需求:在命令行任意输入一组数字(0~9),然后统计这组数据中每个数字出现的个数,然后将统计个数逆序输出
输出样例:
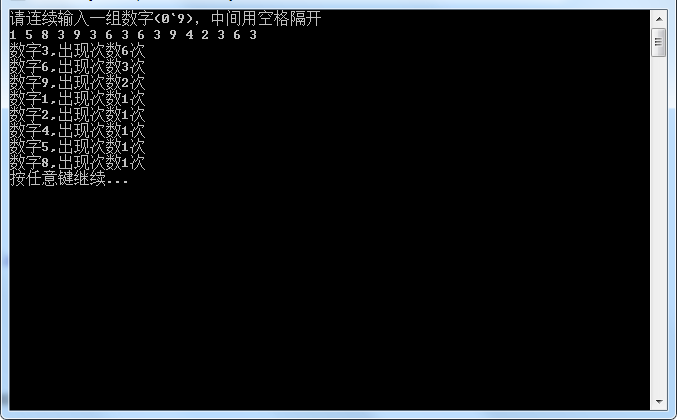
开始分解:
1、首先看到样例输出,第一想到的是什么,怎么从命令行中获取一组数字(根据需求值应该只有0~9)?
2、怎么去除重复的数字?
3、怎样将出现的数字和统计个数结合起来?主要是结合。
4、怎样将数字和计数结合后的集合按照计数的逆序输出?这个很关键。
那好,就剩下就是解决问题了。
第1步:
首先我们知道命令行获读取一般都是字符串,最常用的就是Console.Read和Console.ReadLine。但是这块用Read的话就有些不太方便了,因为你要用循环读取,而且你读过来的是字符的ASCII码值,所以我们用ReadLine方法。
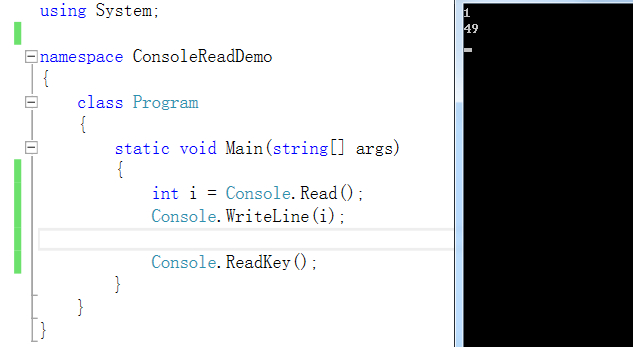
那用ReadLine的话,读取的是字符串,那就需要我们把字符串处理一下,编程一个个的数字即可。那好办了。
关键代码:
static List<int> GetConvertResult(List<string> list)
{
List<int> iList = new List<int>();
int iTemp = 0;
list.ForEach(item =>
{
if (int.TryParse(item, out iTemp))
{
iList.Add(iTemp);
}
});
return iList;
}
List<int> list = GetConvertResult(Console.ReadLine().Split(' ').Where(item => item.Trim() != "").ToList());
上面这句话的意思就是:从命令行读取的字符串,然后用空格(' ')分割,然后筛选出不为“”的,再转成List,传给
GetConvertResult(List<string> list)函数。好了第一个问题解决了
第2步:
去除重复数据,这个简单。List有个扩展方法Distinct(这个方法是通过使用默认的相等比较器对值进行比较返回序列中的非重复元素,也就是说如果是你自定义的类型,Distinct 就不认了,但是这里是int类型,刚好能用)。那这样要解决第二个问题,那就是一句代码了
list = list.Distinct().ToList();但是这里不这么用,可以连着第三步骤一起完成。
第3步:
将数字和计数结合在一起。这块的话方法就多了,可以用Dictionary,也可用List<自定义对象>,也可以用List<KeyValuePair>,也可以用Tuple。
那这里,咱们就用个简单的自定义对象Data.
class Data
{
public int Value { get; set; }
public int Count { get; set; }
public Data()
{
}
public Data(int iValue, int iCount)
{
Value = iValue;
Count = iCount;
}
public override string ToString()
{
return string.Format("数字{0},出现次数{1}次", Value, Count);
}
}
那把第2步和第3步结合起来就是:
static List<Data> GetStatResult(List<int> list)
{
List<Data> dataList = new List<Data>();
list.Distinct().ToList().ForEach(item =>
{
dataList.Add(new Data(item, list.Where(d => d == item).Count()));
});
// 先用值OrderBy进行正序,然后再用OrderByDescending计数逆序
//return dataList.OrderBy(data => data.Value).OrderByDescending(data => data.Count).ToList();
// 用Count逆序排序的同时用Value逆序排序,类似于SQL中的 ORDER BY Count DESC, Id DESC
//return dataList.OrderByDescending(data => data.Count).ThenByDescending(data => data.Value).ToList();
// 用Count逆序的同时用Value正序,这块如果要Value逆序,则只需在x.Value加个-,即-x.Value.CompareTo(y.Value)
//dataList.Sort((x, y) => (x.Value.CompareTo(y.Value) + -x.Count.CompareTo(y.Count) * 2));
//return dataList;
// linq大法,像SQL一样优雅的排序
return (from data in dataList orderby data.Count descending, data.Value ascending select data).ToList();
}
以上代码有好几种方法都可以达到效果,但是感觉Linq的写法还是比较优雅的,所以保留Linq用法。
说道这其实第四部的结合起来也已经实现了,就是那个Data类封装了数字和数字的统计个数,以及ToString的内容格式。
第4步:
没什么内容了。就一个函数。
static void PrintResult(List<Data> list)
{
list.ForEach(item => Console.WriteLine(item.ToString()));
}
好了。这么一个需求就基本完成了。
完整工程代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
/**
*
* #####################################################
* # #
* # _oo0oo_ #
* # o8888888o #
* # 88" . "88 #
* # (| -_- |) #
* # 0 = /0 #
* # ___/`---'\___ #
* # .' \| |# '. #
* # / \||| : |||# #
* # / _||||| -:- |||||- #
* # | | \ - #/ | | #
* # | \_| ''---/'' |_/ | #
* # .-\__ '-' ___/-. / #
* # ___'. .' /--.-- `. .'___ #
* # ."" '< `.___\_<|>_/___.' >' "". #
* # | | : `- \`.;` _ /`;.`/ - ` : | | #
* # `_. \_ __ /__ _/ .-` / / #
* # =====`-.____`.___ \_____/___.-`___.-'===== #
* # `=---=' #
* # ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ #
* # #
* # 佛祖保佑 永无BUG #
* # #
* #####################################################
*/
namespace SoftCountDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Run();
Console.ReadKey();
}
static List<int> GetConvertResult(List<string> list)
{
List<int> iList = new List<int>();
int iTemp = 0;
list.ForEach(item =>
{
if (int.TryParse(item, out iTemp))
{
iList.Add(iTemp);
}
});
return iList;
}
static List<Data> GetStatResult(List<int> list)
{
List<Data> dataList = new List<Data>();
list.Distinct().ToList().ForEach(item =>
{
dataList.Add(new Data(item, list.Where(d => d == item).Count()));
});
// 先用值OrderBy进行正序,然后再用OrderByDescending计数逆序
//return dataList.OrderBy(data => data.Value).OrderByDescending(data => data.Count).ToList();
// 用Count逆序排序的同时用Value逆序排序,类似于SQL中的 ORDER BY Count DESC, Id DESC
//return dataList.OrderByDescending(data => data.Count).ThenByDescending(data => data.Value).ToList();
// 用Count逆序的同时用Value正序,这块如果要Value逆序,则只需在x.Value加个-,即-x.Value.CompareTo(y.Value)
//dataList.Sort((x, y) => (x.Value.CompareTo(y.Value) + -x.Count.CompareTo(y.Count) * 2));
//return dataList;
// linq大法,像SQL一样优雅的排序
return (from data in dataList orderby data.Count descending, data.Value ascending select data).ToList();
}
static void PrintResult(List<Data> list)
{
list.ForEach(item => Console.WriteLine(item.ToString()));
}
static void Run()
{
try
{
do
{
Console.WriteLine("请连续输入一组数字(0`9),中间用空格隔开");
List<int> list = GetConvertResult(Console.ReadLine().Split(' ').Where(item => item.Trim() != "").ToList());
PrintResult(GetStatResult(list));
Console.WriteLine("按任意键继续...");
Console.ReadKey();
} while (true);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
}
class Data
{
public int Value { get; set; }
public int Count { get; set; }
public Data()
{
}
public Data(int iValue, int iCount)
{
Value = iValue;
Count = iCount;
}
public override string ToString()
{
return string.Format("数字{0},出现次数{1}次", Value, Count);
}
}
}