'C', 'D'] -> E
['C', 'D', 'E'] -> F
['D', 'E', 'F'] -> G
['E', 'F', 'G'] -> H
['F', 'G', 'H'] -> I
['G', 'H', 'I'] -> J
['H', 'I', 'J'] -> K
['I', 'J', 'K'] -> L
['J', 'K', 'L'] -> M
['K', 'L', 'M'] -> N
['L', 'M', 'N'] -> O
['M', 'N', 'O'] -> P
['N', 'O', 'P'] -> Q
['O', 'P', 'Q'] -> R
['P', 'Q', 'R'] -> S
['Q', 'R', 'S'] -> T
['R', 'S', 'T'] -> U
['S', 'T', 'U'] -> V
['T', 'U', 'V'] -> W
['U', 'V', 'W'] -> X
['V', 'W', 'X'] -> Y
['W', 'X', 'Y'] -> Z
注意数据格式
X.shape: [samples, time_step, features]
y.shape: [samples, one_hot_encodes]
代码:
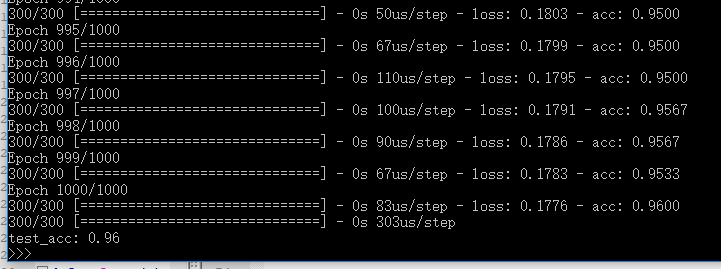
import numpy as np from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Dense from keras.layers import LSTM from keras.utils import np_utils ''' 字母表的一个简单的序列预测问题。 ''' np.random.seed(7) # 原生数据 letters = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ" # 转为数字 data_len = 26 time_steps = 3 X = list(range(data_len)) y = X[time_steps:] # 将数据转化为[样本数, 时间步数, 特征数]的形式 XX = [X[i:i+time_steps] for i in range(data_len-time_steps)] # [samples, time steps * features] XXX = np.reshape(XX, (data_len - time_steps, time_steps, -1)) # [samples, time steps, features] # 归一化 # 数值范围变为0~1,这是LSTM网络使用的s形激活函数(sigmoid)的范围。 X = XXX / data_len # one-hot编码 #y = np_utils.to_categorical(dataY) y = np.eye(data_len)[y] # ================================= model = Sequential() model.add(LSTM(32, input_shape=(X.shape[1], X.shape[2]))) model.add(Dense(y.shape[1], activation='softmax')) # 输出各类的概率(softmax) model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', # 单标签,多分类(categorical_crossentropy) optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy']) model.fit(X, y, epochs=500, batch_size=1, verbose=2) #检查模型在测试集上的表现是否良好 test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(X, y) print('test_acc:', test_acc)
效果图