笔者长期从事于数据库的开发,算了,不提当年了,因为一直用的是小语种(PowerBuilder),还是来说说这两个最常见的控件吧!
RadioButton(单选)和CheckBox(多选)
- 先来看看继承关系吧
- RadioButton必须按组来分,而CheckBox不用,可以自由的玩耍;
- 这里就需要引入了圈养人RadioGroup
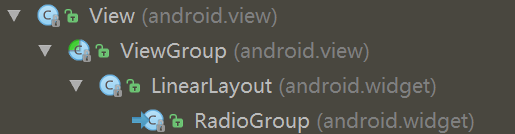
- 这里不难看出,圈养人是LinearLayout的儿子,那么就可以制定方向了
- 上边写RadioButton必须按组来分,这里语义上有点歧义吧,其实他可以不需要圈养人,也可以单独存在,但是单独存在就是去了意义,因为如果没有RadioGroup,每个RadioButton都可以点中,互相之间没有依赖了;
- 默认的RadioButton的圆形选择框在前面,如果想放到后面,可以在RadioButton的xml中加上
android:button="@null"android:drawableRight="@android:drawable/btn_radio"
- 上代码,熟悉下
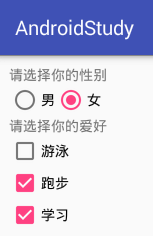
- 布局
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:orientation="vertical"android:padding="10dp"><TextViewandroid:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:text="请选择你的性别"/><RadioGroupandroid:id="@+id/rg_sex"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:orientation="horizontal"><RadioButtonandroid:id="@+id/rb_man"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:text="男"/><RadioButtonandroid:id="@+id/rb_woman"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:text="女"/></RadioGroup><TextViewandroid:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:text="请选择你的爱好"/><CheckBoxandroid:id="@+id/cb_swimming"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:text="游泳"/><CheckBoxandroid:id="@+id/cb_running"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:text="跑步"/><CheckBoxandroid:id="@+id/cb_study"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:text="学习"/></LinearLayout>
- 代码
- publicclassCheckboxAndRadioBoxActivityextendsAppCompatActivityimplementsCompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener,
RadioGroup.OnCheckedChangeListener{privateRadioGroup rg_sex;privateCheckBox cb_swimming;privateCheckBox cb_running;privateCheckBox cb_study;privateList<String> hobby =newArrayList<>();@Overrideprotectedvoid onCreate(@NullableBundle savedInstanceState){super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_checkbox_and_radiobox);rg_sex =(RadioGroup) findViewById(R.id.rg_sex);cb_swimming =(CheckBox) findViewById(R.id.cb_swimming);cb_running =(CheckBox) findViewById(R.id.cb_running);cb_study =(CheckBox) findViewById(R.id.cb_study);rg_sex.setOnCheckedChangeListener(this);cb_swimming.setOnCheckedChangeListener(this);cb_running.setOnCheckedChangeListener(this);cb_study.setOnCheckedChangeListener(this);}@Overridepublicvoid onCheckedChanged(CompoundButton buttonView,boolean isChecked){switch(buttonView.getId()){case R.id.cb_swimming:if(isChecked){hobby.add("游泳");}else{hobby.remove("游泳");}break;case R.id.cb_running:if(isChecked){hobby.add("跑步");}else{hobby.remove("跑步");}break;case R.id.cb_study:if(isChecked){hobby.add("学习");}else{hobby.remove("学习");}break;}String str="";for(int i =0; i < hobby.size(); i++){if(i==0){str = hobby.get(0);}else{str +=","+hobby.get(i);}}Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),"爱好:"+ str,Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();}@Overridepublicvoid onCheckedChanged(RadioGroup group,int checkedId){switch(checkedId){case R.id.rb_man:Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),"性别:男",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();break;case R.id.rb_woman:Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),"性别:女",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();break;}}}
- 这里说说当RadioGroup与CompoundButton的OnCheckedChangeListener出现冲突怎么办?他们的方法都是onCheckedChanged,我这里用Activity同时实现以上两个接口,根据参数的不同,RadioGroup与CompoundButton他们知道自己去调用自己的接口方法,虽然名称一样,但是参数不同呀,这里就要理解两个概念了
- 方法重载:方法名称相同,与返回值无关,参数个数或者类型至少有一样不同
- 方法覆盖: 子类重写了父类的方法,函数名称,参数,返回值必须和父类一模一样,这里可以加注解来判断@Override,系统可以帮你检测方法 的正确性;
- 当初老师的说法是既然这两个接口一样,为什么不写成一个接口,这岂不是违背了面向对象的原理?我认为主要从两方面来考虑:
- RadioGroup.OnCheckedChangeListener是对组的一个点击改变的监听,CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener是对view组件的点击事件改变的监听,group可以有孩子,而后者不可以有孩子,我想这应该是本质的区别吧;
- 我想Google当初设计的还是怕把这两个方法写在一个接口中,担心回调的时候出现混淆吧;
