这个链接讲这个算法讲得很好:点击打开链接
#include<stdio.h>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#define eps 1e-12
#include<string.h>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct point
{
double x,y;
} ch[100],pp[100];
point operator -(point a,point b)//点相减
{
point tmp;
tmp.x=a.x-b.x;
tmp.y=a.y-b.y;
return tmp;
}
bool cmp1(point a,point b)
{
if(a.y==b.y)
return a.x<b.x;
else
return a.y<b.y;
}
int dcmp(double a)//精度判断,判断a是否为0
{
if(fabs(a)<eps) return 0;
else if(a>0) return 1;
else return -1;
}
double dot(point a,point b)//向量的乘法
{
return a.x*b.x+a.y*b.y;
}
double cross(point a,point b)//叉乘
{
return a.x*b.y-b.x*a.y;
}
double dis(point a)//单个向量的模长
{
return sqrt(a.x*a.x+a.y*a.y);
}
double Dis(point a,point b)//a.b两点间的距离
{
return sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y));
}
bool cmp(point a,point b)//极坐标排序,小的在前
{
double tmp=cross(a-pp[0],b-pp[0]);//pp[0]就是选择的坐标参考点,选择原则是x坐标尽量小,y坐标尽量小
if(tmp>0)return true;
if(tmp==0&&Dis(a,pp[0])<Dis(b,pp[0]))return true;
else return false;
}
double convex_hull(int n)//建立凸包
{
// sort(pp,pp+n,cmp1);若开始没找pp[0]点则启用
sort(pp+1,pp+n,cmp);//原始点排序
int i,j,m;
if(n==1)
{
m=0;
ch[0]=pp[0];
}
else if(n==2)
{
m=1;
ch[0]=pp[0];
ch[1]=pp[1];
}
else
{
memset(ch,0,sizeof(ch));
for(i=0; i<=1; i++)
ch[i]=pp[i];
m=1;
for(i=2; i<n; i++)
{
while(m>=1&&(cross(ch[m]-ch[m-1],pp[i]-ch[m-1]))<0)m--;
ch[++m]=pp[i];
}
}
//上面是正常的凸包建立
return m;
}
int main()
{
int t,n,i,j,k,flag;
double incos;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
scanf("%lf%lf",&pp[0].x,&pp[0].y);
int xx,yy,id=0;
xx=pp[0].x;
yy=pp[0].y;
for(i=1; i<n; i++)
{
scanf("%lf%lf",&pp[i].x,&pp[i].y);
if(pp[i].y < yy || (pp[i].y == yy && pp[i].x < xx))
{
xx = pp[i].x;
yy = pp[i].y;
id = i;
}
}
point T;
T=pp[0];
pp[0]=pp[id];
pp[id]=T;
//其实没必要这么麻烦,不用这么千辛万苦找pp[0]点,直接用cmp1
//排一下序就可以了
if(n!=4)
{
printf("NO
");continue;
}
int m=convex_hull(n);
ch[m+1]=ch[0];
flag=1;
// for(i=0;i<=m;i++)printf("%f %f
",ch[i].x,ch[i].y);
incos=((n-2)*1.0/n*1.0)*acos(-1);
for( i=0;i<=m-1;i++)
{
point a=ch[i+1]-ch[i],b=ch[i+2]-ch[i+1];
double cosang=dot(a,b)/(dis(a)*dis(b));
double ang=acos(cosang);
ang=acos(-1)-ang;
// printf("*%f %f
",ang,incos);
if(dcmp(ang-incos)!=0) {flag=false;break;}
}
if(flag) printf("YES
");
else printf("NO
");
}
return 0;
}
/*
3
3
0 0
1 0
1 1
4
0 0
0 1
1 1
1 0
*/
下面直接来道模板题
Surround the Trees
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 11626 Accepted Submission(s): 4484
Problem Description
There are a lot of trees in an area. A peasant wants to buy a rope to surround all these trees. So at first he must know the minimal required length of the rope. However, he does not know how to calculate it. Can you help him?
The diameter and length of the trees are omitted, which means a tree can be seen as a point. The thickness of the rope is also omitted which means a rope can be seen as a line.
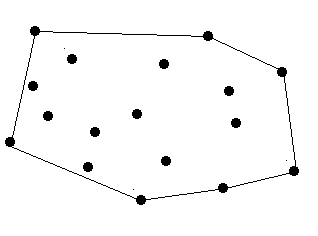
There are no more than 100 trees.
The diameter and length of the trees are omitted, which means a tree can be seen as a point. The thickness of the rope is also omitted which means a rope can be seen as a line.

There are no more than 100 trees.
Input
The input contains one or more data sets. At first line of each input data set is number of trees in this data set, it is followed by series of coordinates of the trees. Each coordinate is a positive integer pair, and each integer is less than 32767. Each pair
is separated by blank.
Zero at line for number of trees terminates the input for your program.
Zero at line for number of trees terminates the input for your program.
Output
The minimal length of the rope. The precision should be 10^-2.
Sample Input
9 12 7 24 9 30 5 41 9 80 7 50 87 22 9 45 1 50 7 0
Sample Output
243.06
题意:给了你n个点,要你建立凸包,并求这个凸包的周长
思路:二维凸包模板,建立完之后直接累加相邻两点的距离
下面是代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#define eps 1e-12
#include<string.h>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct point
{
double x,y;
} ch[100],pp[100];
point operator -(point a,point b)//点相减
{
point tmp;
tmp.x=a.x-b.x;
tmp.y=a.y-b.y;
return tmp;
}
bool cmp1(point a,point b)
{
if(a.y==b.y)
return a.x<b.x;
else
return a.y<b.y;
}
int dcmp(double a)//精度判断,判断a是否为0
{
if(fabs(a)<eps) return 0;
else if(a>0) return 1;
else return -1;
}
double dot(point a,point b)//向量的乘法
{
return a.x*b.x+a.y*b.y;
}
double cross(point a,point b)//叉乘
{
return a.x*b.y-b.x*a.y;
}
double dis(point a)//单个向量的模长
{
return sqrt(a.x*a.x+a.y*a.y);
}
double Dis(point a,point b)//a.b两点间的距离
{
return sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y));
}
bool cmp(point a,point b)//极坐标排序,小的在前
{
double tmp=cross(a-pp[0],b-pp[0]);//pp[0]就是选择的坐标参考点,选择原则是x坐标尽量小,y坐标尽量小
if(tmp>0)return true;
if(tmp==0&&Dis(a,pp[0])<Dis(b,pp[0]))return true;
else return false;
}
double convex_hull(int n)//建立凸包
{
// sort(pp,pp+n,cmp1);若开始没找pp[0]点则启用
sort(pp+1,pp+n,cmp);//原始点排序
int i,j,m;
double ans=0.0;
if(n==1)
{
m=0;
ch[0]=pp[0];
}
else if(n==2)
{
m=1;
ch[0]=pp[0];
ch[1]=pp[1];
}
else
{
memset(ch,0,sizeof(ch));
for(i=0; i<=1; i++)
ch[i]=pp[i];
m=1;
for(i=2; i<n; i++)
{
while(m>=1&&(cross(ch[m]-ch[m-1],pp[i]-ch[m-1]))<0)m--;
ch[++m]=pp[i];
}
}
//上面是正常的凸包建立
//下面开始计算周长
ch[m+1]=ch[0];
for(i=0; i<=m; i++)
ans=ans+Dis(ch[i],ch[i+1]);
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int t,n,i,j,k,flag;
double incos;
while( scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
if(n==0)break;
scanf("%lf%lf",&pp[0].x,&pp[0].y);
int xx,yy,id=0;
xx=pp[0].x;
yy=pp[0].y;
for(i=1; i<n; i++)
{
scanf("%lf%lf",&pp[i].x,&pp[i].y);
if(pp[i].y < yy || (pp[i].y == yy && pp[i].x < xx))
{
xx = pp[i].x;
yy = pp[i].y;
id = i;
}
}
point T;
T=pp[0];
pp[0]=pp[id];
pp[id]=T;
//其实没必要这么麻烦,不用这么千辛万苦找pp[0]点,直接用cmp1
//排一下序就可以了
if(n==1)
printf("%.2f
",0.00);
else if(n==2)
printf("%.2f
",Dis(pp[0],pp[1]));
else printf("%.2f
",convex_hull(n));
}
return 0;
}