Sort a linked list using insertion sort.
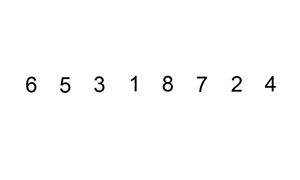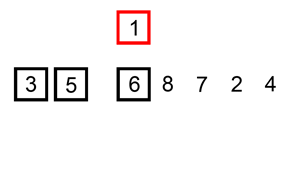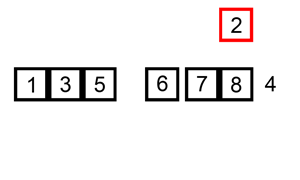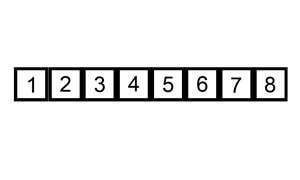
A graphical example of insertion sort. The partial sorted list (black) initially contains only the first element in the list.
With each iteration one element (red) is removed from the input data and inserted in-place into the sorted list
Algorithm of Insertion Sort:
1 Insertion sort iterates, consuming one input element each repetition, and growing a sorted output list. 2 At each iteration, insertion sort removes one element from the input data, finds the location it belongs within the sorted list, and inserts it there. 3 It repeats until no input elements remain.
Example 1:
Input: 4->2->1->3 Output: 1->2->3->4
Example 2:
Input: -1->5->3->4->0 Output: -1->0->3->4->5
解题思路:将原链表中元素一个一个取出来,在新链表中比较进行排序。时间复杂度为O(n2),是一种效率并不是很高的算法,但是空间复杂度为O(1),以高时间复杂度换取了低空间复杂度。
方法一(C++)
1 ListNode* insertionSortList(ListNode* head) { 2 ListNode* dummy=new ListNode(-1),*cur=dummy; 3 while(head){ 4 ListNode* t=head->next; 5 cur=dummy; 6 while(cur->next&&cur->next->val<=head->val) 7 cur=cur->next; 8 head->next=cur->next; 9 cur->next=head; 10 head=t; 11 } 12 return dummy->next; 13 }
(Java)
1 public ListNode insertionSortList(ListNode head) { 2 ListNode dummy=new ListNode(-1),cur=dummy; 3 while(head!=null){ 4 ListNode t=head.next; 5 cur=dummy; 6 while(cur.next!=null&&cur.next.val<=head.val) 7 cur=cur.next; 8 head.next=cur.next; 9 cur.next=head; 10 head=t; 11 } 12 return dummy.next; 13 }
方法二:不符合题目中的要求,只是完成最基本的链表排序功能,借助vector中的sort排序方法。(C++)
1 ListNode* insertionSortList(ListNode* head) { 2 vector<int> m; 3 while(head){ 4 m.push_back(head->val); 5 head=head->next; 6 } 7 sort(m.begin(),m.end()); 8 ListNode* newhead=new ListNode(-1); 9 while(!m.empty()){ 10 ListNode* cur=new ListNode(m.back()); 11 m.pop_back(); 12 cur->next=newhead->next; 13 newhead->next=cur; 14 } 15 return newhead->next; 16 }